Daniel Tamayo
Salamandra Technical Report
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:This work introduces Salamandra, a suite of open-source decoder-only large language models available in three different sizes: 2, 7, and 40 billion parameters. The models were trained from scratch on highly multilingual data that comprises text in 35 European languages and code. Our carefully curated corpus is made exclusively from open-access data compiled from a wide variety of sources. Along with the base models, supplementary checkpoints that were fine-tuned on public-domain instruction data are also released for chat applications. Additionally, we also share our preliminary experiments on multimodality, which serve as proof-of-concept to showcase potential applications for the Salamandra family. Our extensive evaluations on multilingual benchmarks reveal that Salamandra has strong capabilities, achieving competitive performance when compared to similarly sized open-source models. We provide comprehensive evaluation results both on standard downstream tasks as well as key aspects related to bias and safety.With this technical report, we intend to promote open science by sharing all the details behind our design choices, data curation strategy and evaluation methodology. In addition to that, we deviate from the usual practice by making our training and evaluation scripts publicly accessible. We release all models under a permissive Apache 2.0 license in order to foster future research and facilitate commercial use, thereby contributing to the open-source ecosystem of large language models.
Mass-Editing Memory with Attention in Transformers: A cross-lingual exploration of knowledge
Feb 04, 2025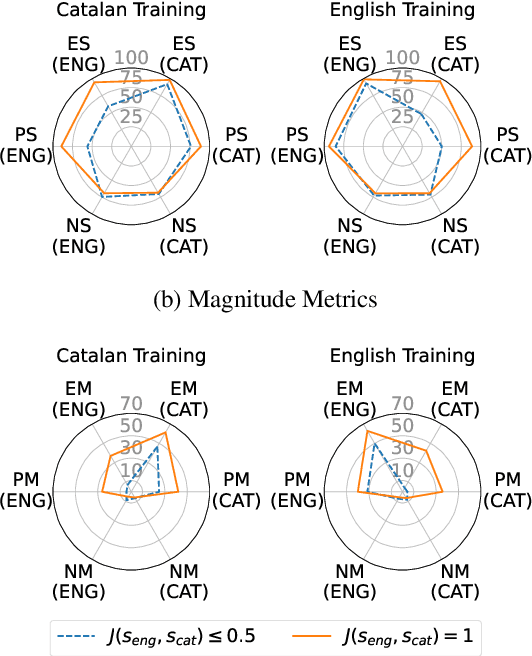
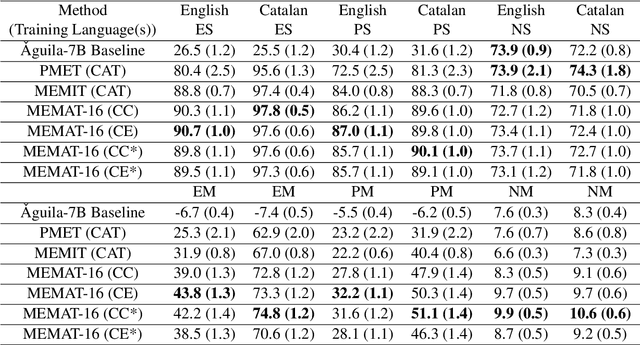
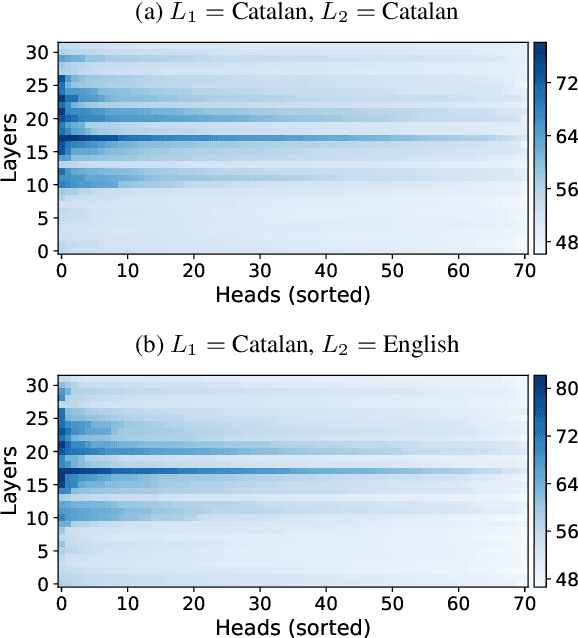
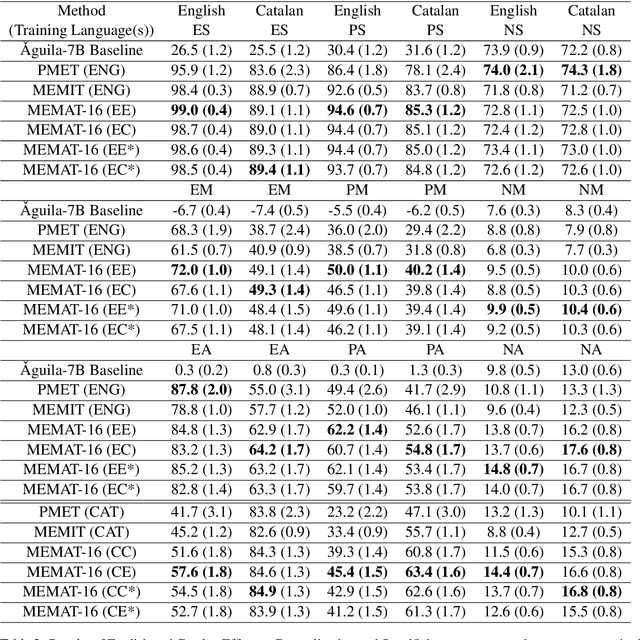
Abstract:Recent research has explored methods for updating and modifying factual knowledge in large language models, often focusing on specific multi-layer perceptron blocks. This study expands on this work by examining the effectiveness of existing knowledge editing methods across languages and delving into the role of attention mechanisms in this process. Drawing from the insights gained, we propose Mass-Editing Memory with Attention in Transformers (MEMAT), a method that achieves significant improvements in all metrics while requiring minimal parameter modifications. MEMAT delivers a remarkable 10% increase in magnitude metrics, benefits languages not included in the training data and also demonstrates a high degree of portability. Our code and data are at https://github.com/dtamayo-nlp/MEMAT.
SPOCK 2.0: Update to the FeatureClassifier in the Stability of Planetary Orbital Configurations Klassifier
Jan 25, 2025
Abstract:The Stability of Planetary Orbital Configurations Klassifier (SPOCK) package collects machine learning models for predicting the stability and collisional evolution of compact planetary systems. In this paper we explore improvements to SPOCK's binary stability classifier (FeatureClassifier), which predicts orbital stability by collecting data over a short N-body integration of a system. We find that by using a system-specific timescale (rather than a fixed $10^4$ orbits) for the integration, and by using this timescale as an additional feature, we modestly improve the model's AUC metric from 0.943 to 0.950 (AUC=1 for a perfect model). We additionally discovered that $\approx 10\%$ of N-body integrations in SPOCK's original training dataset were duplicated by accident, and that $<1\%$ were misclassified as stable when they in fact led to ejections. We provide a cleaned dataset of 100,000+ unique integrations, release a newly trained stability classification model, and make minor updates to the API.
Accelerating Giant Impact Simulations with Machine Learning
Aug 16, 2024



Abstract:Constraining planet formation models based on the observed exoplanet population requires generating large samples of synthetic planetary systems, which can be computationally prohibitive. A significant bottleneck is simulating the giant impact phase, during which planetary embryos evolve gravitationally and combine to form planets, which may themselves experience later collisions. To accelerate giant impact simulations, we present a machine learning (ML) approach to predicting collisional outcomes in multiplanet systems. Trained on more than 500,000 $N$-body simulations of three-planet systems, we develop an ML model that can accurately predict which two planets will experience a collision, along with the state of the post-collision planets, from a short integration of the system's initial conditions. Our model greatly improves on non-ML baselines that rely on metrics from dynamics theory, which struggle to accurately predict which pair of planets will experience a collision. By combining with a model for predicting long-term stability, we create an efficient ML-based giant impact emulator, which can predict the outcomes of giant impact simulations with a speedup of up to four orders of magnitude. We expect our model to enable analyses that would not otherwise be computationally feasible. As such, we release our full training code, along with an easy-to-use API for our collision outcome model and giant impact emulator.
A Bayesian neural network predicts the dissolution of compact planetary systems
Jan 11, 2021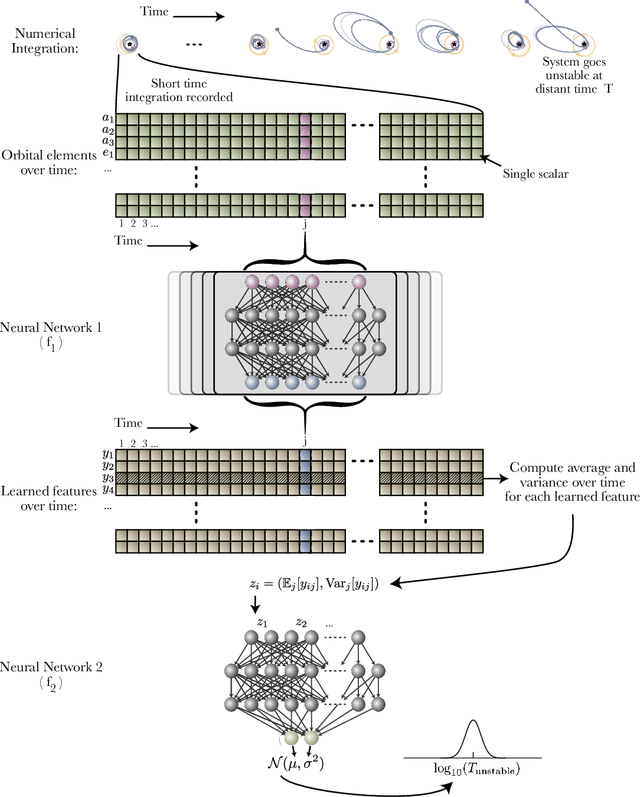
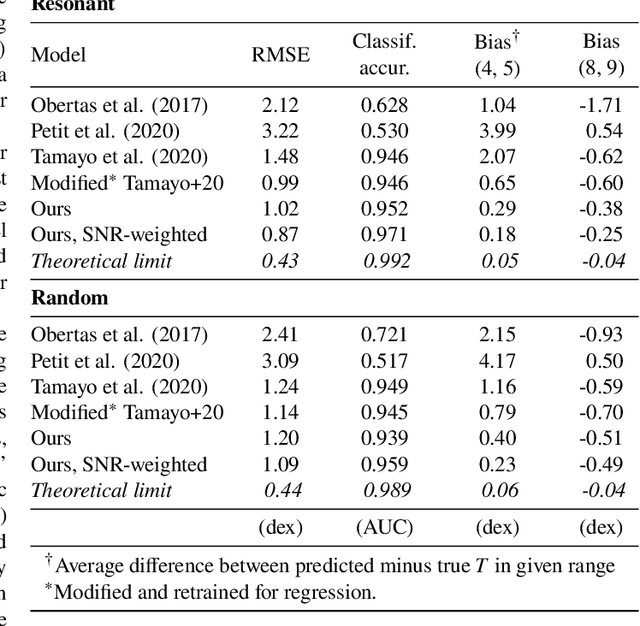
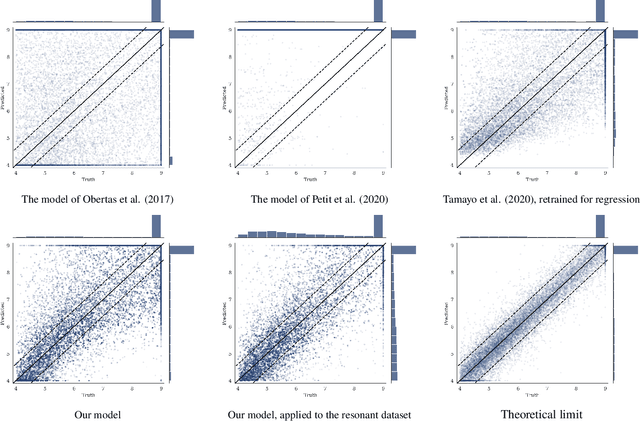
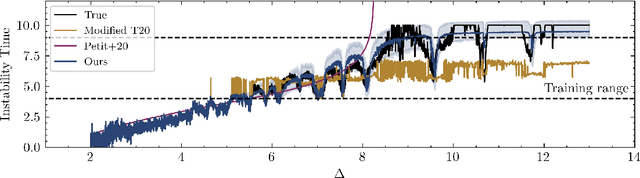
Abstract:Despite over three hundred years of effort, no solutions exist for predicting when a general planetary configuration will become unstable. We introduce a deep learning architecture to push forward this problem for compact systems. While current machine learning algorithms in this area rely on scientist-derived instability metrics, our new technique learns its own metrics from scratch, enabled by a novel internal structure inspired from dynamics theory. Our Bayesian neural network model can accurately predict not only if, but also when a compact planetary system with three or more planets will go unstable. Our model, trained directly from short N-body time series of raw orbital elements, is more than two orders of magnitude more accurate at predicting instability times than analytical estimators, while also reducing the bias of existing machine learning algorithms by nearly a factor of three. Despite being trained on compact resonant and near-resonant three-planet configurations, the model demonstrates robust generalization to both non-resonant and higher multiplicity configurations, in the latter case outperforming models fit to that specific set of integrations. The model computes instability estimates up to five orders of magnitude faster than a numerical integrator, and unlike previous efforts provides confidence intervals on its predictions. Our inference model is publicly available in the SPOCK package, with training code open-sourced.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge