Chengyu Dai
University of Michigan
A Data Science Approach to Understanding Residential Water Contamination in Flint
Jul 05, 2017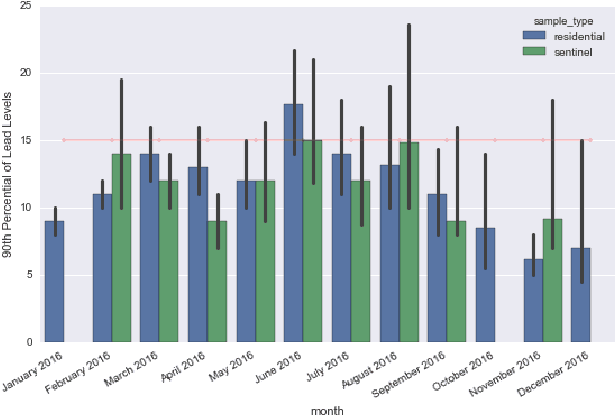
Abstract:When the residents of Flint learned that lead had contaminated their water system, the local government made water-testing kits available to them free of charge. The city government published the results of these tests, creating a valuable dataset that is key to understanding the causes and extent of the lead contamination event in Flint. This is the nation's largest dataset on lead in a municipal water system. In this paper, we predict the lead contamination for each household's water supply, and we study several related aspects of Flint's water troubles, many of which generalize well beyond this one city. For example, we show that elevated lead risks can be (weakly) predicted from observable home attributes. Then we explore the factors associated with elevated lead. These risk assessments were developed in part via a crowd sourced prediction challenge at the University of Michigan. To inform Flint residents of these assessments, they have been incorporated into a web and mobile application funded by \texttt{Google.org}. We also explore questions of self-selection in the residential testing program, examining which factors are linked to when and how frequently residents voluntarily sample their water.
Flint Water Crisis: Data-Driven Risk Assessment Via Residential Water Testing
Sep 30, 2016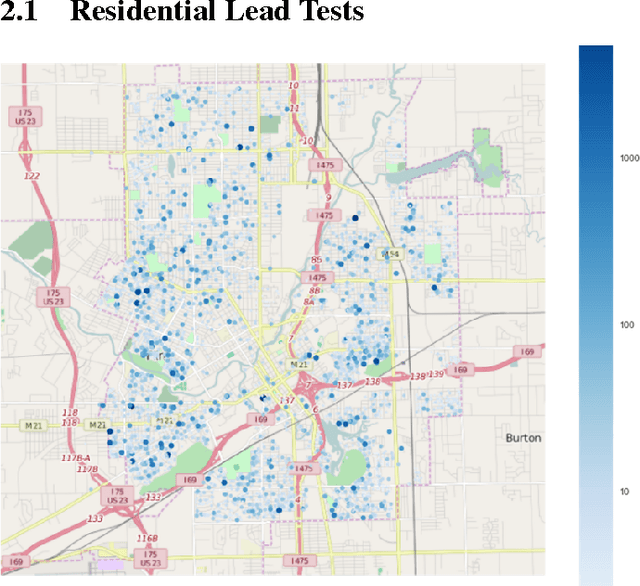
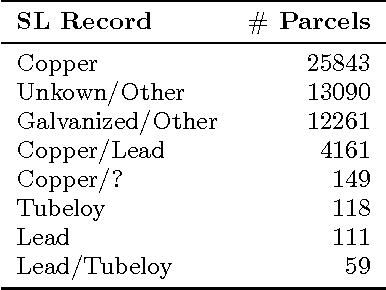
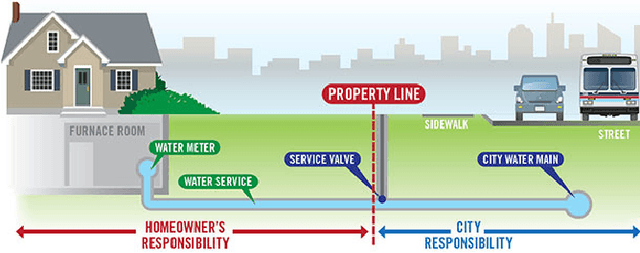
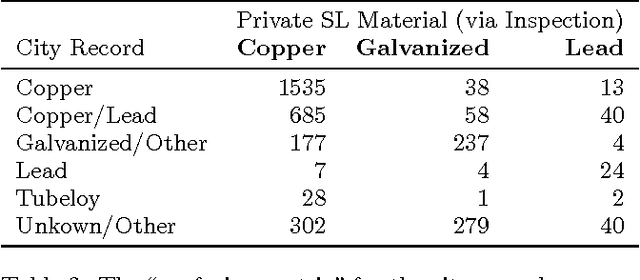
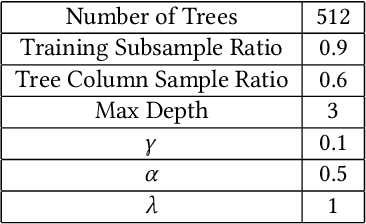
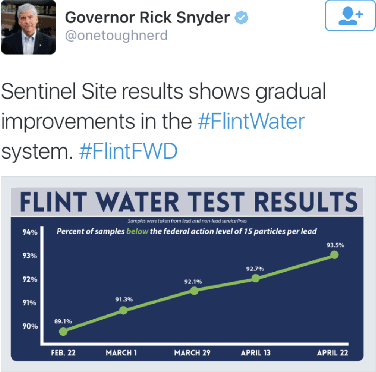
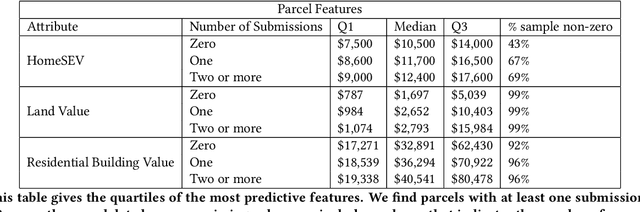
Abstract:Recovery from the Flint Water Crisis has been hindered by uncertainty in both the water testing process and the causes of contamination. In this work, we develop an ensemble of predictive models to assess the risk of lead contamination in individual homes and neighborhoods. To train these models, we utilize a wide range of data sources, including voluntary residential water tests, historical records, and city infrastructure data. Additionally, we use our models to identify the most prominent factors that contribute to a high risk of lead contamination. In this analysis, we find that lead service lines are not the only factor that is predictive of the risk of lead contamination of water. These results could be used to guide the long-term recovery efforts in Flint, minimize the immediate damages, and improve resource-allocation decisions for similar water infrastructure crises.
Data Science in Service of Performing Arts: Applying Machine Learning to Predicting Audience Preferences
Sep 30, 2016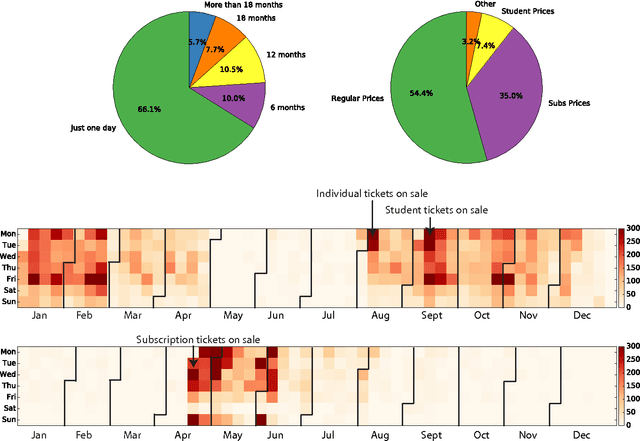
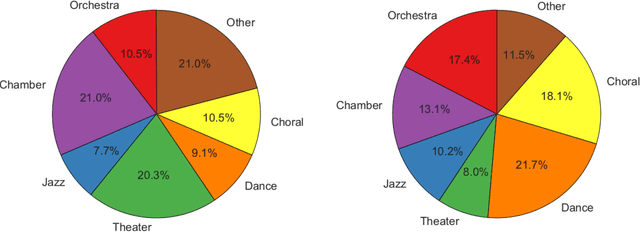
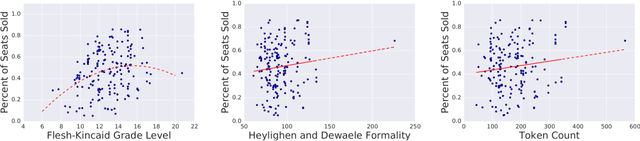
Abstract:Performing arts organizations aim to enrich their communities through the arts. To do this, they strive to match their performance offerings to the taste of those communities. Success relies on understanding audience preference and predicting their behavior. Similar to most e-commerce or digital entertainment firms, arts presenters need to recommend the right performance to the right customer at the right time. As part of the Michigan Data Science Team (MDST), we partnered with the University Musical Society (UMS), a non-profit performing arts presenter housed in the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. We are providing UMS with analysis and business intelligence, utilizing historical individual-level sales data. We built a recommendation system based on collaborative filtering, gaining insights into the artistic preferences of customers, along with the similarities between performances. To better understand audience behavior, we used statistical methods from customer-base analysis. We characterized customer heterogeneity via segmentation, and we modeled customer cohorts to understand and predict ticket purchasing patterns. Finally, we combined statistical modeling with natural language processing (NLP) to explore the impact of wording in program descriptions. These ongoing efforts provide a platform to launch targeted marketing campaigns, helping UMS carry out its mission by allocating its resources more efficiently. Celebrating its 138th season, UMS is a 2014 recipient of the National Medal of Arts, and it continues to enrich communities by connecting world-renowned artists with diverse audiences, especially students in their formative years. We aim to contribute to that mission through data science and customer analytics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge