Chenguang Dai
SuperMapNet for Long-Range and High-Accuracy Vectorized HD Map Construction
May 20, 2025Abstract:Vectorized HD map is essential for autonomous driving. Remarkable work has been achieved in recent years, but there are still major issues: (1) in the generation of the BEV features, single modality-based methods are of limited perception capability, while direct concatenation-based multi-modal methods fail to capture synergies and disparities between different modalities, resulting in limited ranges with feature holes; (2) in the classification and localization of map elements, only point information is used without the consideration of element infor-mation and neglects the interaction between point information and element information, leading to erroneous shapes and element entanglement with low accuracy. To address above issues, we introduce SuperMapNet for long-range and high-accuracy vectorized HD map construction. It uses both camera images and LiDAR point clouds as input, and first tightly couple semantic information from camera images and geometric information from LiDAR point clouds by a cross-attention based synergy enhancement module and a flow-based disparity alignment module for long-range BEV feature generation. And then, local features from point queries and global features from element queries are tightly coupled by three-level interactions for high-accuracy classification and localization, where Point2Point interaction learns local geometric information between points of the same element and of each point, Element2Element interaction learns relation constraints between different elements and semantic information of each elements, and Point2Element interaction learns complement element information for its constituent points. Experiments on the nuScenes and Argoverse2 datasets demonstrate superior performances, surpassing SOTAs over 14.9/8.8 mAP and 18.5/3.1 mAP under hard/easy settings, respectively. The code is made publicly available1.
Deep Semantic Graph Matching for Large-scale Outdoor Point Clouds Registration
Aug 10, 2023Abstract:The current point cloud registration methods are mainly based on geometric information and usually ignore the semantic information in the point clouds. In this paper, we treat the point cloud registration problem as semantic instance matching and registration task, and propose a deep semantic graph matching method for large-scale outdoor point cloud registration. Firstly, the semantic category labels of 3D point clouds are obtained by utilizing large-scale point cloud semantic segmentation network. The adjacent points with the same category labels are then clustered together by using Euclidean clustering algorithm to obtain the semantic instances. Secondly, the semantic adjacency graph is constructed based on the spatial adjacency relation of semantic instances. Three kinds of high-dimensional features including geometric shape features, semantic categorical features and spatial distribution features are learned through graph convolutional network, and enhanced based on attention mechanism. Thirdly, the semantic instance matching problem is modeled as an optimal transport problem, and solved through an optimal matching layer. Finally, according to the matched semantic instances, the geometric transformation matrix between two point clouds is first obtained by SVD algorithm and then refined by ICP algorithm. The experiments are cconducted on the KITTI Odometry dataset, and the average relative translation error and average relative rotation error of the proposed method are 6.6cm and 0.229{\deg} respectively.
Neural Gaussian Mirror for Controlled Feature Selection in Neural Networks
Oct 13, 2020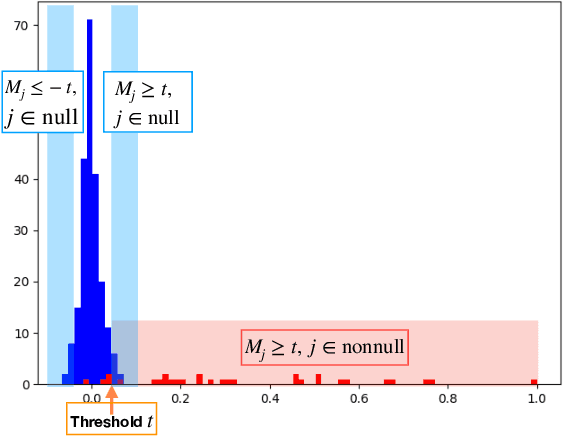
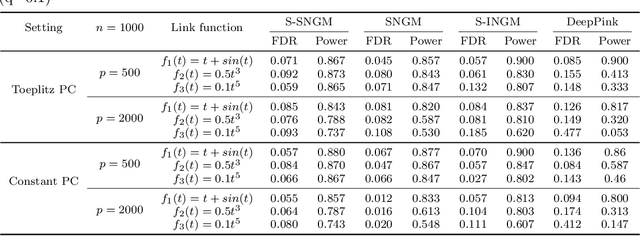
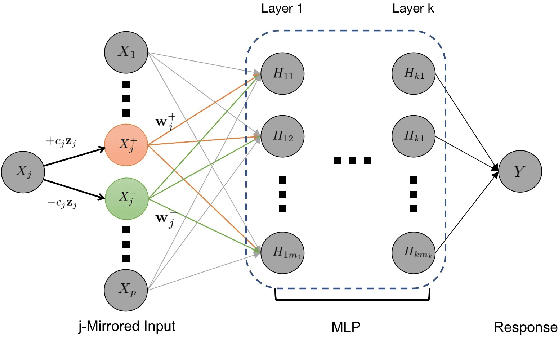
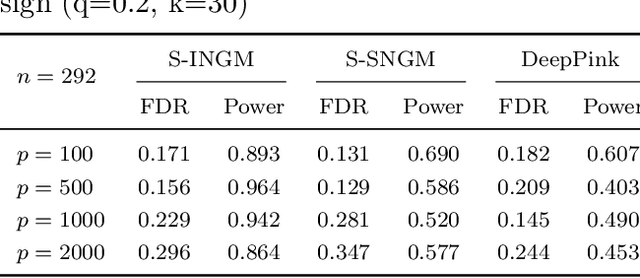
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) have become increasingly popular and achieved outstanding performance in predictive tasks. However, the DNN framework itself cannot inform the user which features are more or less relevant for making the prediction, which limits its applicability in many scientific fields. We introduce neural Gaussian mirrors (NGMs), in which mirrored features are created, via a structured perturbation based on a kernel-based conditional dependence measure, to help evaluate feature importance. We design two modifications of the DNN architecture for incorporating mirrored features and providing mirror statistics to measure feature importance. As shown in simulated and real data examples, the proposed method controls the feature selection error rate at a predefined level and maintains a high selection power even with the presence of highly correlated features.
The Wang-Landau Algorithm as Stochastic Optimization and its Acceleration
Jul 27, 2019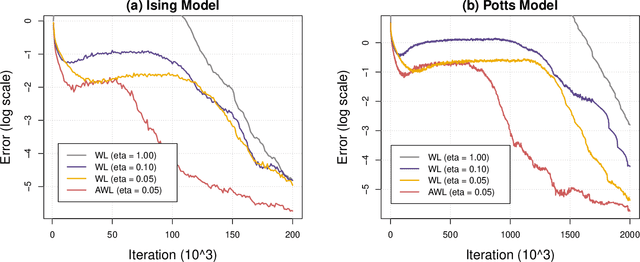
Abstract:We show that the Wang-Landau algorithm can be formulated as a stochastic gradient descent algorithm minimizing a smooth and convex objective function, of which the gradient is estimated using Markov Chain Monte Carlo iterations. The optimization formulation provides a new perspective for improving the efficiency of the Wang-Landau algorithm using optimization tools. We propose one possible improvement, based on the momentum method and the adaptive learning rate idea, and demonstrate it on a two-dimensional Ising model and a two-dimensional ten-state Potts model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge