Carlos Cordeiro
Towards Integrated Sensing and Communications in IEEE 802.11bf Wi-Fi Networks
Dec 28, 2022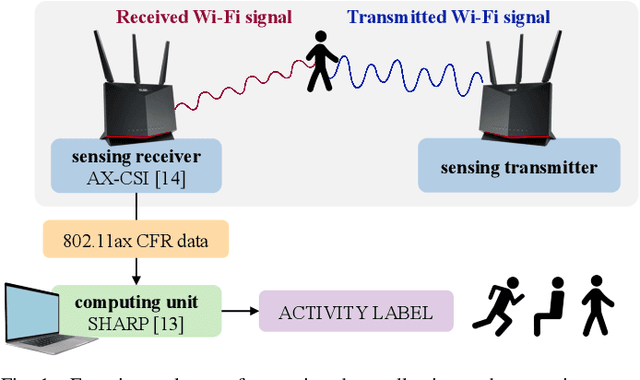
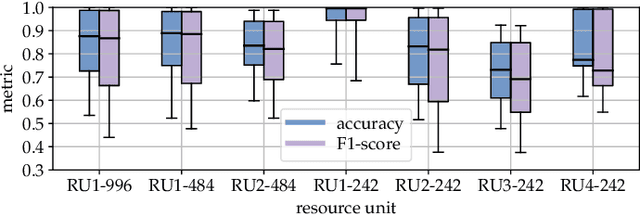
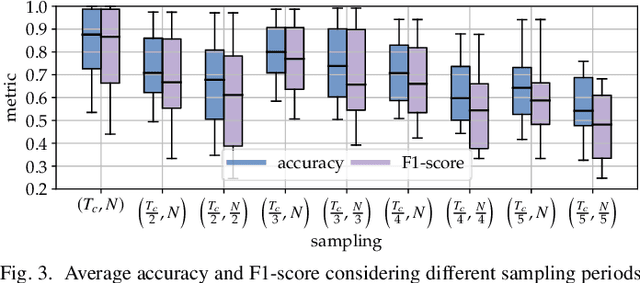
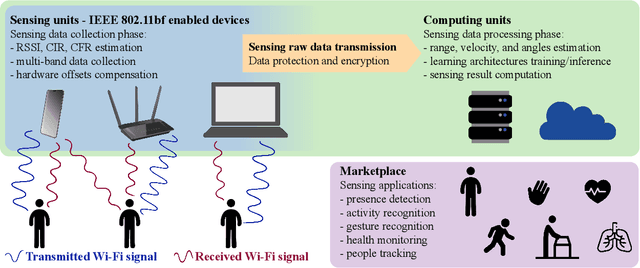
Abstract:As Wi-Fi becomes ubiquitous in public and private spaces, it becomes natural to leverage its intrinsic ability to sense the surrounding environment to implement groundbreaking wireless sensing applications such as human presence detection, activity recognition, and object tracking. For this reason, the IEEE 802.11bf Task Group is defining the appropriate modifications to existing Wi-Fi standards to enhance sensing capabilities through 802.11-compliant devices. However, the new standard is expected to leave the specific sensing algorithms open to implementation. To fill this gap, this article explores the practical implications of integrating sensing and communications into Wi-Fi networks. We provide an overview of the support that will enable sensing applications, together with an in-depth analysis of the role of different devices in a Wi-Fi sensing system and a description of the open research challenges. Moreover, an experimental evaluation with off-the-shelf devices provides suggestions about the parameters to be considered when designing Wi-Fi sensing systems. To make such an evaluation replicable, we pledge to release all of our dataset and code to the community.
Cooperative Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Reliable and Energy-Efficient Mobile Access via Multi-UAV Control
Oct 03, 2022


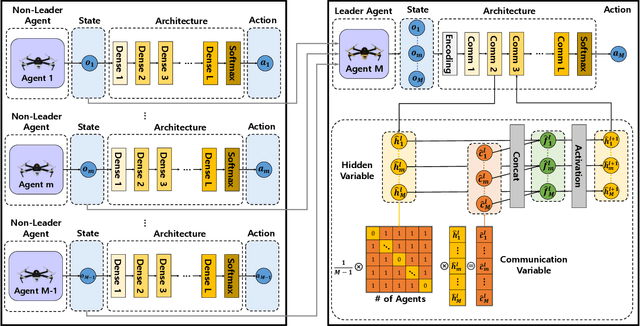
Abstract:This paper addresses a novel multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (MADRL)-based multiple unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) positioning algorithm for reliable mobile access services (i.e., UAVs work as mobile base stations), where the MADRL is designed by the concept of centralized training and distributed execution (CTDE) for multi-agent cooperation and coordination. The reliable mobile access services can be achieved in following two ways, i.e., (i) energy-efficient UAV operation and (ii) reliable wireless communication services. For energy-efficient UAV operation, the reward of our proposed MADRL algorithm contains the features for UAV energy consumption models in order to realize efficient operations. Furthermore, for reliable wireless communication services, the quality of service (QoS) requirements of individual users are considered as a part of rewards and 60GHz mmWave radio is used for mobile access. This paper considers the 60GHz mmWave access for utilizing the benefits of (i) ultra-wide-bandwidth for multi-Gbps high-speed communications and (ii) high-directional communications for spatial reuse that is obviously good for densely deployed users. Lastly, the performance of our proposed MADRL-based multi-UAV positioning algorithm is evaluated; and it can be confirmed that the proposed algorithm outperforms the other existing algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge