Changchun Hua
Structure-Preserving Margin Distribution Learning for High-Order Tensor Data with Low-Rank Decomposition
Sep 18, 2025



Abstract:The Large Margin Distribution Machine (LMDM) is a recent advancement in classifier design that optimizes not just the minimum margin (as in SVM) but the entire margin distribution, thereby improving generalization. However, existing LMDM formulations are limited to vectorized inputs and struggle with high-dimensional tensor data due to the need for flattening, which destroys the data's inherent multi-mode structure and increases computational burden. In this paper, we propose a Structure-Preserving Margin Distribution Learning for High-Order Tensor Data with Low-Rank Decomposition (SPMD-LRT) that operates directly on tensor representations without vectorization. The SPMD-LRT preserves multi-dimensional spatial structure by incorporating first-order and second-order tensor statistics (margin mean and variance) into the objective, and it leverages low-rank tensor decomposition techniques including rank-1(CP), higher-rank CP, and Tucker decomposition to parameterize the weight tensor. An alternating optimization (double-gradient descent) algorithm is developed to efficiently solve the SPMD-LRT, iteratively updating factor matrices and core tensor. This approach enables SPMD-LRT to maintain the structural information of high-order data while optimizing margin distribution for improved classification. Extensive experiments on diverse datasets (including MNIST, images and fMRI neuroimaging) demonstrate that SPMD-LRT achieves superior classification accuracy compared to conventional SVM, vector-based LMDM, and prior tensor-based SVM extensions (Support Tensor Machines and Support Tucker Machines). Notably, SPMD-LRT with Tucker decomposition attains the highest accuracy, highlighting the benefit of structure preservation. These results confirm the effectiveness and robustness of SPMD-LRT in handling high-dimensional tensor data for classification.
A Unified Empirical Risk Minimization Framework for Flexible N-Tuples Weak Supervision
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:To alleviate the annotation burden in supervised learning, N-tuples learning has recently emerged as a powerful weakly-supervised method. While existing N-tuples learning approaches extend pairwise learning to higher-order comparisons and accommodate various real-world scenarios, they often rely on task-specific designs and lack a unified theoretical foundation. In this paper, we propose a general N-tuples learning framework based on empirical risk minimization, which systematically integrates pointwise unlabeled data to enhance learning performance. This paper first unifies the data generation processes of N-tuples and pointwise unlabeled data under a shared probabilistic formulation. Based on this unified view, we derive an unbiased empirical risk estimator that generalizes a broad class of existing N-tuples models. We further establish a generalization error bound for theoretical support. To demonstrate the flexibility of the framework, we instantiate it in four representative weakly supervised scenarios, each recoverable as a special case of our general model. Additionally, to address overfitting issues arising from negative risk terms, we adopt correction functions to adjust the empirical risk. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets validate the effectiveness of the proposed framework and demonstrate that leveraging pointwise unlabeled data consistently improves generalization across various N-tuples learning tasks.
ZISVFM: Zero-Shot Object Instance Segmentation in Indoor Robotic Environments with Vision Foundation Models
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:Service robots operating in unstructured environments must effectively recognize and segment unknown objects to enhance their functionality. Traditional supervised learningbased segmentation techniques require extensive annotated datasets, which are impractical for the diversity of objects encountered in real-world scenarios. Unseen Object Instance Segmentation (UOIS) methods aim to address this by training models on synthetic data to generalize to novel objects, but they often suffer from the simulation-to-reality gap. This paper proposes a novel approach (ZISVFM) for solving UOIS by leveraging the powerful zero-shot capability of the segment anything model (SAM) and explicit visual representations from a selfsupervised vision transformer (ViT). The proposed framework operates in three stages: (1) generating object-agnostic mask proposals from colorized depth images using SAM, (2) refining these proposals using attention-based features from the selfsupervised ViT to filter non-object masks, and (3) applying K-Medoids clustering to generate point prompts that guide SAM towards precise object segmentation. Experimental validation on two benchmark datasets and a self-collected dataset demonstrates the superior performance of ZISVFM in complex environments, including hierarchical settings such as cabinets, drawers, and handheld objects. Our source code is available at https://github.com/Yinmlmaoliang/zisvfm.
Environment Modeling for Service Robots From a Task Execution Perspective
Jan 10, 2025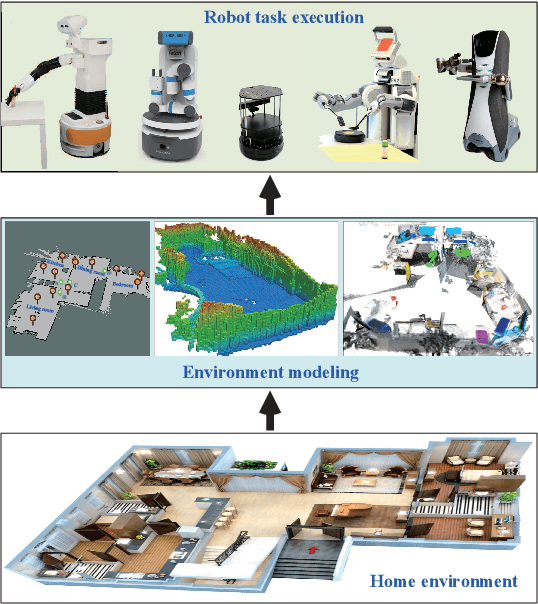
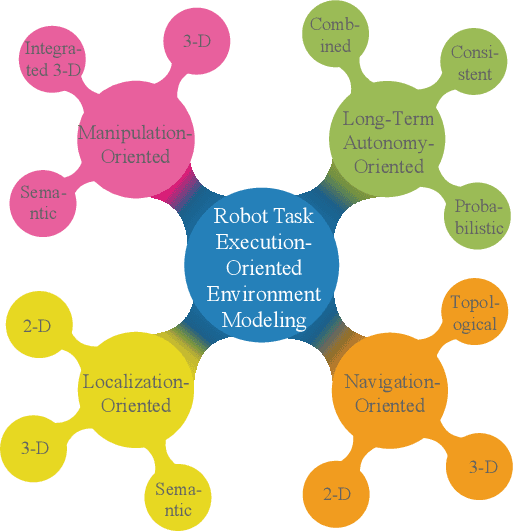
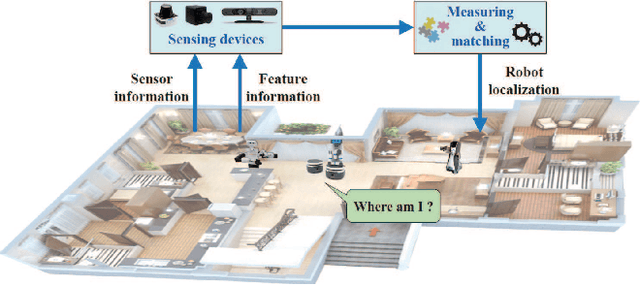
Abstract:Service robots are increasingly entering the home to provide domestic tasks for residents. However, when working in an open, dynamic, and unstructured home environment, service robots still face challenges such as low intelligence for task execution and poor long-term autonomy (LTA), which has limited their deployment. As the basis of robotic task execution, environment modeling has attracted significant attention. This integrates core technologies such as environment perception, understanding, and representation to accurately recognize environmental information. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of environmental modeling from a new task-executionoriented perspective. In particular, guided by the requirements of robots in performing domestic service tasks in the home environment, we systematically review the progress that has been made in task-execution-oriented environmental modeling in four respects: 1) localization, 2) navigation, 3) manipulation, and 4) LTA. Current challenges are discussed, and potential research opportunities are also highlighted.
* 16 pages, 9 figures; This article has been accepted for publication in a future issue of IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, but has not been fully edited. Content may change prior to final publication
Air-Ground Collaborative Robots for Fire and Rescue Missions: Towards Mapping and Navigation Perspective
Dec 30, 2024Abstract:Air-ground collaborative robots have shown great potential in the field of fire and rescue, which can quickly respond to rescue needs and improve the efficiency of task execution. Mapping and navigation, as the key foundation for air-ground collaborative robots to achieve efficient task execution, have attracted a great deal of attention. This growing interest in collaborative robot mapping and navigation is conducive to improving the intelligence of fire and rescue task execution, but there has been no comprehensive investigation of this field to highlight their strengths. In this paper, we present a systematic review of the ground-to-ground cooperative robots for fire and rescue from a new perspective of mapping and navigation. First, an air-ground collaborative robots framework for fire and rescue missions based on unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) mapping and unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) navigation is introduced. Then, the research progress of mapping and navigation under this framework is systematically summarized, including UAV mapping, UAV/UGV co-localization, and UGV navigation, with their main achievements and limitations. Based on the needs of fire and rescue missions, the collaborative robots with different numbers of UAVs and UGVs are classified, and their practicality in fire and rescue tasks is elaborated, with a focus on the discussion of their merits and demerits. In addition, the application examples of air-ground collaborative robots in various firefighting and rescue scenarios are given. Finally, this paper emphasizes the current challenges and potential research opportunities, rounding up references for practitioners and researchers willing to engage in this vibrant area of air-ground collaborative robots.
Bi-AM-RRT*: A Fast and Efficient Sampling-Based Motion Planning Algorithm in Dynamic Environments
Jan 27, 2023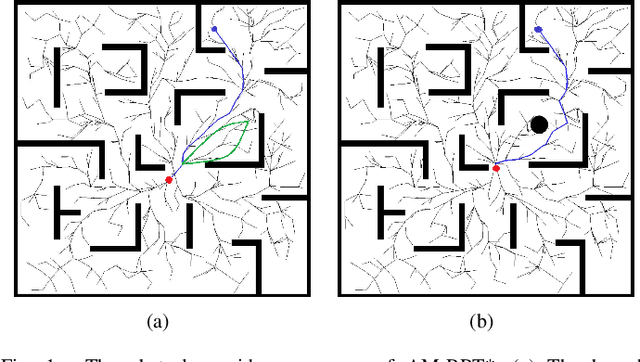
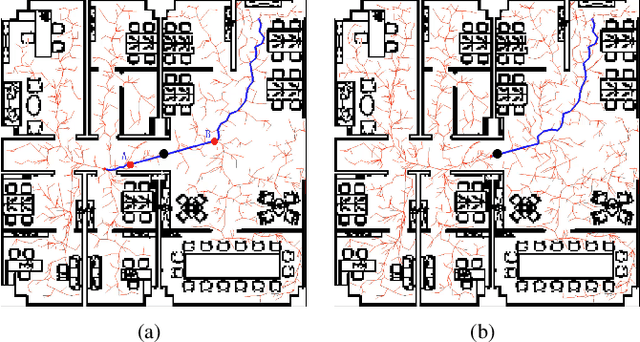
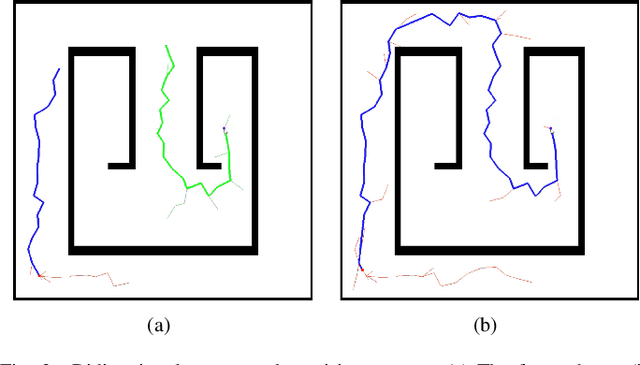
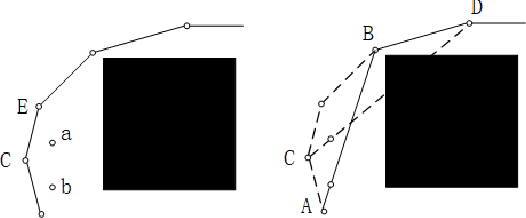
Abstract:The efficiency of sampling-based motion planning brings wide application in autonomous mobile robots. Conventional rapidly exploring random tree (RRT) algorithm and its variants have gained great successes, but there are still challenges for the real-time optimal motion planning of mobile robots in dynamic environments. In this paper, based on Bidirectional RRT (Bi-RRT) and the use of an assisting metric (AM), we propose a novel motion planning algorithm, namely Bi-AM-RRT*. Different from the existing RRT-based methods, the AM is introduced in this paper to optimize the performance of robot motion planning in dynamic environments with obstacles. On this basis, the bidirectional search sampling strategy is employed, in order to increase the planning efficiency. Further, we present an improved rewiring method to shorten path lengths. The effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed Bi-AM-RRT* are proved through comparative experiments in different environments. Experimental results show that the Bi-AM-RRT* algorithm can achieve better performance in terms of path length and search time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge