Dario Onorati
Investigating the Impact of Data Contamination of Large Language Models in Text-to-SQL Translation
Feb 12, 2024



Abstract:Understanding textual description to generate code seems to be an achieved capability of instruction-following Large Language Models (LLMs) in zero-shot scenario. However, there is a severe possibility that this translation ability may be influenced by having seen target textual descriptions and the related code. This effect is known as Data Contamination. In this study, we investigate the impact of Data Contamination on the performance of GPT-3.5 in the Text-to-SQL code-generating tasks. Hence, we introduce a novel method to detect Data Contamination in GPTs and examine GPT-3.5's Text-to-SQL performances using the known Spider Dataset and our new unfamiliar dataset Termite. Furthermore, we analyze GPT-3.5's efficacy on databases with modified information via an adversarial table disconnection (ATD) approach, complicating Text-to-SQL tasks by removing structural pieces of information from the database. Our results indicate a significant performance drop in GPT-3.5 on the unfamiliar Termite dataset, even with ATD modifications, highlighting the effect of Data Contamination on LLMs in Text-to-SQL translation tasks.
A Trip Towards Fairness: Bias and De-Biasing in Large Language Models
May 23, 2023Abstract:An outbreak in the popularity of transformer-based Language Models (such as GPT (Brown et al., 2020) and PaLM (Chowdhery et al., 2022)) has opened the doors to new Machine Learning applications. In particular, in Natural Language Processing and how pre-training from large text, corpora is essential in achieving remarkable results in downstream tasks. However, these Language Models seem to have inherent biases toward certain demographics reflected in their training data. While research has attempted to mitigate this problem, existing methods either fail to remove bias altogether, degrade performance, or are expensive. This paper examines the bias produced by promising Language Models when varying parameters and pre-training data. Finally, we propose a de-biasing technique that produces robust de-bias models that maintain performance on downstream tasks.
The Dark Side of the Language: Pre-trained Transformers in the DarkNet
Feb 09, 2022

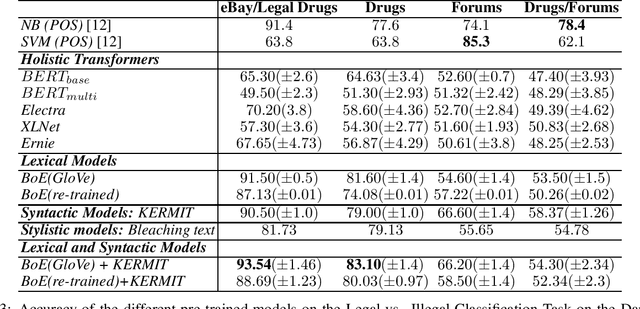
Abstract:Pre-trained Transformers are challenging human performances in many natural language processing tasks. The gigantic datasets used for pre-training seem to be the key for their success on existing tasks. In this paper, we explore how a range of pre-trained natural language understanding models perform on truly novel and unexplored data, provided by classification tasks over a DarkNet corpus. Surprisingly, results show that syntactic and lexical neural networks largely outperform pre-trained Transformers. This seems to suggest that pre-trained Transformers have serious difficulties in adapting to radically novel texts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge