Charles Roques-Carmes
Computational metaoptics for imaging
Nov 14, 2024



Abstract:Metasurfaces -- ultrathin structures composed of subwavelength optical elements -- have revolutionized light manipulation by enabling precise control over electromagnetic waves' amplitude, phase, polarization, and spectral properties. Concurrently, computational imaging leverages algorithms to reconstruct images from optically processed signals, overcoming limitations of traditional imaging systems. This review explores the synergistic integration of metaoptics and computational imaging, "computational metaoptics," which combines the physical wavefront shaping ability of metasurfaces with advanced computational algorithms to enhance imaging performance beyond conventional limits. We discuss how computational metaoptics addresses the inherent limitations of single-layer metasurfaces in achieving multifunctionality without compromising efficiency. By treating metasurfaces as physical preconditioners and co-designing them with reconstruction algorithms through end-to-end (inverse) design, it is possible to jointly optimize the optical hardware and computational software. This holistic approach allows for the automatic discovery of optimal metasurface designs and reconstruction methods that significantly improve imaging capabilities. Advanced applications enabled by computational metaoptics are highlighted, including phase imaging and quantum state measurement, which benefit from the metasurfaces' ability to manipulate complex light fields and the computational algorithms' capacity to reconstruct high-dimensional information. We also examine performance evaluation challenges, emphasizing the need for new metrics that account for the combined optical and computational nature of these systems. Finally, we identify new frontiers in computational metaoptics which point toward a future where computational metaoptics may play a central role in advancing imaging science and technology.
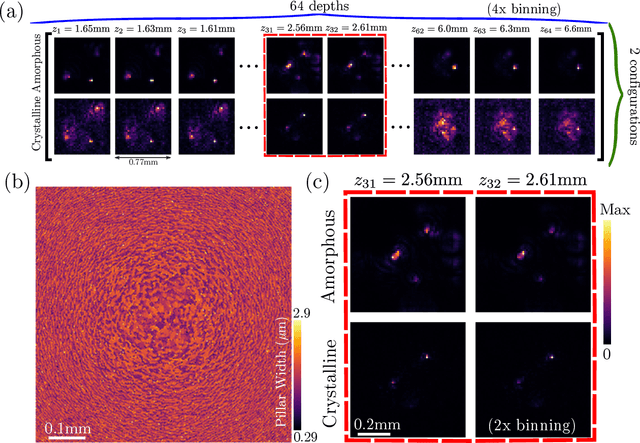
Transcending shift-invariance in the paraxial regime via end-to-end inverse design of freeform nanophotonics
Feb 03, 2023Abstract:Traditional optical elements and conventional metasurfaces obey shift-invariance in the paraxial regime. For imaging systems obeying paraxial shift-invariance, a small shift in input angle causes a corresponding shift in the sensor image. Shift-invariance has deep implications for the design and functionality of optical devices, such as the necessity of free space between components (as in compound objectives made of several curved surfaces). We present a method for nanophotonic inverse design of compact imaging systems whose resolution is not constrained by paraxial shift-invariance. Our method is end-to-end, in that it integrates density-based full-Maxwell topology optimization with a fully iterative elastic-net reconstruction algorithm. By the design of nanophotonic structures that scatter light in a non-shift-invariant manner, our optimized nanophotonic imaging system overcomes the limitations of paraxial shift-invariance, achieving accurate, noise-robust image reconstruction beyond shift-invariant resolution.
End-to-End Optimization of Metasurfaces for Imaging with Compressed Sensing
Jan 28, 2022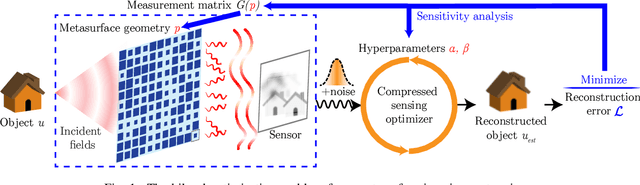
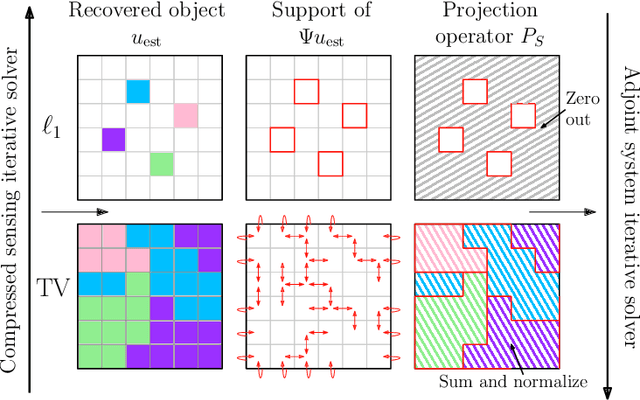
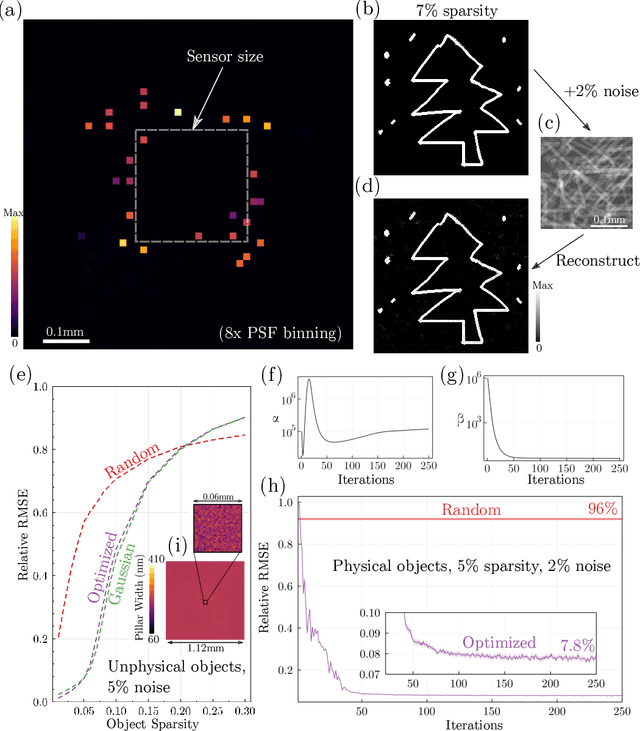
Abstract:We present a method for the end-to-end optimization of computational imaging systems that reconstruct targets using compressed sensing. Using an adjoint analysis of the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker conditions, we incorporate a fully iterative compressed sensing algorithm that solves an $\ell_1$-regularized minimization problem, nested within the end-to-end optimization pipeline. We apply this method to jointly optimize the optical and computational parameters of metasurface-based imaging systems for underdetermined recovery problems. This allows us to investigate the interplay of nanoscale optics with the design goals of compressed sensing imaging systems. Our optimized metasurface imaging systems are robust to noise, significantly improving over random scattering surfaces and approaching the ideal compressed sensing performance of a Gaussian matrix.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge