Can Yi
Tabular Foundation Models are Strong Graph Anomaly Detectors
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Graph anomaly detection (GAD), which aims to identify abnormal nodes that deviate from the majority, has become increasingly important in high-stakes Web domains. However, existing GAD methods follow a "one model per dataset" paradigm, leading to high computational costs, substantial data demands, and poor generalization when transferred to new datasets. This calls for a foundation model that enables a "one-for-all" GAD solution capable of detecting anomalies across diverse graphs without retraining. Yet, achieving this is challenging due to the large structural and feature heterogeneity across domains. In this paper, we propose TFM4GAD, a simple yet effective framework that adapts tabular foundation models (TFMs) for graph anomaly detection. Our key insight is that the core challenges of foundation GAD, handling heterogeneous features, generalizing across domains, and operating with scarce labels, are the exact problems that modern TFMs are designed to solve via synthetic pre-training and powerful in-context learning. The primary challenge thus becomes structural: TFMs are agnostic to graph topology. TFM4GAD bridges this gap by "flattening" the graph, constructing an augmented feature table that enriches raw node features with Laplacian embeddings, local and global structural characteristics, and anomaly-sensitive neighborhood aggregations. This augmented table is processed by a TFM in a fully in-context regime. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets with various TFM backbones reveal that TFM4GAD surprisingly achieves significant performance gains over specialized GAD models trained from scratch. Our work offers a new perspective and a practical paradigm for leveraging TFMs as powerful, generalist graph anomaly detectors.
Careful Queries, Credible Results: Teaching RAG Models Advanced Web Search Tools with Reinforcement Learning
Aug 11, 2025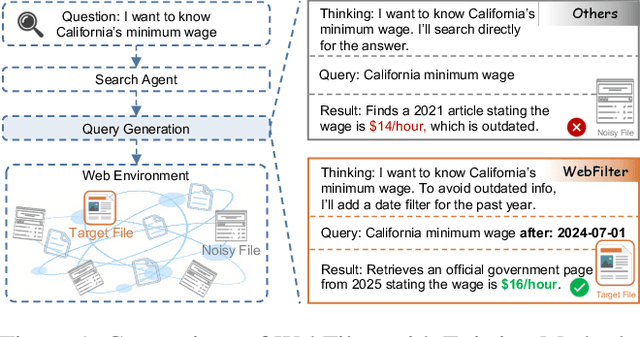
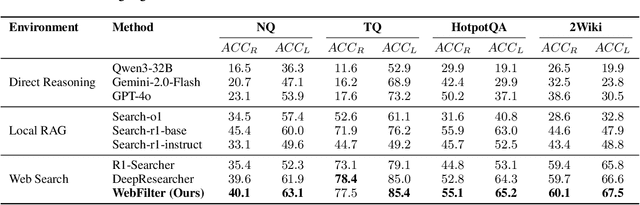
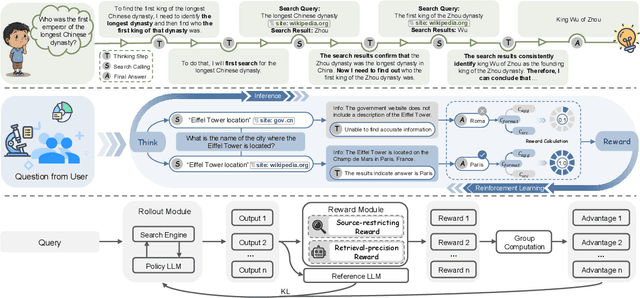
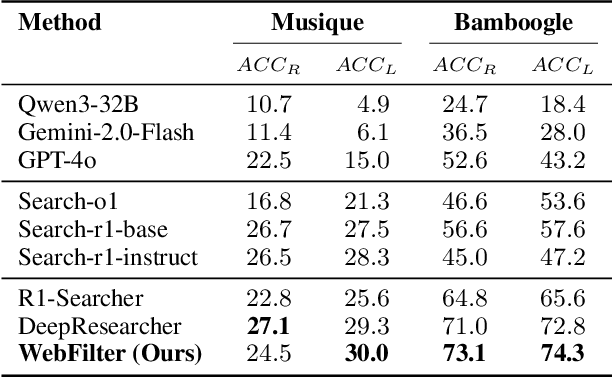
Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances large language models (LLMs) by integrating up-to-date external knowledge, yet real-world web environments present unique challenges. These limitations manifest as two key challenges: pervasive misinformation in the web environment, which introduces unreliable or misleading content that can degrade retrieval accuracy, and the underutilization of web tools, which, if effectively employed, could enhance query precision and help mitigate this noise, ultimately improving the retrieval results in RAG systems. To address these issues, we propose WebFilter, a novel RAG framework that generates source-restricted queries and filters out unreliable content. This approach combines a retrieval filtering mechanism with a behavior- and outcome-driven reward strategy, optimizing both query formulation and retrieval outcomes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that WebFilter improves answer quality and retrieval precision, outperforming existing RAG methods on both in-domain and out-of-domain benchmarks.
AIGT: AI Generative Table Based on Prompt
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:Tabular data, which accounts for over 80% of enterprise data assets, is vital in various fields. With growing concerns about privacy protection and data-sharing restrictions, generating high-quality synthetic tabular data has become essential. Recent advancements show that large language models (LLMs) can effectively gener-ate realistic tabular data by leveraging semantic information and overcoming the challenges of high-dimensional data that arise from one-hot encoding. However, current methods do not fully utilize the rich information available in tables. To address this, we introduce AI Generative Table (AIGT) based on prompt enhancement, a novel approach that utilizes meta data information, such as table descriptions and schemas, as prompts to generate ultra-high quality synthetic data. To overcome the token limit constraints of LLMs, we propose long-token partitioning algorithms that enable AIGT to model tables of any scale. AIGT achieves state-of-the-art performance on 14 out of 20 public datasets and two real industry datasets within the Alipay risk control system.
XUAT-Copilot: Multi-Agent Collaborative System for Automated User Acceptance Testing with Large Language Model
Jan 10, 2024Abstract:In past years, we have been dedicated to automating user acceptance testing (UAT) process of WeChat Pay, one of the most influential mobile payment applications in China. A system titled XUAT has been developed for this purpose. However, there is still a human-labor-intensive stage, i.e, test scripts generation, in the current system. Therefore, in this paper, we concentrate on methods of boosting the automation level of the current system, particularly the stage of test scripts generation. With recent notable successes, large language models (LLMs) demonstrate significant potential in attaining human-like intelligence and there has been a growing research area that employs LLMs as autonomous agents to obtain human-like decision-making capabilities. Inspired by these works, we propose an LLM-powered multi-agent collaborative system, named XUAT-Copilot, for automated UAT. The proposed system mainly consists of three LLM-based agents responsible for action planning, state checking and parameter selecting, respectively, and two additional modules for state sensing and case rewriting. The agents interact with testing device, make human-like decision and generate action command in a collaborative way. The proposed multi-agent system achieves a close effectiveness to human testers in our experimental studies and gains a significant improvement of Pass@1 accuracy compared with single-agent architecture. More importantly, the proposed system has launched in the formal testing environment of WeChat Pay mobile app, which saves a considerable amount of manpower in the daily development work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge