Chumin Liu
Uncertainty of Thoughts: Uncertainty-Aware Planning Enhances Information Seeking in Large Language Models
Feb 05, 2024


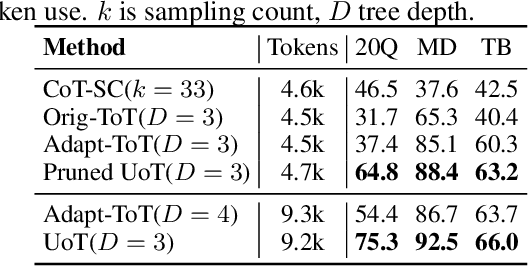
Abstract:In the face of uncertainty, the ability to seek information is of fundamental importance. In many practical applications, such as medical diagnosis and troubleshooting, the information needed to solve the task is not initially given, and has to be actively sought by asking follow-up questions (for example, a doctor asking a patient for more details about their symptoms). In this work, we introduce Uncertainty of Thoughts (UoT), an algorithm to augment large language models with the ability to actively seek information by asking effective questions. UoT combines 1) an uncertainty-aware simulation approach which enables the model to simulate possible future scenarios and how likely they are to occur, 2) uncertainty-based rewards motivated by information gain which incentivizes the model to seek information, and 3) a reward propagation scheme to select the optimal question to ask in a way that maximizes the expected reward. In experiments on medical diagnosis, troubleshooting and the '20 Questions' game, UoT achieves an average performance improvement of 57.8% in the rate of successful task completion across multiple LLMs compared with direct prompting, and also improves efficiency (i.e., the number of questions needed to complete the task).
PoetryDiffusion: Towards Joint Semantic and Metrical Manipulation in Poetry Generation
Jun 14, 2023Abstract:Poetry generation is a typical and popular task in natural language generation. While prior works have shown success in controlling either semantic or metrical aspects of poetry generation, there are still challenges in addressing both perspectives simultaneously. In this paper, we employ the Diffusion model to generate poetry in Sonnet and SongCi in Chinese for the first time to tackle such challenges. Different from autoregressive generation, our PoetryDiffusion model, based on Diffusion model, generates the complete sentence or poetry by taking into account the whole sentence information, resulting in improved semantic expression. Additionally, we incorporate a novel metrical controller to manipulate and evaluate metrics (format and rhythm). The denoising process in PoetryDiffusion allows for gradual enhancement of semantics and flexible integration of the metrical controller. Experimental results on two datasets demonstrate that our model outperforms existing models in terms of semantic, metrical and overall performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge