Cédric Vincent-Cuaz
Revisiting Automatic Data Curation for Vision Foundation Models in Digital Pathology
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Vision foundation models (FMs) are accelerating the development of digital pathology algorithms and transforming biomedical research. These models learn, in a self-supervised manner, to represent histological features in highly heterogeneous tiles extracted from whole-slide images (WSIs) of real-world patient samples. The performance of these FMs is significantly influenced by the size, diversity, and balance of the pre-training data. However, data selection has been primarily guided by expert knowledge at the WSI level, focusing on factors such as disease classification and tissue types, while largely overlooking the granular details available at the tile level. In this paper, we investigate the potential of unsupervised automatic data curation at the tile-level, taking into account 350 million tiles. Specifically, we apply hierarchical clustering trees to pre-extracted tile embeddings, allowing us to sample balanced datasets uniformly across the embedding space of the pretrained FM. We further identify these datasets are subject to a trade-off between size and balance, potentially compromising the quality of representations learned by FMs, and propose tailored batch sampling strategies to mitigate this effect. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method through improved performance on a diverse range of clinically relevant downstream tasks.
Distributional Reduction: Unifying Dimensionality Reduction and Clustering with Gromov-Wasserstein Projection
Feb 03, 2024Abstract:Unsupervised learning aims to capture the underlying structure of potentially large and high-dimensional datasets. Traditionally, this involves using dimensionality reduction methods to project data onto interpretable spaces or organizing points into meaningful clusters. In practice, these methods are used sequentially, without guaranteeing that the clustering aligns well with the conducted dimensionality reduction. In this work, we offer a fresh perspective: that of distributions. Leveraging tools from optimal transport, particularly the Gromov-Wasserstein distance, we unify clustering and dimensionality reduction into a single framework called distributional reduction. This allows us to jointly address clustering and dimensionality reduction with a single optimization problem. Through comprehensive experiments, we highlight the versatility and interpretability of our method and show that it outperforms existing approaches across a variety of image and genomics datasets.
Interpolating between Clustering and Dimensionality Reduction with Gromov-Wasserstein
Oct 05, 2023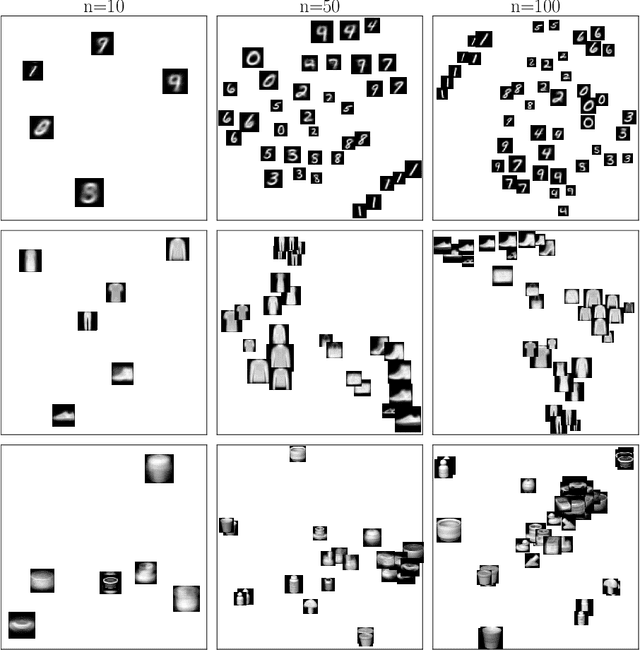
Abstract:We present a versatile adaptation of existing dimensionality reduction (DR) objectives, enabling the simultaneous reduction of both sample and feature sizes. Correspondances between input and embedding samples are computed through a semi-relaxed Gromov-Wasserstein optimal transport (OT) problem. When the embedding sample size matches that of the input, our model recovers classical popular DR models. When the embedding's dimensionality is unconstrained, we show that the OT plan delivers a competitive hard clustering. We emphasize the importance of intermediate stages that blend DR and clustering for summarizing real data and apply our method to visualize datasets of images.
Template based Graph Neural Network with Optimal Transport Distances
May 31, 2022
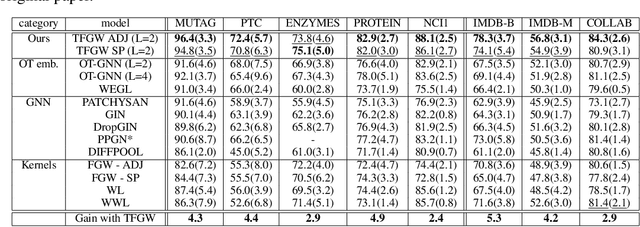
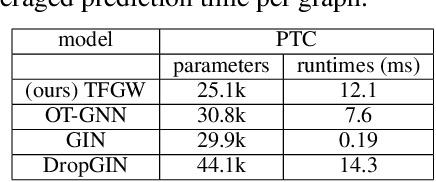
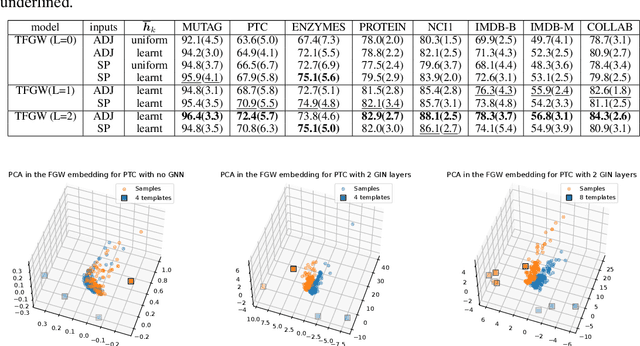
Abstract:Current Graph Neural Networks (GNN) architectures generally rely on two important components: node features embedding through message passing, and aggregation with a specialized form of pooling. The structural (or topological) information is implicitly taken into account in these two steps. We propose in this work a novel point of view, which places distances to some learnable graph templates at the core of the graph representation. This distance embedding is constructed thanks to an optimal transport distance: the Fused Gromov-Wasserstein (FGW) distance, which encodes simultaneously feature and structure dissimilarities by solving a soft graph-matching problem. We postulate that the vector of FGW distances to a set of template graphs has a strong discriminative power, which is then fed to a non-linear classifier for final predictions. Distance embedding can be seen as a new layer, and can leverage on existing message passing techniques to promote sensible feature representations. Interestingly enough, in our work the optimal set of template graphs is also learnt in an end-to-end fashion by differentiating through this layer. After describing the corresponding learning procedure, we empirically validate our claim on several synthetic and real life graph classification datasets, where our method is competitive or surpasses kernel and GNN state-of-the-art approaches. We complete our experiments by an ablation study and a sensitivity analysis to parameters.
Semi-relaxed Gromov Wasserstein divergence with applications on graphs
Oct 06, 2021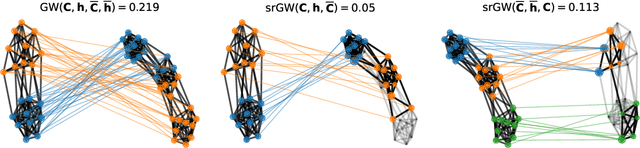
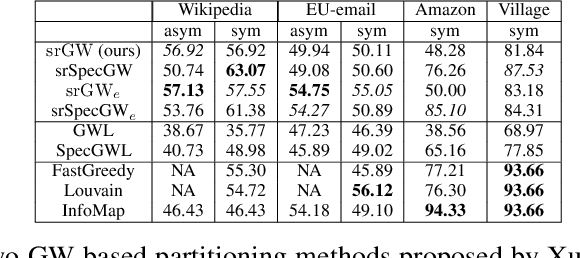
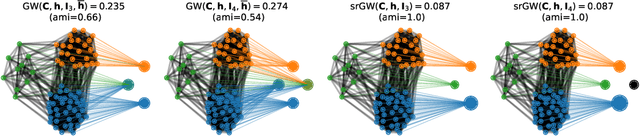
Abstract:Comparing structured objects such as graphs is a fundamental operation involved in many learning tasks. To this end, the Gromov-Wasserstein (GW) distance, based on Optimal Transport (OT), has proven to be successful in handling the specific nature of the associated objects. More specifically, through the nodes connectivity relations, GW operates on graphs, seen as probability measures over specific spaces. At the core of OT is the idea of conservation of mass, which imposes a coupling between all the nodes from the two considered graphs. We argue in this paper that this property can be detrimental for tasks such as graph dictionary or partition learning, and we relax it by proposing a new semi-relaxed Gromov-Wasserstein divergence. Aside from immediate computational benefits, we discuss its properties, and show that it can lead to an efficient graph dictionary learning algorithm. We empirically demonstrate its relevance for complex tasks on graphs such as partitioning, clustering and completion.
Online Graph Dictionary Learning
Feb 12, 2021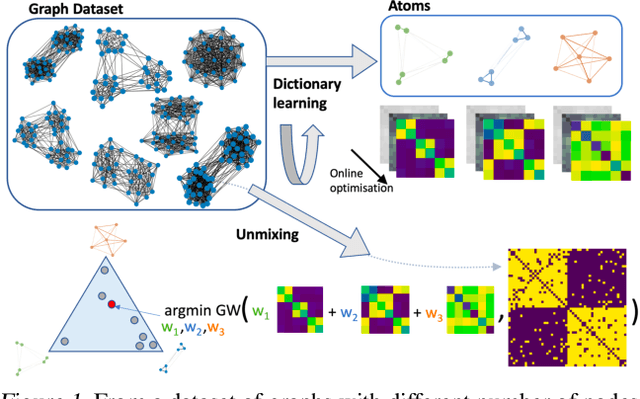
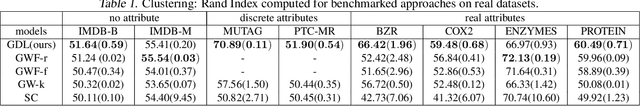
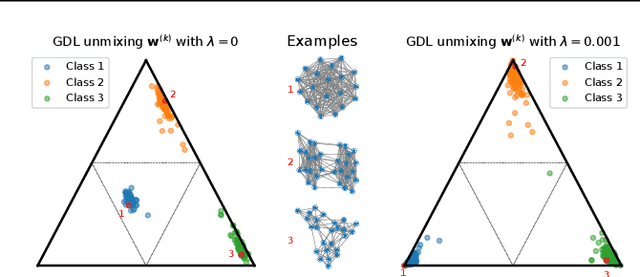
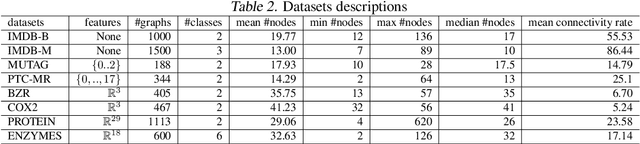
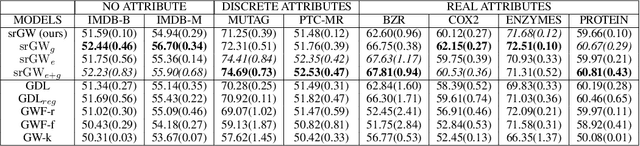
Abstract:Dictionary learning is a key tool for representation learning, that explains the data as linear combination of few basic elements. Yet, this analysis is not amenable in the context of graph learning, as graphs usually belong to different metric spaces. We fill this gap by proposing a new online Graph Dictionary Learning approach, which uses the Gromov Wasserstein divergence for the data fitting term. In our work, graphs are encoded through their nodes' pairwise relations and modeled as convex combination of graph atoms, i.e. dictionary elements, estimated thanks to an online stochastic algorithm, which operates on a dataset of unregistered graphs with potentially different number of nodes. Our approach naturally extends to labeled graphs, and is completed by a novel upper bound that can be used as a fast approximation of Gromov Wasserstein in the embedding space. We provide numerical evidences showing the interest of our approach for unsupervised embedding of graph datasets and for online graph subspace estimation and tracking.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge