Cagri Toraman
OpenEthics: A Comprehensive Ethical Evaluation of Open-Source Generative Large Language Models
May 21, 2025Abstract:Generative large language models present significant potential but also raise critical ethical concerns. Most studies focus on narrow ethical dimensions, and also limited diversity of languages and models. To address these gaps, we conduct a broad ethical evaluation of 29 recent open-source large language models using a novel data collection including four ethical aspects: Robustness, reliability, safety, and fairness. We analyze model behavior in both a commonly used language, English, and a low-resource language, Turkish. Our aim is to provide a comprehensive ethical assessment and guide safer model development by filling existing gaps in evaluation breadth, language coverage, and model diversity. Our experimental results, based on LLM-as-a-Judge, reveal that optimization efforts for many open-source models appear to have prioritized safety and fairness, and demonstrated good robustness while reliability remains a concern. We demonstrate that ethical evaluation can be effectively conducted independently of the language used. In addition, models with larger parameter counts tend to exhibit better ethical performance, with Gemma and Qwen models demonstrating the most ethical behavior among those evaluated.
Evaluating the Quality of Benchmark Datasets for Low-Resource Languages: A Case Study on Turkish
Apr 13, 2025



Abstract:The reliance on translated or adapted datasets from English or multilingual resources introduces challenges regarding linguistic and cultural suitability. This study addresses the need for robust and culturally appropriate benchmarks by evaluating the quality of 17 commonly used Turkish benchmark datasets. Using a comprehensive framework that assesses six criteria, both human and LLM-judge annotators provide detailed evaluations to identify dataset strengths and shortcomings. Our results reveal that 70% of the benchmark datasets fail to meet our heuristic quality standards. The correctness of the usage of technical terms is the strongest criterion, but 85% of the criteria are not satisfied in the examined datasets. Although LLM judges demonstrate potential, they are less effective than human annotators, particularly in understanding cultural common sense knowledge and interpreting fluent, unambiguous text. GPT-4o has stronger labeling capabilities for grammatical and technical tasks, while Llama3.3-70B excels at correctness and cultural knowledge evaluation. Our findings emphasize the urgent need for more rigorous quality control in creating and adapting datasets for low-resource languages.
LlamaTurk: Adapting Open-Source Generative Large Language Models for Low-Resource Language
May 13, 2024Abstract:Despite advancements in English-dominant generative large language models, further development is needed for low-resource languages to enhance global accessibility. The primary methods for representing these languages are monolingual and multilingual pretraining. Monolingual pretraining is expensive due to hardware requirements, and multilingual models often have uneven performance across languages. This study explores an alternative solution by adapting large language models, primarily trained on English, to low-resource languages. We assess various strategies, including continual training, instruction fine-tuning, task-specific fine-tuning, and vocabulary extension. The results show that continual training improves language comprehension, as reflected in perplexity scores, and task-specific tuning generally enhances performance of downstream tasks. However, extending the vocabulary shows no substantial benefits. Additionally, while larger models improve task performance with few-shot tuning, multilingual models perform worse than their monolingual counterparts when adapted.
PejorativITy: Disambiguating Pejorative Epithets to Improve Misogyny Detection in Italian Tweets
Apr 03, 2024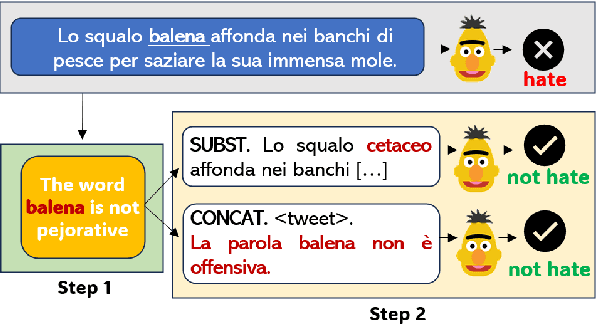
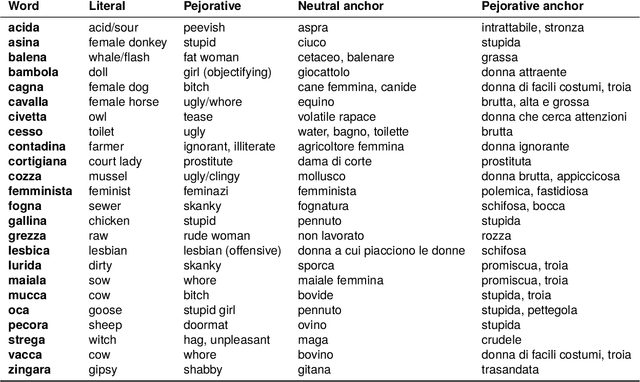
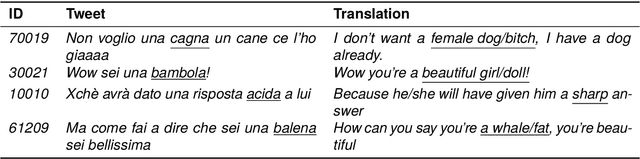
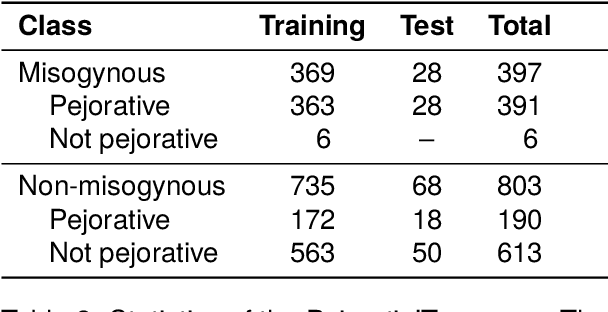
Abstract:Misogyny is often expressed through figurative language. Some neutral words can assume a negative connotation when functioning as pejorative epithets. Disambiguating the meaning of such terms might help the detection of misogyny. In order to address such task, we present PejorativITy, a novel corpus of 1,200 manually annotated Italian tweets for pejorative language at the word level and misogyny at the sentence level. We evaluate the impact of injecting information about disambiguated words into a model targeting misogyny detection. In particular, we explore two different approaches for injection: concatenation of pejorative information and substitution of ambiguous words with univocal terms. Our experimental results, both on our corpus and on two popular benchmarks on Italian tweets, show that both approaches lead to a major classification improvement, indicating that word sense disambiguation is a promising preliminary step for misogyny detection. Furthermore, we investigate LLMs' understanding of pejorative epithets by means of contextual word embeddings analysis and prompting.
ARC-NLP at PAN 2023: Hierarchical Long Text Classification for Trigger Detection
Jul 27, 2023



Abstract:Fanfiction, a popular form of creative writing set within established fictional universes, has gained a substantial online following. However, ensuring the well-being and safety of participants has become a critical concern in this community. The detection of triggering content, material that may cause emotional distress or trauma to readers, poses a significant challenge. In this paper, we describe our approach for the Trigger Detection shared task at PAN CLEF 2023, where we want to detect multiple triggering content in a given Fanfiction document. For this, we build a hierarchical model that uses recurrence over Transformer-based language models. In our approach, we first split long documents into smaller sized segments and use them to fine-tune a Transformer model. Then, we extract feature embeddings from the fine-tuned Transformer model, which are used as input in the training of multiple LSTM models for trigger detection in a multi-label setting. Our model achieves an F1-macro score of 0.372 and F1-micro score of 0.736 on the validation set, which are higher than the baseline results shared at PAN CLEF 2023.
ARC-NLP at PAN 2023: Transition-Focused Natural Language Inference for Writing Style Detection
Jul 27, 2023Abstract:The task of multi-author writing style detection aims at finding any positions of writing style change in a given text document. We formulate the task as a natural language inference problem where two consecutive paragraphs are paired. Our approach focuses on transitions between paragraphs while truncating input tokens for the task. As backbone models, we employ different Transformer-based encoders with warmup phase during training. We submit the model version that outperforms baselines and other proposed model versions in our experiments. For the easy and medium setups, we submit transition-focused natural language inference based on DeBERTa with warmup training, and the same model without transition for the hard setup.
ARC-NLP at Multimodal Hate Speech Event Detection 2023: Multimodal Methods Boosted by Ensemble Learning, Syntactical and Entity Features
Jul 25, 2023
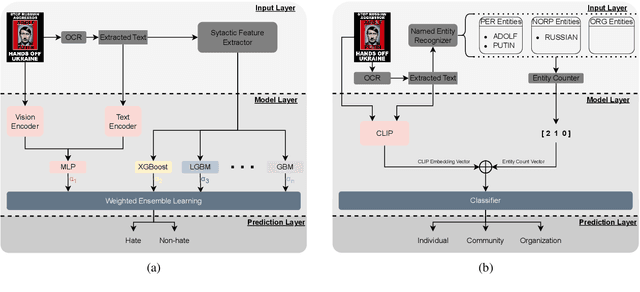


Abstract:Text-embedded images can serve as a means of spreading hate speech, propaganda, and extremist beliefs. Throughout the Russia-Ukraine war, both opposing factions heavily relied on text-embedded images as a vehicle for spreading propaganda and hate speech. Ensuring the effective detection of hate speech and propaganda is of utmost importance to mitigate the negative effect of hate speech dissemination. In this paper, we outline our methodologies for two subtasks of Multimodal Hate Speech Event Detection 2023. For the first subtask, hate speech detection, we utilize multimodal deep learning models boosted by ensemble learning and syntactical text attributes. For the second subtask, target detection, we employ multimodal deep learning models boosted by named entity features. Through experimentation, we demonstrate the superior performance of our models compared to all textual, visual, and text-visual baselines employed in multimodal hate speech detection. Furthermore, our models achieve the first place in both subtasks on the final leaderboard of the shared task.
Tweets Under the Rubble: Detection of Messages Calling for Help in Earthquake Disaster
Feb 26, 2023Abstract:The importance of social media is again exposed in the recent tragedy of the 2023 Turkey and Syria earthquake. Many victims who were trapped under the rubble called for help by posting messages in Twitter. We present an interactive tool to provide situational awareness for missing and trapped people, and disaster relief for rescue and donation efforts. The system (i) collects tweets, (ii) classifies the ones calling for help, (iii) extracts important entity tags, and (iv) visualizes them in an interactive map screen. Our initial experiments show that the performance in terms of the F1 score is up to 98.30 for tweet classification, and 84.32 for entity extraction. The demonstration, dataset, and other related files can be accessed at https://github.com/avaapm/deprem
Not Good Times for Lies: Misinformation Detection on the Russia-Ukraine War, COVID-19, and Refugees
Oct 11, 2022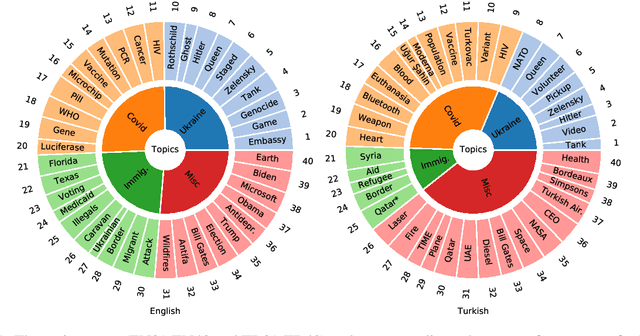
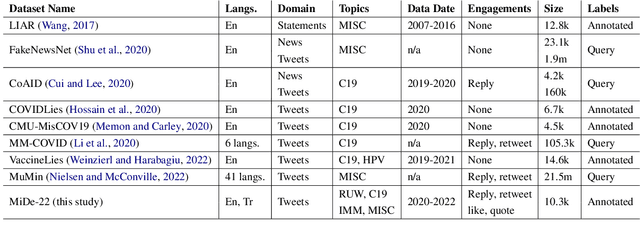

Abstract:Misinformation spread in online social networks is an urgent-to-solve problem having harmful consequences that threaten human health, public safety, economics, and so on. In this study, we construct a novel dataset, called MiDe-22, having 5,284 English and 5,064 Turkish tweets with their misinformation labels under several recent events, including the Russia-Ukraine war, COVID-19 pandemic, and Refugees. Moreover, we provide the user engagements to the tweets in terms of likes, replies, retweets, and quotes. We present a detailed data analysis with descriptive statistics and temporal analysis, and provide the experimental results of a benchmark evaluation for misinformation detection on our novel dataset.
Impact of Tokenization on Language Models: An Analysis for Turkish
Apr 19, 2022
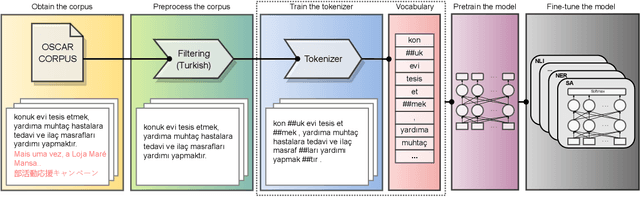

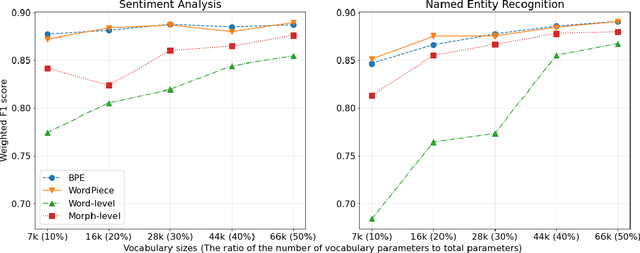
Abstract:Tokenization is an important text preprocessing step to prepare input tokens for deep language models. WordPiece and BPE are de facto methods employed by important models, such as BERT and GPT. However, the impact of tokenization can be different for morphologically rich languages, such as Turkic languages, where many words can be generated by adding prefixes and suffixes. We compare five tokenizers at different granularity levels, i.e. their outputs vary from smallest pieces of characters to the surface form of words, including a Morphological-level tokenizer. We train these tokenizers and pretrain medium-sized language models using RoBERTa pretraining procedure on the Turkish split of the OSCAR corpus. We then fine-tune our models on six downstream tasks. Our experiments, supported by statistical tests, reveal that Morphological-level tokenizer has challenging performance with de facto tokenizers. Furthermore, we find that increasing the vocabulary size improves the performance of Morphological and Word-level tokenizers more than that of de facto tokenizers. The ratio of the number of vocabulary parameters to the total number of model parameters can be empirically chosen as 20% for de facto tokenizers and 40% for other tokenizers to obtain a reasonable trade-off between model size and performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge