Bogdan Penkovsky
Exploring polymer classification with a hybrid single-photon quantum approach
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Polymers exhibit complex architectures and diverse properties that place them at the center of contemporary research in chemistry and materials science. As conventional computational techniques, even multi-scale ones, struggle to capture this complexity, quantum computing offers a promising alternative framework for extracting structure-property relationships. Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) devices are commonly used to explore the implementation of algorithms, including quantum neural networks for classification tasks, despite ongoing debate regarding their practical impact. We present a hybrid classical-quantum formalism that couples a classical deep neural network for polymer featurization with a single-photon-based quantum classifier native to photonic quantum computing. This pipeline successfully classifies polymer species by their optical gap, with performance in line between CPU-based noisy simulations and a proof-of-principle run on Quandela's Ascella quantum processor. These findings demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed computational workflow and indicate that chemistryfrelated classification tasks can already be tackled under the constraints of today's NISQ devices.
Photonic Quantum Computing For Polymer Classification
Nov 22, 2022Abstract:We present a hybrid classical-quantum approach to the binary classification of polymer structures. Two polymer classes visual (VIS) and near-infrared (NIR) are defined based on the size of the polymer gaps. The hybrid approach combines one of the three methods, Gaussian Kernel Method, Quantum-Enhanced Random Kitchen Sinks or Variational Quantum Classifier, implemented by linear quantum photonic circuits (LQPCs), with a classical deep neural network (DNN) feature extractor. The latter extracts from the classical data information about samples chemical structure. It also reduces the data dimensions yielding compact 2-dimensional data vectors that are then fed to the LQPCs. We adopt the photonic-based data-embedding scheme, proposed by Gan et al. [EPJ Quantum Technol. 9, 16 (2022)] to embed the classical 2-dimensional data vectors into the higher-dimensional Fock space. This hybrid classical-quantum strategy permits to obtain accurate noisy intermediate-scale quantum-compatible classifiers by leveraging Fock states with only a few photons. The models obtained using either of the three hybrid methods successfully classified the VIS and NIR polymers. Their accuracy is comparable as measured by their scores ranging from 0.86 to 0.88. These findings demonstrate that our hybrid approach that uses photonic quantum computing captures chemistry and structure-property correlation patterns in real polymer data. They also open up perspectives of employing quantum computing to complex chemical structures when a larger number of logical qubits is available.
Implementing Binarized Neural Networks with Magnetoresistive RAM without Error Correction
Aug 12, 2019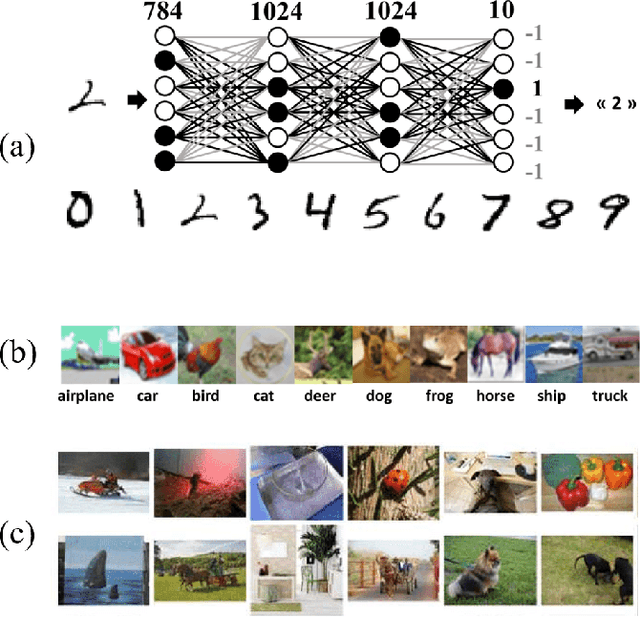
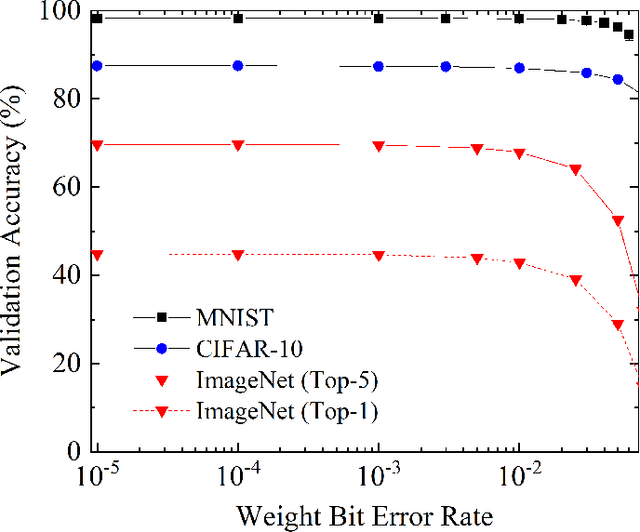
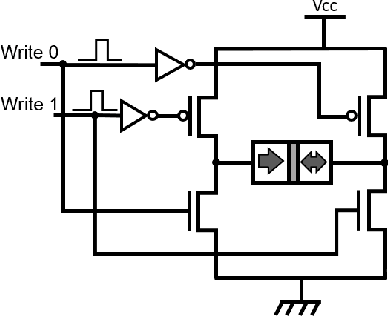
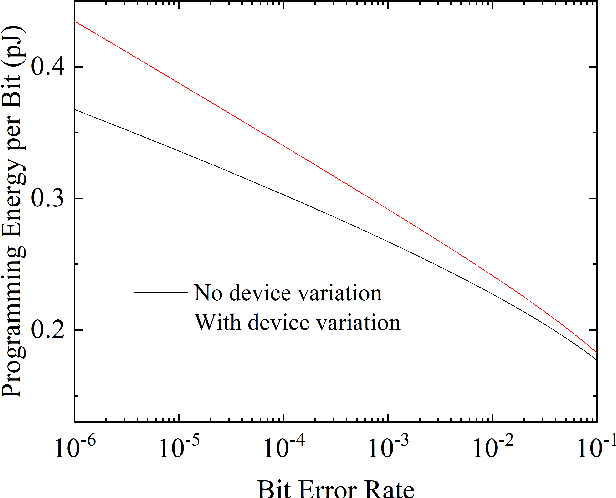
Abstract:One of the most exciting applications of Spin Torque Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory (ST-MRAM) is the in-memory implementation of deep neural networks, which could allow improving the energy efficiency of Artificial Intelligence by orders of magnitude with regards to its implementation on computers and graphics cards. In particular, ST-MRAM could be ideal for implementing Binarized Neural Networks (BNNs), a type of deep neural networks discovered in 2016, which can achieve state-of-the-art performance with a highly reduced memory footprint with regards to conventional artificial intelligence approaches. The challenge of ST-MRAM, however, is that it is prone to write errors and usually requires the use of error correction. In this work, we show that these bit errors can be tolerated by BNNs to an outstanding level, based on examples of image recognition tasks (MNIST, CIFAR-10 and ImageNet): bit error rates of ST-MRAM up to 0.1% have little impact on recognition accuracy. The requirements for ST-MRAM are therefore considerably relaxed for BNNs with regards to traditional applications. By consequence, we show that for BNNs, ST-MRAMs can be programmed with weak (low-energy) programming conditions, without error correcting codes. We show that this result can allow the use of low energy and low area ST-MRAM cells, and show that the energy savings at the system level can reach a factor two.
Efficient Design of Hardware-Enabled Reservoir Computing in FPGAs
Oct 02, 2018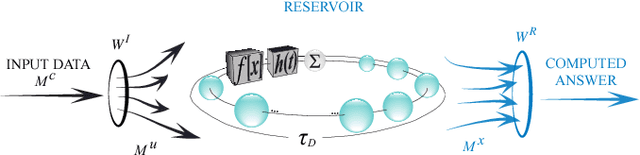
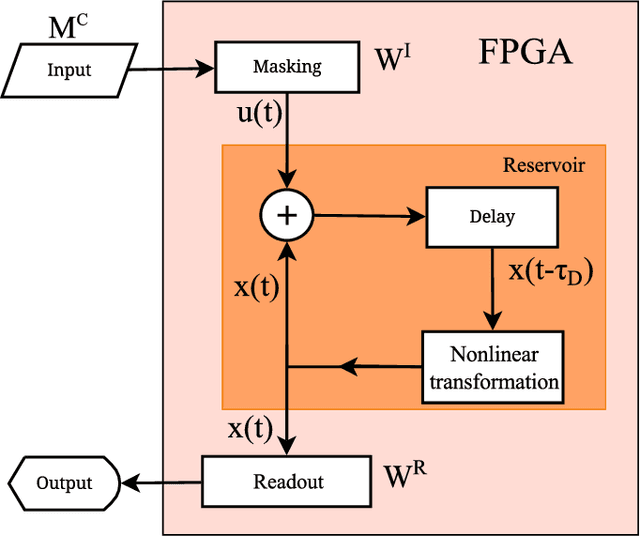
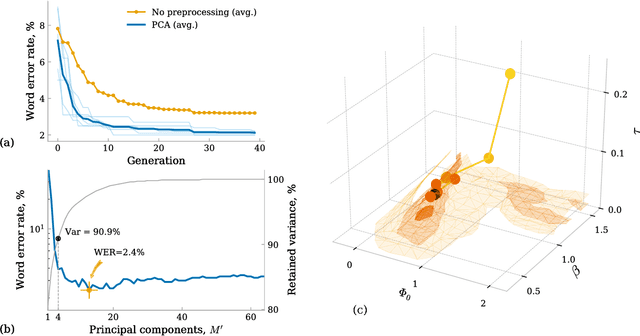
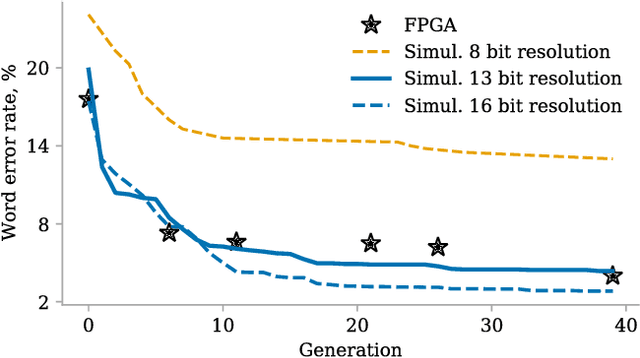
Abstract:In this work, we propose a new approach towards the efficient optimization and implementation of reservoir computing hardware reducing the required domain expert knowledge and optimization effort. First, we adapt the reservoir input mask to the structure of the data via linear autoencoders. We therefore incorporate the advantages of dimensionality reduction and dimensionality expansion achieved by conventional algorithmically efficient linear algebra procedures of principal component analysis. Second, we employ evolutionary-inspired genetic algorithm techniques resulting in a highly efficient optimization of reservoir dynamics with dramatically reduced number of evaluations comparing to exhaustive search. We illustrate the method on the so-called single-node reservoir computing architecture, especially suitable for implementation in ultrahigh-speed hardware. The combination of both methods and the resulting reduction of time required for performance optimization of a hardware system establish a strategy towards machine learning hardware capable of self-adaption to optimally solve specific problems. We confirm the validity of those principles building reservoir computing hardware based on a field-programmable gate array.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge