Adrien F. Vincent
Implementing Binarized Neural Networks with Magnetoresistive RAM without Error Correction
Aug 12, 2019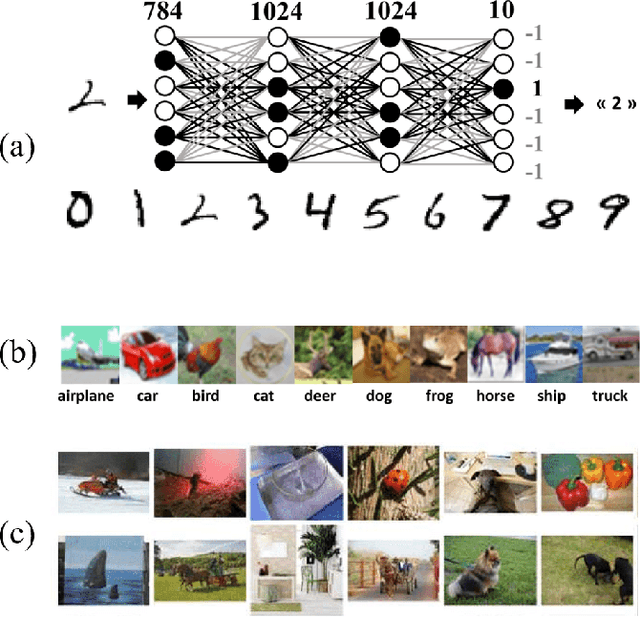
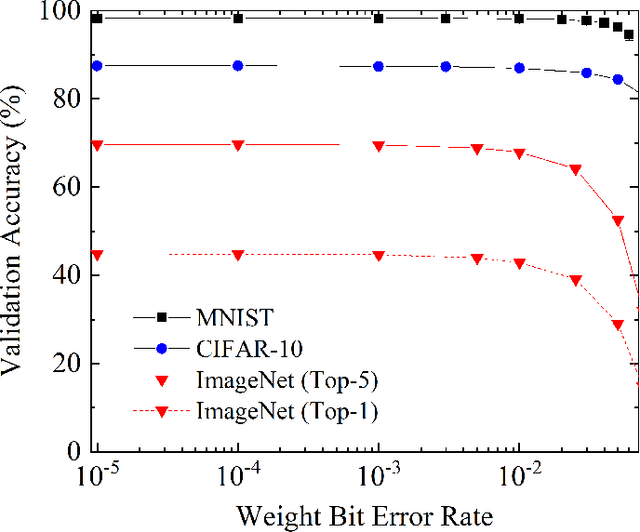
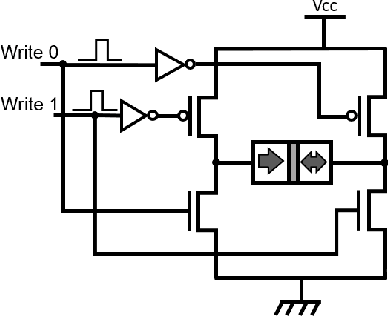
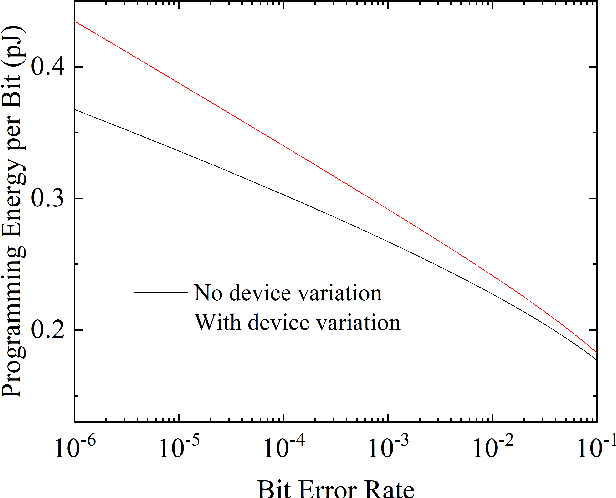
Abstract:One of the most exciting applications of Spin Torque Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory (ST-MRAM) is the in-memory implementation of deep neural networks, which could allow improving the energy efficiency of Artificial Intelligence by orders of magnitude with regards to its implementation on computers and graphics cards. In particular, ST-MRAM could be ideal for implementing Binarized Neural Networks (BNNs), a type of deep neural networks discovered in 2016, which can achieve state-of-the-art performance with a highly reduced memory footprint with regards to conventional artificial intelligence approaches. The challenge of ST-MRAM, however, is that it is prone to write errors and usually requires the use of error correction. In this work, we show that these bit errors can be tolerated by BNNs to an outstanding level, based on examples of image recognition tasks (MNIST, CIFAR-10 and ImageNet): bit error rates of ST-MRAM up to 0.1% have little impact on recognition accuracy. The requirements for ST-MRAM are therefore considerably relaxed for BNNs with regards to traditional applications. By consequence, we show that for BNNs, ST-MRAMs can be programmed with weak (low-energy) programming conditions, without error correcting codes. We show that this result can allow the use of low energy and low area ST-MRAM cells, and show that the energy savings at the system level can reach a factor two.
Exploiting the Short-term to Long-term Plasticity Transition in Memristive Nanodevice Learning Architectures
Jun 27, 2016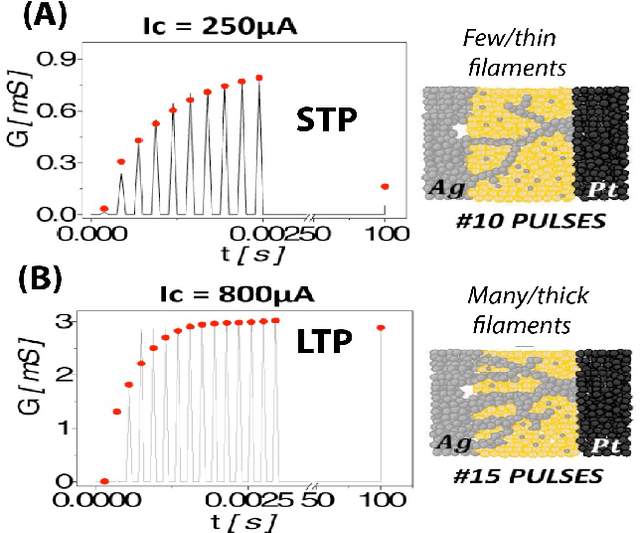
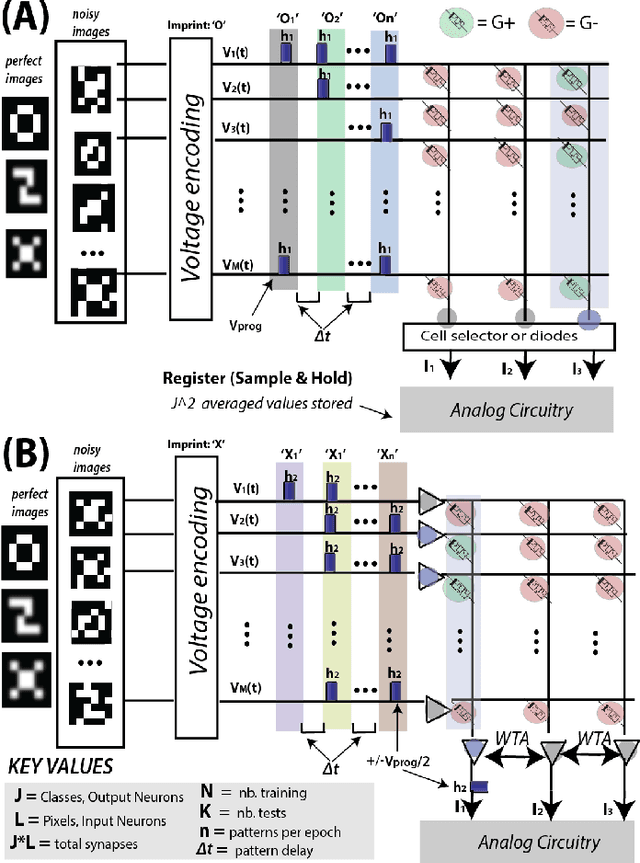
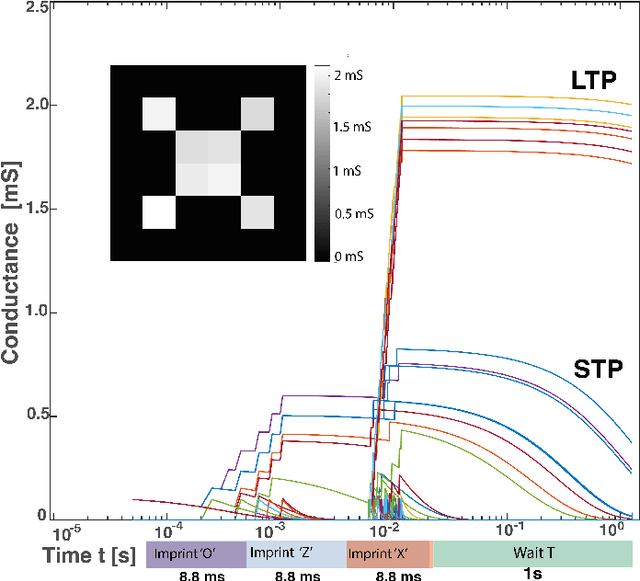
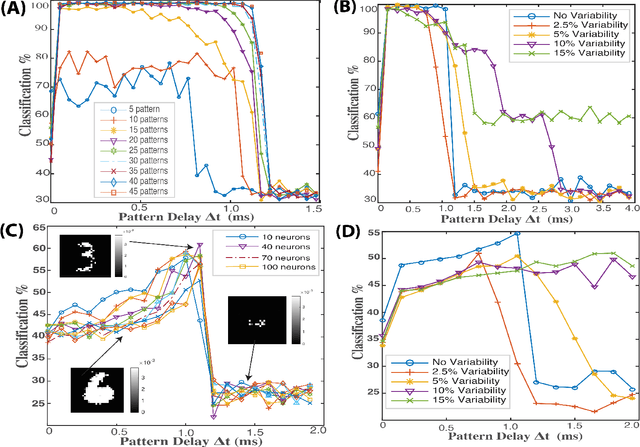
Abstract:Memristive nanodevices offer new frontiers for computing systems that unite arithmetic and memory operations on-chip. Here, we explore the integration of electrochemical metallization cell (ECM) nanodevices with tunable filamentary switching in nanoscale learning systems. Such devices offer a natural transition between short-term plasticity (STP) and long-term plasticity (LTP). In this work, we show that this property can be exploited to efficiently solve noisy classification tasks. A single crossbar learning scheme is first introduced and evaluated. Perfect classification is possible only for simple input patterns, within critical timing parameters, and when device variability is weak. To overcome these limitations, a dual-crossbar learning system partly inspired by the extreme learning machine (ELM) approach is then introduced. This approach outperforms a conventional ELM-inspired system when the first layer is imprinted before training and testing, and especially so when variability in device timing evolution is considered: variability is therefore transformed from an issue to a feature. In attempting to classify the MNIST database under the same conditions, conventional ELM obtains 84% classification, the imprinted, uniform device system obtains 88% classification, and the imprinted, variable device system reaches 92% classification. We discuss benefits and drawbacks of both systems in terms of energy, complexity, area imprint, and speed. All these results highlight that tuning and exploiting intrinsic device timing parameters may be of central interest to future bio-inspired approximate computing systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge