Chengdong Lan
Saliency-Aware Spatio-Temporal Artifact Detection for Compressed Video Quality Assessment
Jan 03, 2023Abstract:Compressed videos often exhibit visually annoying artifacts, known as Perceivable Encoding Artifacts (PEAs), which dramatically degrade video visual quality. Subjective and objective measures capable of identifying and quantifying various types of PEAs are critical in improving visual quality. In this paper, we investigate the influence of four spatial PEAs (i.e. blurring, blocking, bleeding, and ringing) and two temporal PEAs (i.e. flickering and floating) on video quality. For spatial artifacts, we propose a visual saliency model with a low computational cost and higher consistency with human visual perception. In terms of temporal artifacts, self-attention based TimeSFormer is improved to detect temporal artifacts. Based on the six types of PEAs, a quality metric called Saliency-Aware Spatio-Temporal Artifacts Measurement (SSTAM) is proposed. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art metrics. We believe that SSTAM will be beneficial for optimizing video coding techniques.
Multi-View Video Coding with GAN Latent Learning
May 07, 2022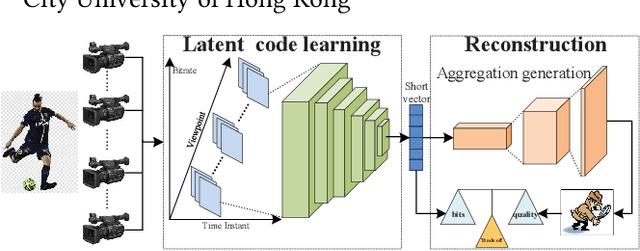
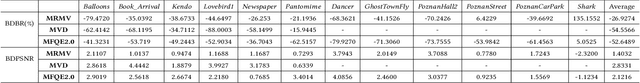
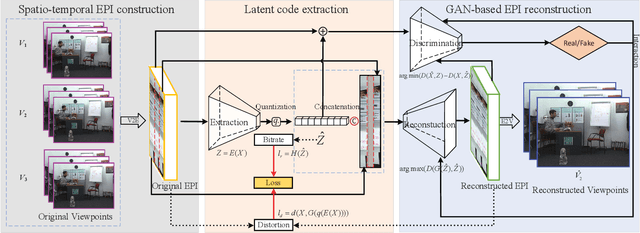
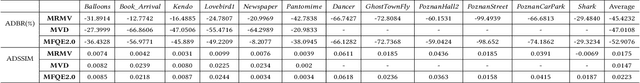
Abstract:The introduction of multiple viewpoints inevitably increases the bitrates to store and transmit video scenes. To reduce the compressed bitrates, researchers have developed to skip intermediate viewpoints during compression and delivery, and finally reconstruct them with Side Information (SI). Generally, the depth maps can be utilized to construct SI; however, it shows inferior performance with inaccurate reconstruction or high bitrates. In this paper, we propose a multi-view video coding based on SI of Generative Adversarial Network (GAN). At the encoder, we construct a spatio-temporal Epipolar Plane Image (EPI) and further utilize convolutional network to extract the latent code of GAN as SI; while at the decoder side, we combine the SI and adjacent viewpoints to reconstruct intermediate views by the generator of GAN. In particular, we set a joint encoder constraint of reconstruction cost and SI entropy, in order to achieve an optimal tradeoff between reconstruction quality and bitrate overhead. Experiments show a significantly improved Rate-Distortion (RD) performance compared with the state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge