Danyal Maqbool
Opportunistic Promptable Segmentation: Leveraging Routine Radiological Annotations to Guide 3D CT Lesion Segmentation
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:The development of machine learning models for CT imaging depends on the availability of large, high-quality, and diverse annotated datasets. Although large volumes of CT images and reports are readily available in clinical picture archiving and communication systems (PACS), 3D segmentations of critical findings are costly to obtain, typically requiring extensive manual annotation by radiologists. On the other hand, it is common for radiologists to provide limited annotations of findings during routine reads, such as line measurements and arrows, that are often stored in PACS as GSPS objects. We posit that these sparse annotations can be extracted along with CT volumes and converted into 3D segmentations using promptable segmentation models, a paradigm we term Opportunistic Promptable Segmentation. To enable this paradigm, we propose SAM2CT, the first promptable segmentation model designed to convert radiologist annotations into 3D segmentations in CT volumes. SAM2CT builds upon SAM2 by extending the prompt encoder to support arrow and line inputs and by introducing Memory-Conditioned Memories (MCM), a memory encoding strategy tailored to 3D medical volumes. On public lesion segmentation benchmarks, SAM2CT outperforms existing promptable segmentation models and similarly trained baselines, achieving Dice similarity coefficients of 0.649 for arrow prompts and 0.757 for line prompts. Applying the model to pre-existing GSPS annotations from a clinical PACS (N = 60), SAM2CT generates 3D segmentations that are clinically acceptable or require only minor adjustments in 87% of cases, as scored by radiologists. Additionally, SAM2CT demonstrates strong zero-shot performance on select Emergency Department findings. These results suggest that large-scale mining of historical GSPS annotations represents a promising and scalable approach for generating 3D CT segmentation datasets.
PETAR: Localized Findings Generation with Mask-Aware Vision-Language Modeling for PET Automated Reporting
Oct 31, 2025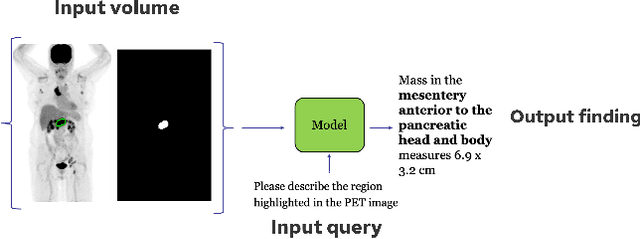
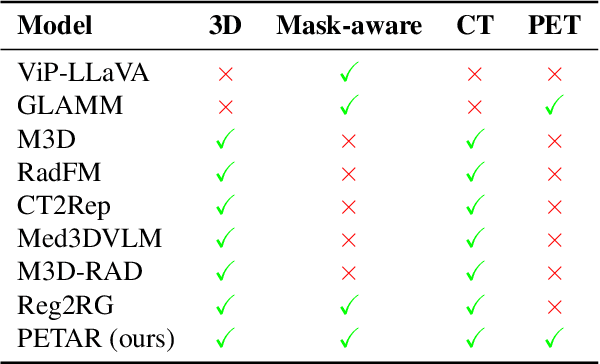
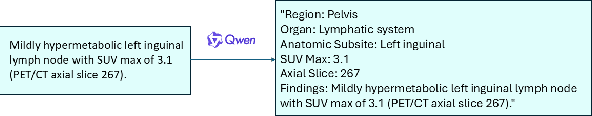
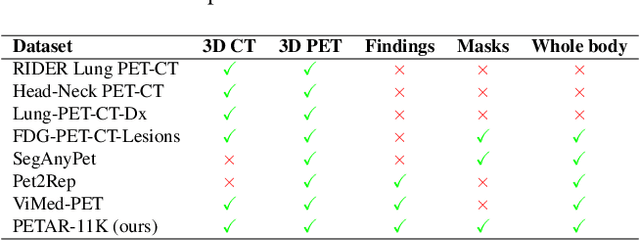
Abstract:Recent advances in vision-language models (VLMs) have enabled impressive multimodal reasoning, yet most medical applications remain limited to 2D imaging. In this work, we extend VLMs to 3D positron emission tomography and computed tomography (PET/CT), a domain characterized by large volumetric data, small and dispersed lesions, and lengthy radiology reports. We introduce a large-scale dataset comprising over 11,000 lesion-level descriptions paired with 3D segmentations from more than 5,000 PET/CT exams, extracted via a hybrid rule-based and large language model (LLM) pipeline. Building upon this dataset, we propose PETAR-4B, a 3D mask-aware vision-language model that integrates PET, CT, and lesion contours for spatially grounded report generation. PETAR bridges global contextual reasoning with fine-grained lesion awareness, producing clinically coherent and localized findings. Comprehensive automated and human evaluations demonstrate that PETAR substantially improves PET/CT report generation quality, advancing 3D medical vision-language understanding.
COMMA: A Communicative Multimodal Multi-Agent Benchmark
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:The rapid advances of multi-modal agents built on large foundation models have largely overlooked their potential for language-based communication between agents in collaborative tasks. This oversight presents a critical gap in understanding their effectiveness in real-world deployments, particularly when communicating with humans. Existing agentic benchmarks fail to address key aspects of inter-agent communication and collaboration, particularly in scenarios where agents have unequal access to information and must work together to achieve tasks beyond the scope of individual capabilities. To fill this gap, we introduce a novel benchmark designed to evaluate the collaborative performance of multimodal multi-agent systems through language communication. Our benchmark features a variety of scenarios, providing a comprehensive evaluation across four key categories of agentic capability in a communicative collaboration setting. By testing both agent-agent and agent-human collaborations using open-source and closed-source models, our findings reveal surprising weaknesses in state-of-the-art models, including proprietary models like GPT-4o. These models struggle to outperform even a simple random agent baseline in agent-agent collaboration and only surpass the random baseline when a human is involved.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge