Chuangbai Xiao
ConSinger: Efficient High-Fidelity Singing Voice Generation with Minimal Steps
Oct 20, 2024Abstract:Singing voice synthesis (SVS) system is expected to generate high-fidelity singing voice from given music scores (lyrics, duration and pitch). Recently, diffusion models have performed well in this field. However, sacrificing inference speed to exchange with high-quality sample generation limits its application scenarios. In order to obtain high quality synthetic singing voice more efficiently, we propose a singing voice synthesis method based on the consistency model, ConSinger, to achieve high-fidelity singing voice synthesis with minimal steps. The model is trained by applying consistency constraint and the generation quality is greatly improved at the expense of a small amount of inference speed. Our experiments show that ConSinger is highly competitive with the baseline model in terms of generation speed and quality. Audio samples are available at https://keylxiao.github.io/consinger.
Self-Supervised Multi-Scale Network for Blind Image Deblurring via Alternating Optimization
Sep 02, 2024Abstract:Blind image deblurring is a challenging low-level vision task that involves estimating the unblurred image when the blur kernel is unknown. In this paper, we present a self-supervised multi-scale blind image deblurring method to jointly estimate the latent image and the blur kernel via alternating optimization. In the image estimation step, we construct a multi-scale generator network with multiple inputs and multiple outputs to collaboratively estimate latent images at various scales, supervised by an image pyramid constructed from only the blurred image. This generator places architectural constraints on the network and avoids the need for mathematical expression of image priors. In the blur kernel estimation step, the blur kernel at each scale is independently estimated with a direct solution to a quadratic regularized least-squares model for its flexible adaptation to the proposed multi-scale generator for image estimation. Thanks to the collaborative estimation across multiple scales, our method avoids the computationally intensive coarse-to-fine propagation and additional image deblurring processes used in traditional mathematical optimization-based methods. Quantitative and qualitative experimental results on synthetic and realistic datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our method, especially for handling large and real-world blurs.
COSPLAY: Concept Set Guided Personalized Dialogue Generation Across Both Party Personas
May 15, 2022



Abstract:Maintaining a consistent persona is essential for building a human-like conversational model. However, the lack of attention to the partner makes the model more egocentric: they tend to show their persona by all means such as twisting the topic stiffly, pulling the conversation to their own interests regardless, and rambling their persona with little curiosity to the partner. In this work, we propose COSPLAY(COncept Set guided PersonaLized dialogue generation Across both partY personas) that considers both parties as a "team": expressing self-persona while keeping curiosity toward the partner, leading responses around mutual personas, and finding the common ground. Specifically, we first represent self-persona, partner persona and mutual dialogue all in the concept sets. Then, we propose the Concept Set framework with a suite of knowledge-enhanced operations to process them such as set algebras, set expansion, and set distance. Based on these operations as medium, we train the model by utilizing 1) concepts of both party personas, 2) concept relationship between them, and 3) their relationship to the future dialogue. Extensive experiments on a large public dataset, Persona-Chat, demonstrate that our model outperforms state-of-the-art baselines for generating less egocentric, more human-like, and higher quality responses in both automatic and human evaluations.
Edge-Based Blur Kernel Estimation Using Sparse Representation and Self-Similarity
Nov 17, 2018



Abstract:Blind image deconvolution is the problem of recovering the latent image from the only observed blurry image when the blur kernel is unknown. In this paper, we propose an edge-based blur kernel estimation method for blind motion deconvolution. In our previous work, we incorporate both sparse representation and self-similarity of image patches as priors into our blind deconvolution model to regularize the recovery of the latent image. Since almost any natural image has properties of sparsity and multi-scale self-similarity, we construct a sparsity regularizer and a cross-scale non-local regularizer based on our patch priors. It has been observed that our regularizers often favor sharp images over blurry ones only for image patches of the salient edges and thus we define an edge mask to locate salient edges that we want to apply our regularizers. Experimental results on both simulated and real blurry images demonstrate that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art blind deblurring methods even for handling of very large blurs, thanks to the use of the edge mask.
A Convolutional Neural Network for Aspect Sentiment Classification
Jul 04, 2018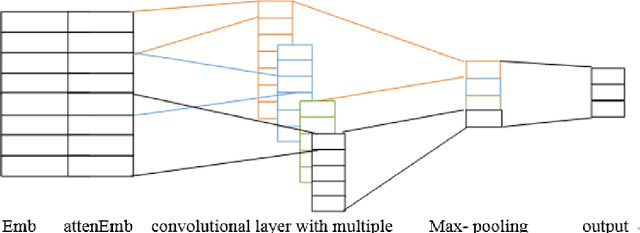
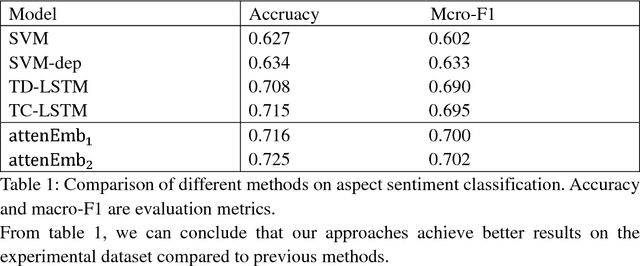
Abstract:With the development of the Internet, natural language processing (NLP), in which sentiment analysis is an important task, became vital in information processing.Sentiment analysis includes aspect sentiment classification. Aspect sentiment can provide complete and in-depth results with increased attention on aspect-level. Different context words in a sentence influence the sentiment polarity of a sentence variably, and polarity varies based on the different aspects in a sentence. Take the sentence, 'I bought a new camera. The picture quality is amazing but the battery life is too short.'as an example. If the aspect is picture quality, then the expected sentiment polarity is 'positive', if the battery life aspect is considered, then the sentiment polarity should be 'negative'; therefore, aspect is important to consider when we explore aspect sentiment in the sentence. Recurrent neural network (RNN) is regarded as a good model to deal with natural language processing, and RNNs has get good performance on aspect sentiment classification including Target-Dependent LSTM (TD-LSTM) ,Target-Connection LSTM (TC-LSTM) (Tang, 2015a, b), AE-LSTM, AT-LSTM, AEAT-LSTM (Wang et al., 2016).There are also extensive literatures on sentiment classification utilizing convolutional neural network, but there is little literature on aspect sentiment classification using convolutional neural network. In our paper, we develop attention-based input layers in which aspect information is considered by input layer. We then incorporate attention-based input layers into convolutional neural network (CNN) to introduce context words information. In our experiment, incorporating aspect information into CNN improves the latter's aspect sentiment classification performance without using syntactic parser or external sentiment lexicons in a benchmark dataset from Twitter but get better performance compared with other models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge