Chris Hays
Statistical Guarantees in the Search for Less Discriminatory Algorithms
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Recent scholarship has argued that firms building data-driven decision systems in high-stakes domains like employment, credit, and housing should search for "less discriminatory algorithms" (LDAs) (Black et al., 2024). That is, for a given decision problem, firms considering deploying a model should make a good-faith effort to find equally performant models with lower disparate impact across social groups. Evidence from the literature on model multiplicity shows that randomness in training pipelines can lead to multiple models with the same performance, but meaningful variations in disparate impact. This suggests that developers can find LDAs simply by randomly retraining models. Firms cannot continue retraining forever, though, which raises the question: What constitutes a good-faith effort? In this paper, we formalize LDA search via model multiplicity as an optimal stopping problem, where a model developer with limited information wants to produce strong evidence that they have sufficiently explored the space of models. Our primary contribution is an adaptive stopping algorithm that yields a high-probability upper bound on the gains achievable from a continued search, allowing the developer to certify (e.g., to a court) that their search was sufficient. We provide a framework under which developers can impose stronger assumptions about the distribution of models, yielding correspondingly stronger bounds. We validate the method on real-world credit, employment and housing datasets.
Double Machine Learning for Causal Inference under Shared-State Interference
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Researchers and practitioners often wish to measure treatment effects in settings where units interact via markets and recommendation systems. In these settings, units are affected by certain shared states, like prices, algorithmic recommendations or social signals. We formalize this structure, calling it shared-state interference, and argue that our formulation captures many relevant applied settings. Our key modeling assumption is that individuals' potential outcomes are independent conditional on the shared state. We then prove an extension of a double machine learning (DML) theorem providing conditions for achieving efficient inference under shared-state interference. We also instantiate our general theorem in several models of interest where it is possible to efficiently estimate the average direct effect (ADE) or global average treatment effect (GATE).
From Fairness to Infinity: Outcome-Indistinguishable (Omni)Prediction in Evolving Graphs
Nov 26, 2024
Abstract:Professional networks provide invaluable entree to opportunity through referrals and introductions. A rich literature shows they also serve to entrench and even exacerbate a status quo of privilege and disadvantage. Hiring platforms, equipped with the ability to nudge link formation, provide a tantalizing opening for beneficial structural change. We anticipate that key to this prospect will be the ability to estimate the likelihood of edge formation in an evolving graph. Outcome-indistinguishable prediction algorithms ensure that the modeled world is indistinguishable from the real world by a family of statistical tests. Omnipredictors ensure that predictions can be post-processed to yield loss minimization competitive with respect to a benchmark class of predictors for many losses simultaneously, with appropriate post-processing. We begin by observing that, by combining a slightly modified form of the online K29 star algorithm of Vovk (2007) with basic facts from the theory of reproducing kernel Hilbert spaces, one can derive simple and efficient online algorithms satisfying outcome indistinguishability and omniprediction, with guarantees that improve upon, or are complementary to, those currently known. This is of independent interest. We apply these techniques to evolving graphs, obtaining online outcome-indistinguishable omnipredictors for rich -- possibly infinite -- sets of distinguishers that capture properties of pairs of nodes, and their neighborhoods. This yields, inter alia, multicalibrated predictions of edge formation with respect to pairs of demographic groups, and the ability to simultaneously optimize loss as measured by a variety of social welfare functions.
Simplistic Collection and Labeling Practices Limit the Utility of Benchmark Datasets for Twitter Bot Detection
Jan 17, 2023



Abstract:Accurate bot detection is necessary for the safety and integrity of online platforms. It is also crucial for research on the influence of bots in elections, the spread of misinformation, and financial market manipulation. Platforms deploy infrastructure to flag or remove automated accounts, but their tools and data are not publicly available. Thus, the public must rely on third-party bot detection. These tools employ machine learning and often achieve near perfect performance for classification on existing datasets, suggesting bot detection is accurate, reliable and fit for use in downstream applications. We provide evidence that this is not the case and show that high performance is attributable to limitations in dataset collection and labeling rather than sophistication of the tools. Specifically, we show that simple decision rules -- shallow decision trees trained on a small number of features -- achieve near-state-of-the-art performance on most available datasets and that bot detection datasets, even when combined together, do not generalize well to out-of-sample datasets. Our findings reveal that predictions are highly dependent on each dataset's collection and labeling procedures rather than fundamental differences between bots and humans. These results have important implications for both transparency in sampling and labeling procedures and potential biases in research using existing bot detection tools for pre-processing.
The Effect of the Rooney Rule on Implicit Bias in the Long Term
Oct 21, 2020

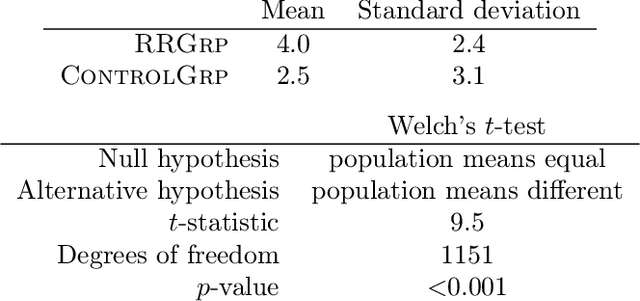

Abstract:A robust body of evidence demonstrates the adverse effects of implicit bias in various contexts--from hiring to health care. The Rooney Rule is an intervention developed to counter implicit bias and has been implemented in the private and public sectors. The Rooney Rule requires that a selection panel include at least one candidate from an underrepresented group in their shortlist of candidates. Recently, Kleinberg and Raghavan proposed a model of implicit bias and studied the effectiveness of the Rooney Rule when applied to a single selection decision. However, selection decisions often occur repeatedly over time. Further, it has been observed that, given consistent counterstereotypical feedback, implicit biases against underrepresented candidates can change. We consider a model of how a selection panel's implicit bias changes over time given their hiring decisions either with or without the Rooney Rule in place. Our main result is that, when the panel is constrained by the Rooney Rule, their implicit bias roughly reduces at a rate that is the inverse of the size of the shortlist--independent of the number of candidates, whereas without the Rooney Rule, the rate is inversely proportional to the number of candidates. Thus, when the number of candidates is much larger than the size of the shortlist, the Rooney Rule enables a faster reduction in implicit bias, providing an additional reason in favor of using it as a strategy to mitigate implicit bias. Towards empirically evaluating the long-term effect of the Rooney Rule in repeated selection decisions, we conduct an iterative candidate selection experiment on Amazon MTurk. We observe that, indeed, decision-makers subject to the Rooney Rule select more minority candidates in addition to those required by the rule itself than they would if no rule is in effect, and do so without considerably decreasing the utility of candidates selected.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge