Umitcan Sahin
ARC-NLP at PAN 2023: Hierarchical Long Text Classification for Trigger Detection
Jul 27, 2023



Abstract:Fanfiction, a popular form of creative writing set within established fictional universes, has gained a substantial online following. However, ensuring the well-being and safety of participants has become a critical concern in this community. The detection of triggering content, material that may cause emotional distress or trauma to readers, poses a significant challenge. In this paper, we describe our approach for the Trigger Detection shared task at PAN CLEF 2023, where we want to detect multiple triggering content in a given Fanfiction document. For this, we build a hierarchical model that uses recurrence over Transformer-based language models. In our approach, we first split long documents into smaller sized segments and use them to fine-tune a Transformer model. Then, we extract feature embeddings from the fine-tuned Transformer model, which are used as input in the training of multiple LSTM models for trigger detection in a multi-label setting. Our model achieves an F1-macro score of 0.372 and F1-micro score of 0.736 on the validation set, which are higher than the baseline results shared at PAN CLEF 2023.
ARC-NLP at PAN 2023: Transition-Focused Natural Language Inference for Writing Style Detection
Jul 27, 2023Abstract:The task of multi-author writing style detection aims at finding any positions of writing style change in a given text document. We formulate the task as a natural language inference problem where two consecutive paragraphs are paired. Our approach focuses on transitions between paragraphs while truncating input tokens for the task. As backbone models, we employ different Transformer-based encoders with warmup phase during training. We submit the model version that outperforms baselines and other proposed model versions in our experiments. For the easy and medium setups, we submit transition-focused natural language inference based on DeBERTa with warmup training, and the same model without transition for the hard setup.
ARC-NLP at Multimodal Hate Speech Event Detection 2023: Multimodal Methods Boosted by Ensemble Learning, Syntactical and Entity Features
Jul 25, 2023
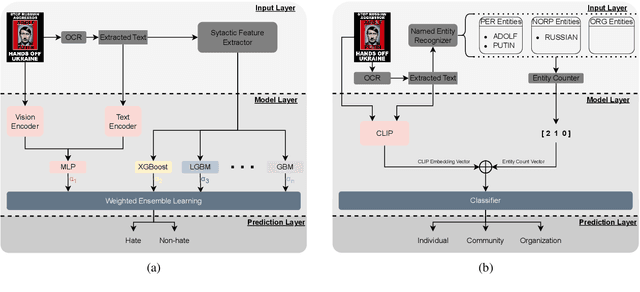


Abstract:Text-embedded images can serve as a means of spreading hate speech, propaganda, and extremist beliefs. Throughout the Russia-Ukraine war, both opposing factions heavily relied on text-embedded images as a vehicle for spreading propaganda and hate speech. Ensuring the effective detection of hate speech and propaganda is of utmost importance to mitigate the negative effect of hate speech dissemination. In this paper, we outline our methodologies for two subtasks of Multimodal Hate Speech Event Detection 2023. For the first subtask, hate speech detection, we utilize multimodal deep learning models boosted by ensemble learning and syntactical text attributes. For the second subtask, target detection, we employ multimodal deep learning models boosted by named entity features. Through experimentation, we demonstrate the superior performance of our models compared to all textual, visual, and text-visual baselines employed in multimodal hate speech detection. Furthermore, our models achieve the first place in both subtasks on the final leaderboard of the shared task.
Tweets Under the Rubble: Detection of Messages Calling for Help in Earthquake Disaster
Feb 26, 2023Abstract:The importance of social media is again exposed in the recent tragedy of the 2023 Turkey and Syria earthquake. Many victims who were trapped under the rubble called for help by posting messages in Twitter. We present an interactive tool to provide situational awareness for missing and trapped people, and disaster relief for rescue and donation efforts. The system (i) collects tweets, (ii) classifies the ones calling for help, (iii) extracts important entity tags, and (iv) visualizes them in an interactive map screen. Our initial experiments show that the performance in terms of the F1 score is up to 98.30 for tweet classification, and 84.32 for entity extraction. The demonstration, dataset, and other related files can be accessed at https://github.com/avaapm/deprem
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge