Christian Schulze
Violence Detection in Videos
Sep 18, 2021



Abstract:In the recent years, there has been a tremendous increase in the amount of video content uploaded to social networking and video sharing websites like Facebook and Youtube. As of result of this, the risk of children getting exposed to adult and violent content on the web also increased. To address this issue, an approach to automatically detect violent content in videos is proposed in this work. Here, a novel attempt is made also to detect the category of violence present in a video. A system which can automatically detect violence from both Hollywood movies and videos from the web is extremely useful not only in parental control but also for applications related to movie ratings, video surveillance, genre classification and so on. Here, both audio and visual features are used to detect violence. MFCC features are used as audio cues. Blood, Motion, and SentiBank features are used as visual cues. Binary SVM classifiers are trained on each of these features to detect violence. Late fusion using a weighted sum of classification scores is performed to get final classification scores for each of the violence class target by the system. To determine optimal weights for each of the violence classes an approach based on grid search is employed. Publicly available datasets, mainly Violent Scene Detection (VSD), are used for classifier training, weight calculation, and testing. The performance of the system is evaluated on two classification tasks, Multi-Class classification, and Binary Classification. The results obtained for Binary Classification are better than the baseline results from MediaEval-2014.
Detection of Accounting Anomalies in the Latent Space using Adversarial Autoencoder Neural Networks
Aug 02, 2019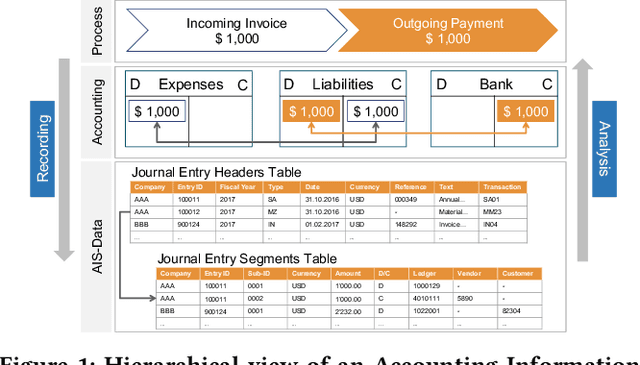
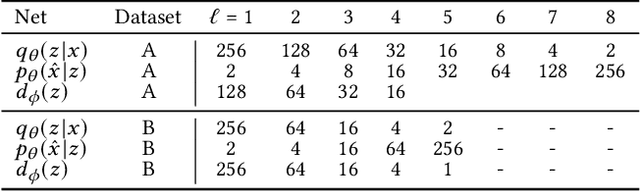
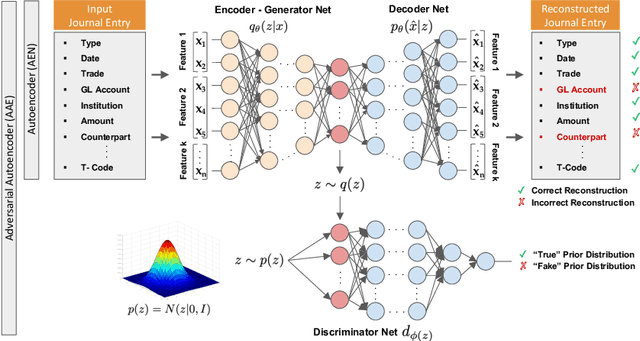
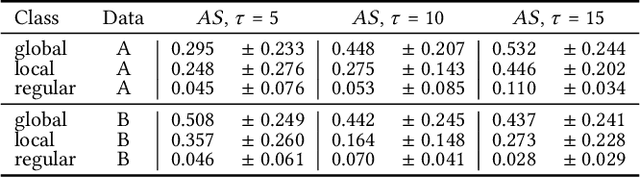
Abstract:The detection of fraud in accounting data is a long-standing challenge in financial statement audits. Nowadays, the majority of applied techniques refer to handcrafted rules derived from known fraud scenarios. While fairly successful, these rules exhibit the drawback that they often fail to generalize beyond known fraud scenarios and fraudsters gradually find ways to circumvent them. In contrast, more advanced approaches inspired by the recent success of deep learning often lack seamless interpretability of the detected results. To overcome this challenge, we propose the application of adversarial autoencoder networks. We demonstrate that such artificial neural networks are capable of learning a semantic meaningful representation of real-world journal entries. The learned representation provides a holistic view on a given set of journal entries and significantly improves the interpretability of detected accounting anomalies. We show that such a representation combined with the networks reconstruction error can be utilized as an unsupervised and highly adaptive anomaly assessment. Experiments on two datasets and initial feedback received by forensic accountants underpinned the effectiveness of the approach.
AudioPairBank: Towards A Large-Scale Tag-Pair-Based Audio Content Analysis
Jan 08, 2018



Abstract:Recently, sound recognition has been used to identify sounds, such as car and river. However, sounds have nuances that may be better described by adjective-noun pairs such as slow car, and verb-noun pairs such as flying insects, which are under explored. Therefore, in this work we investigate the relation between audio content and both adjective-noun pairs and verb-noun pairs. Due to the lack of datasets with these kinds of annotations, we collected and processed the AudioPairBank corpus consisting of a combined total of 1,123 pairs and over 33,000 audio files. One contribution is the previously unavailable documentation of the challenges and implications of collecting audio recordings with these type of labels. A second contribution is to show the degree of correlation between the audio content and the labels through sound recognition experiments, which yielded results of 70% accuracy, hence also providing a performance benchmark. The results and study in this paper encourage further exploration of the nuances in audio and are meant to complement similar research performed on images and text in multimedia analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge