Boming Miao
Bridging the Gap Between Ideal and Real-world Evaluation: Benchmarking AI-Generated Image Detection in Challenging Scenarios
Sep 11, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid advancement of generative models, highly realistic image synthesis has posed new challenges to digital security and media credibility. Although AI-generated image detection methods have partially addressed these concerns, a substantial research gap remains in evaluating their performance under complex real-world conditions. This paper introduces the Real-World Robustness Dataset (RRDataset) for comprehensive evaluation of detection models across three dimensions: 1) Scenario Generalization: RRDataset encompasses high-quality images from seven major scenarios (War and Conflict, Disasters and Accidents, Political and Social Events, Medical and Public Health, Culture and Religion, Labor and Production, and everyday life), addressing existing dataset gaps from a content perspective. 2) Internet Transmission Robustness: examining detector performance on images that have undergone multiple rounds of sharing across various social media platforms. 3) Re-digitization Robustness: assessing model effectiveness on images altered through four distinct re-digitization methods. We benchmarked 17 detectors and 10 vision-language models (VLMs) on RRDataset and conducted a large-scale human study involving 192 participants to investigate human few-shot learning capabilities in detecting AI-generated images. The benchmarking results reveal the limitations of current AI detection methods under real-world conditions and underscore the importance of drawing on human adaptability to develop more robust detection algorithms.
An Efficient Framework for Enhancing Discriminative Models via Diffusion Techniques
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:Image classification serves as the cornerstone of computer vision, traditionally achieved through discriminative models based on deep neural networks. Recent advancements have introduced classification methods derived from generative models, which offer the advantage of zero-shot classification. However, these methods suffer from two main drawbacks: high computational overhead and inferior performance compared to discriminative models. Inspired by the coordinated cognitive processes of rapid-slow pathway interactions in the human brain during visual signal recognition, we propose the Diffusion-Based Discriminative Model Enhancement Framework (DBMEF). This framework seamlessly integrates discriminative and generative models in a training-free manner, leveraging discriminative models for initial predictions and endowing deep neural networks with rethinking capabilities via diffusion models. Consequently, DBMEF can effectively enhance the classification accuracy and generalization capability of discriminative models in a plug-and-play manner. We have conducted extensive experiments across 17 prevalent deep model architectures with different training methods, including both CNN-based models such as ResNet and Transformer-based models like ViT, to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed DBMEF. Specifically, the framework yields a 1.51\% performance improvement for ResNet-50 on the ImageNet dataset and 3.02\% on the ImageNet-A dataset. In conclusion, our research introduces a novel paradigm for image classification, demonstrating stable improvements across different datasets and neural networks.
Noise Diffusion for Enhancing Semantic Faithfulness in Text-to-Image Synthesis
Nov 25, 2024
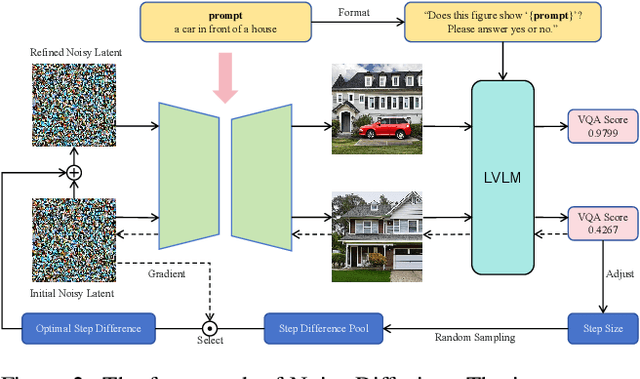
Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved impressive success in generating photorealistic images, but challenges remain in ensuring precise semantic alignment with input prompts. Optimizing the initial noisy latent offers a more efficient alternative to modifying model architectures or prompt engineering for improving semantic alignment. A latest approach, InitNo, refines the initial noisy latent by leveraging attention maps; however, these maps capture only limited information, and the effectiveness of InitNo is highly dependent on the initial starting point, as it tends to converge on a local optimum near this point. To this end, this paper proposes leveraging the language comprehension capabilities of large vision-language models (LVLMs) to guide the optimization of the initial noisy latent, and introduces the Noise Diffusion process, which updates the noisy latent to generate semantically faithful images while preserving distribution consistency. Furthermore, we provide a theoretical analysis of the condition under which the update improves semantic faithfulness. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and adaptability of our framework, consistently enhancing semantic alignment across various diffusion models. The code is available at https://github.com/Bomingmiao/NoiseDiffusion.
AdvLogo: Adversarial Patch Attack against Object Detectors based on Diffusion Models
Sep 11, 2024



Abstract:With the rapid development of deep learning, object detectors have demonstrated impressive performance; however, vulnerabilities still exist in certain scenarios. Current research exploring the vulnerabilities using adversarial patches often struggles to balance the trade-off between attack effectiveness and visual quality. To address this problem, we propose a novel framework of patch attack from semantic perspective, which we refer to as AdvLogo. Based on the hypothesis that every semantic space contains an adversarial subspace where images can cause detectors to fail in recognizing objects, we leverage the semantic understanding of the diffusion denoising process and drive the process to adversarial subareas by perturbing the latent and unconditional embeddings at the last timestep. To mitigate the distribution shift that exposes a negative impact on image quality, we apply perturbation to the latent in frequency domain with the Fourier Transform. Experimental results demonstrate that AdvLogo achieves strong attack performance while maintaining high visual quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge