Christophe Guettier
WarNav: An Autonomous Driving Benchmark for Segmentation of Navigable Zones in War Scenes
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:We introduce WarNav, a novel real-world dataset constructed from images of the open-source DATTALION repository, specifically tailored to enable the development and benchmarking of semantic segmentation models for autonomous ground vehicle navigation in unstructured, conflict-affected environments. This dataset addresses a critical gap between conventional urban driving resources and the unique operational scenarios encountered by unmanned systems in hazardous and damaged war-zones. We detail the methodological challenges encountered, ranging from data heterogeneity to ethical considerations, providing guidance for future efforts that target extreme operational contexts. To establish performance references, we report baseline results on WarNav using several state-of-the-art semantic segmentation models trained on structured urban scenes. We further analyse the impact of training data environments and propose a first step towards effective navigability in challenging environments with the constraint of having no annotation of the targeted images. Our goal is to foster impactful research that enhances the robustness and safety of autonomous vehicles in high-risk scenarios while being frugal in annotated data.
Adaptive Bias Generalized Rollout Policy Adaptation on the Flexible Job-Shop Scheduling Problem
May 13, 2025Abstract:The Flexible Job-Shop Scheduling Problem (FJSSP) is an NP-hard combinatorial optimization problem, with several application domains, especially for manufacturing purposes. The objective is to efficiently schedule multiple operations on dissimilar machines. These operations are gathered into jobs, and operations pertaining to the same job need to be scheduled sequentially. Different methods have been previously tested to solve this problem, such as Constraint Solving, Tabu Search, Genetic Algorithms, or Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS). We propose a novel algorithm derived from the Generalized Nested Rollout Policy Adaptation, developed to solve the FJSSP. We report encouraging experimental results, as our algorithm performs better than other MCTS-based approaches, even if makespans obtained on large instances are still far from known upper bounds.
Weakly Supervised Test-Time Domain Adaptation for Object Detection
Jul 08, 2024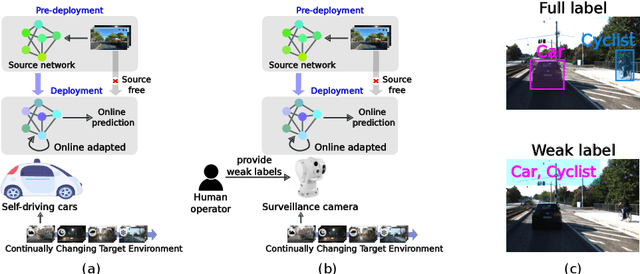
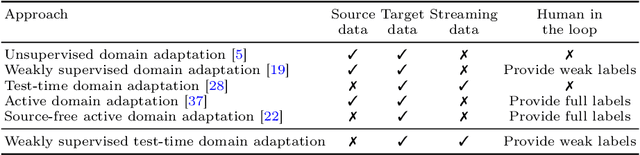
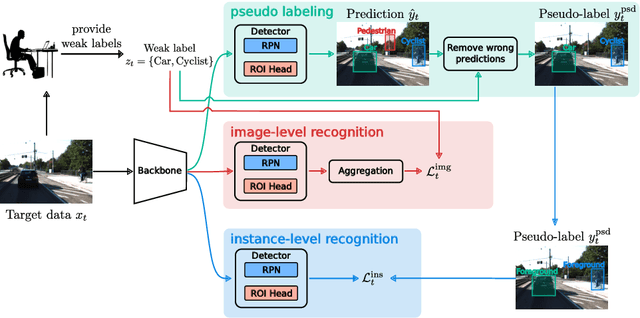

Abstract:Prior to deployment, an object detector is trained on a dataset compiled from a previous data collection campaign. However, the environment in which the object detector is deployed will invariably evolve, particularly in outdoor settings where changes in lighting, weather and seasons will significantly affect the appearance of the scene and target objects. It is almost impossible for all potential scenarios that the object detector may come across to be present in a finite training dataset. This necessitates continuous updates to the object detector to maintain satisfactory performance. Test-time domain adaptation techniques enable machine learning models to self-adapt based on the distributions of the testing data. However, existing methods mainly focus on fully automated adaptation, which makes sense for applications such as self-driving cars. Despite the prevalence of fully automated approaches, in some applications such as surveillance, there is usually a human operator overseeing the system's operation. We propose to involve the operator in test-time domain adaptation to raise the performance of object detection beyond what is achievable by fully automated adaptation. To reduce manual effort, the proposed method only requires the operator to provide weak labels, which are then used to guide the adaptation process. Furthermore, the proposed method can be performed in a streaming setting, where each online sample is observed only once. We show that the proposed method outperforms existing works, demonstrating a great benefit of human-in-the-loop test-time domain adaptation. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/dzungdoan6/WSTTA
Planning and Learning: A Review of Methods involving Path-Planning for Autonomous Vehicles
Jul 26, 2022



Abstract:This short review aims to make the reader familiar with state-of-the-art works relating to planning, scheduling and learning. First, we study state-of-the-art planning algorithms. We give a brief introduction of neural networks. Then we explore in more detail graph neural networks, a recent variant of neural networks suited for processing graph-structured inputs. We describe briefly the concept of reinforcement learning algorithms and some approaches designed to date. Next, we study some successful approaches combining neural networks for path-planning. Lastly, we focus on temporal planning problems with uncertainty.
Solving Disjunctive Temporal Networks with Uncertainty under Restricted Time-Based Controllability using Tree Search and Graph Neural Networks
Mar 30, 2022



Abstract:Planning under uncertainty is an area of interest in artificial intelligence. We present a novel approach based on tree search and graph machine learning for the scheduling problem known as Disjunctive Temporal Networks with Uncertainty (DTNU). Dynamic Controllability (DC) of DTNUs seeks a reactive scheduling strategy to satisfy temporal constraints in response to uncontrollable action durations. We introduce new semantics for reactive scheduling: Time-based Dynamic Controllability (TDC) and a restricted subset of TDC, R-TDC. We design a tree search algorithm to determine whether or not a DTNU is R-TDC. Moreover, we leverage a graph neural network as a heuristic for tree search guidance. Finally, we conduct experiments on a known benchmark on which we show R-TDC to retain significant completeness with regard to DC, while being faster to prove. This results in the tree search processing fifty percent more DTNU problems in R-TDC than the state-of-the-art DC solver does in DC with the same time budget. We also observe that graph neural network search guidance leads to substantial performance gains on benchmarks of more complex DTNUs, with up to eleven times more problems solved than the baseline tree search.
* Thirty-Sixth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. This version includes the technical appendix. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2108.01068
Time-based Dynamic Controllability of Disjunctive Temporal Networks with Uncertainty: A Tree Search Approach with Graph Neural Network Guidance
Aug 02, 2021



Abstract:Scheduling in the presence of uncertainty is an area of interest in artificial intelligence due to the large number of applications. We study the problem of dynamic controllability (DC) of disjunctive temporal networks with uncertainty (DTNU), which seeks a strategy to satisfy all constraints in response to uncontrollable action durations. We introduce a more restricted, stronger form of controllability than DC for DTNUs, time-based dynamic controllability (TDC), and present a tree search approach to determine whether or not a DTNU is TDC. Moreover, we leverage the learning capability of a message passing neural network (MPNN) as a heuristic for tree search guidance. Finally, we conduct experiments for which the tree search shows superior results to state-of-the-art timed-game automata (TGA) based approaches. We observe that using an MPNN for tree search guidance leads to a significant increase in solving performance and scalability to harder DTNU problems.
Learning-based Preference Prediction for Constrained Multi-Criteria Path-Planning
Aug 02, 2021



Abstract:Learning-based methods are increasingly popular for search algorithms in single-criterion optimization problems. In contrast, for multiple-criteria optimization there are significantly fewer approaches despite the existence of numerous applications. Constrained path-planning for Autonomous Ground Vehicles (AGV) is one such application, where an AGV is typically deployed in disaster relief or search and rescue applications in off-road environments. The agent can be faced with the following dilemma : optimize a source-destination path according to a known criterion and an uncertain criterion under operational constraints. The known criterion is associated to the cost of the path, representing the distance. The uncertain criterion represents the feasibility of driving through the path without requiring human intervention. It depends on various external parameters such as the physics of the vehicle, the state of the explored terrains or weather conditions. In this work, we leverage knowledge acquired through offline simulations by training a neural network model to predict the uncertain criterion. We integrate this model inside a path-planner which can solve problems online. Finally, we conduct experiments on realistic AGV scenarios which illustrate that the proposed framework requires human intervention less frequently, trading for a limited increase in the path distance.
* arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2108.00978
Optimal Solving of Constrained Path-Planning Problems with Graph Convolutional Networks and Optimized Tree Search
Aug 02, 2021



Abstract:Learning-based methods are growing prominence for planning purposes. However, there are very few approaches for learning-assisted constrained path-planning on graphs, while there are multiple downstream practical applications. This is the case for constrained path-planning for Autonomous Unmanned Ground Vehicles (AUGV), typically deployed in disaster relief or search and rescue applications. In off-road environments, the AUGV must dynamically optimize a source-destination path under various operational constraints, out of which several are difficult to predict in advance and need to be addressed on-line. We propose a hybrid solving planner that combines machine learning models and an optimal solver. More specifically, a graph convolutional network (GCN) is used to assist a branch and bound (B&B) algorithm in handling the constraints. We conduct experiments on realistic scenarios and show that GCN support enables substantial speedup and smoother scaling to harder problems.
Constrained Shortest Path Search with Graph Convolutional Neural Networks
Aug 02, 2021



Abstract:Planning for Autonomous Unmanned Ground Vehicles (AUGV) is still a challenge, especially in difficult, off-road, critical situations. Automatic planning can be used to reach mission objectives, to perform navigation or maneuvers. Most of the time, the problem consists in finding a path from a source to a destination, while satisfying some operational constraints. In a graph without negative cycles, the computation of the single-pair shortest path from a start node to an end node is solved in polynomial time. Additional constraints on the solution path can however make the problem harder to solve. This becomes the case when we need the path to pass through a few mandatory nodes without requiring a specific order of visit. The complexity grows exponentially with the number of mandatory nodes to visit. In this paper, we focus on shortest path search with mandatory nodes on a given connected graph. We propose a hybrid model that combines a constraint-based solver and a graph convolutional neural network to improve search performance. Promising results are obtained on realistic scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge