Chang Jia
Meta Mask Correction for Nuclei Segmentation in Histopathological Image
Nov 24, 2021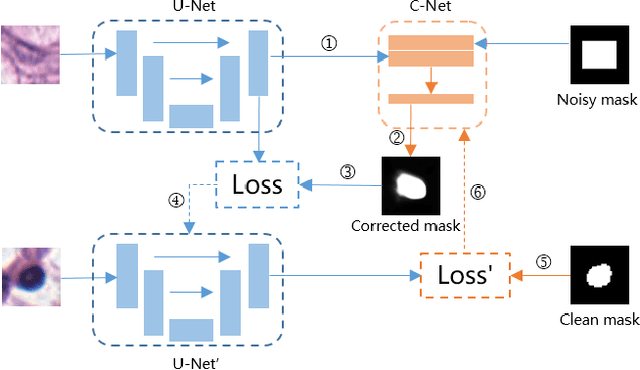
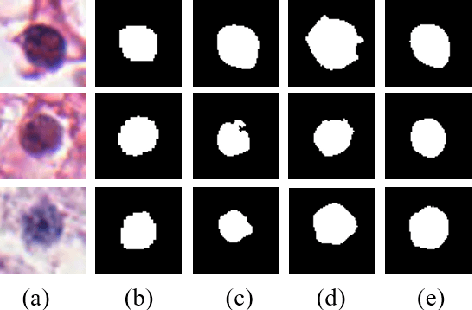
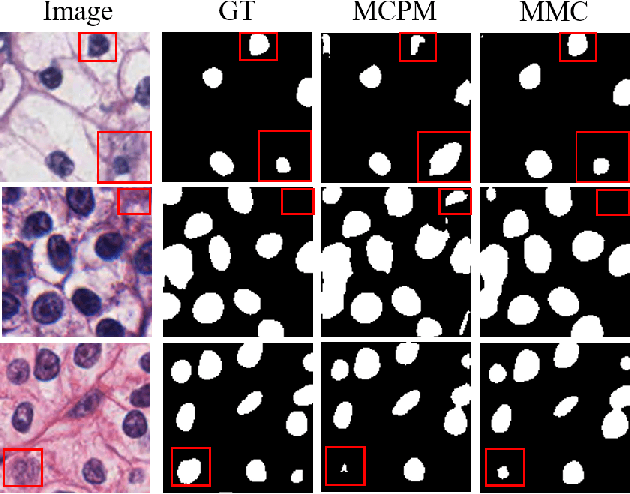
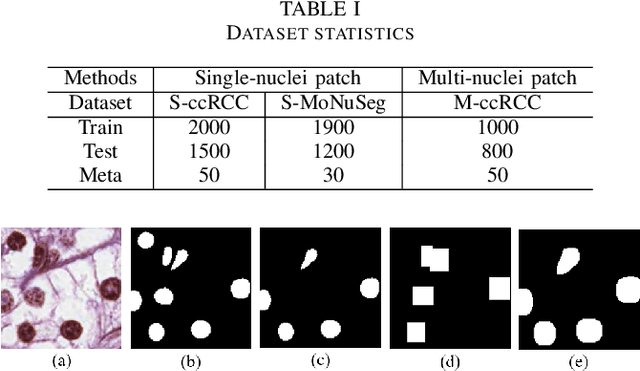
Abstract:Nuclei segmentation is a fundamental task in digital pathology analysis and can be automated by deep learning-based methods. However, the development of such an automated method requires a large amount of data with precisely annotated masks which is hard to obtain. Training with weakly labeled data is a popular solution for reducing the workload of annotation. In this paper, we propose a novel meta-learning-based nuclei segmentation method which follows the label correction paradigm to leverage data with noisy masks. Specifically, we design a fully conventional meta-model that can correct noisy masks using a small amount of clean meta-data. Then the corrected masks can be used to supervise the training of the segmentation model. Meanwhile, a bi-level optimization method is adopted to alternately update the parameters of the main segmentation model and the meta-model in an end-to-end way. Extensive experimental results on two nuclear segmentation datasets show that our method achieves the state-of-the-art result. It even achieves comparable performance with the model training on supervised data in some noisy settings.
Instance-based Vision Transformer for Subtyping of Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma in Histopathological Image
Jun 23, 2021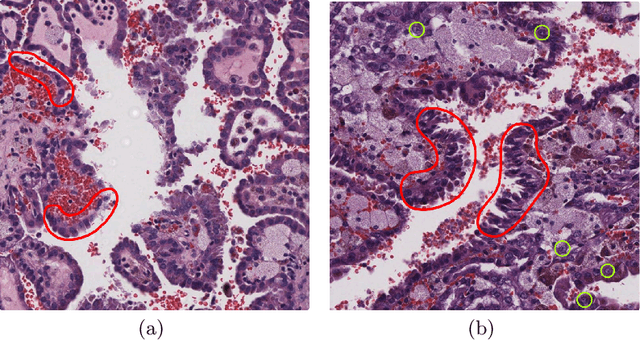
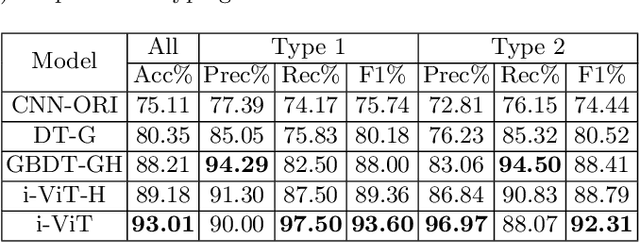
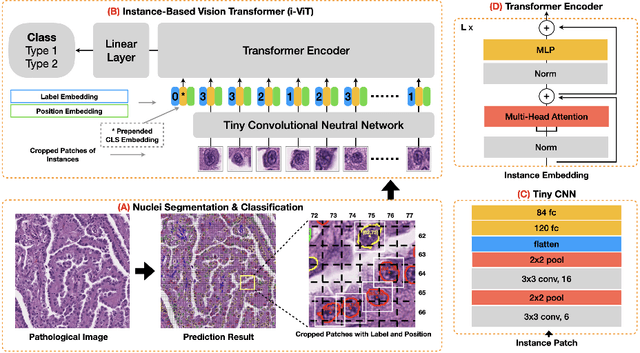
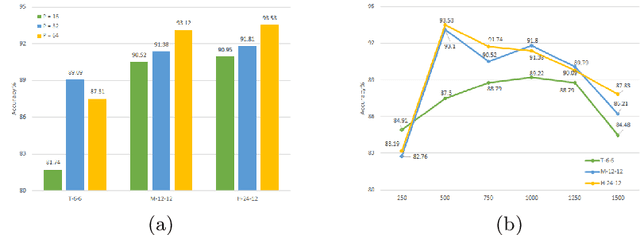
Abstract:Histological subtype of papillary (p) renal cell carcinoma (RCC), type 1 vs. type 2, is an essential prognostic factor. The two subtypes of pRCC have a similar pattern, i.e., the papillary architecture, yet some subtle differences, including cellular and cell-layer level patterns. However, the cellular and cell-layer level patterns almost cannot be captured by existing CNN-based models in large-size histopathological images, which brings obstacles to directly applying these models to such a fine-grained classification task. This paper proposes a novel instance-based Vision Transformer (i-ViT) to learn robust representations of histopathological images for the pRCC subtyping task by extracting finer features from instance patches (by cropping around segmented nuclei and assigning predicted grades). The proposed i-ViT takes top-K instances as input and aggregates them for capturing both the cellular and cell-layer level patterns by a position-embedding layer, a grade-embedding layer, and a multi-head multi-layer self-attention module. To evaluate the performance of the proposed framework, experienced pathologists are invited to selected 1162 regions of interest from 171 whole slide images of type 1 and type 2 pRCC. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves better performance than existing CNN-based models with a significant margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge