Bobak H. Baghi
Device-Free Human State Estimation using UWB Multi-Static Radios
Dec 26, 2023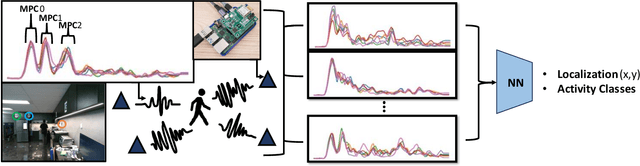
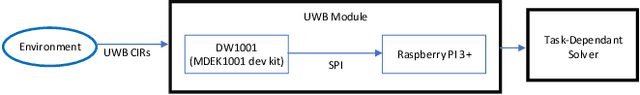
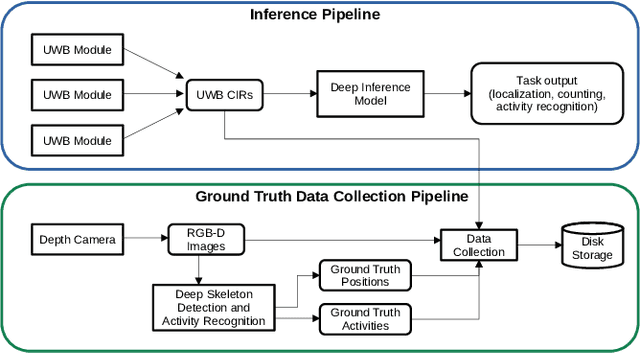
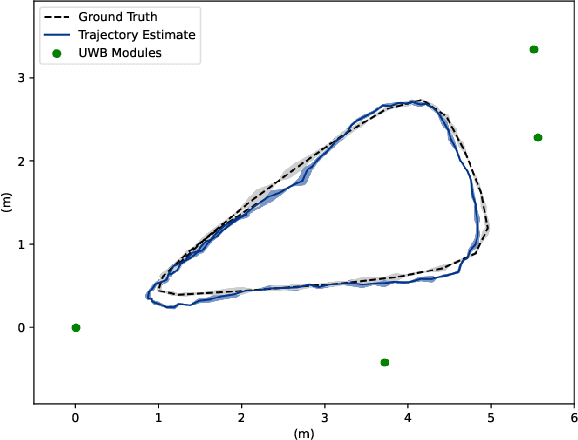
Abstract:We present a human state estimation framework that allows us to estimate the location, and even the activities, of people in an indoor environment without the requirement that they carry a specific devices with them. To achieve this "device free" localization we use a small number of low-cost Ultra-Wide Band (UWB) sensors distributed across the environment of interest. To achieve high quality estimation from the UWB signals merely reflected of people in the environment, we exploit a deep network that can learn to make inferences. The hardware setup consists of commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) single antenna UWB modules for sensing, paired with Raspberry PI units for computational processing and data transfer. We make use of the channel impulse response (CIR) measurements from the UWB sensors to estimate the human state - comprised of location and activity - in a given area. Additionally, we can also estimate the number of humans that occupy this region of interest. In our approach, first, we pre-process the CIR data which involves meticulous aggregation of measurements and extraction of key statistics. Afterwards, we leverage a convolutional deep neural network to map the CIRs into precise location estimates with sub-30 cm accuracy. Similarly, we achieve accurate human activity recognition and occupancy counting results. We show that we can quickly fine-tune our model for new out-of-distribution users, a process that requires only a few minutes of data and a few epochs of training. Our results show that UWB is a promising solution for adaptable smart-home localization and activity recognition problems.
A Study of Human-Robot Handover through Human-Human Object Transfer
Nov 21, 2023



Abstract:In this preliminary study, we investigate changes in handover behaviour when transferring hazardous objects with the help of a high-resolution touch sensor. Participants were asked to hand over a safe and hazardous object (a full cup and an empty cup) while instrumented with a modified STS sensor. Our data shows a clear distinction in the length of handover for the full cup vs the empty one, with the former being slower. Sensor data further suggests a change in tactile behaviour dependent on the object's risk factor. The results of this paper motivate a deeper study of tactile factors which could characterize a risky handover, allowing for safer human-robot interactions in the future.
CARTIER: Cartographic lAnguage Reasoning Targeted at Instruction Execution for Robots
Jul 21, 2023Abstract:This work explores the capacity of large language models (LLMs) to address problems at the intersection of spatial planning and natural language interfaces for navigation.Our focus is on following relatively complex instructions that are more akin to natural conversation than traditional explicit procedural directives seen in robotics. Unlike most prior work, where navigation directives are provided as imperative commands (e.g., go to the fridge), we examine implicit directives within conversational interactions. We leverage the 3D simulator AI2Thor to create complex and repeatable scenarios at scale, and augment it by adding complex language queries for 40 object types. We demonstrate that a robot can better parse descriptive language queries than existing methods by using an LLM to interpret the user interaction in the context of a list of the objects in the scene.
Sample Efficient Social Navigation Using Inverse Reinforcement Learning
Jun 18, 2021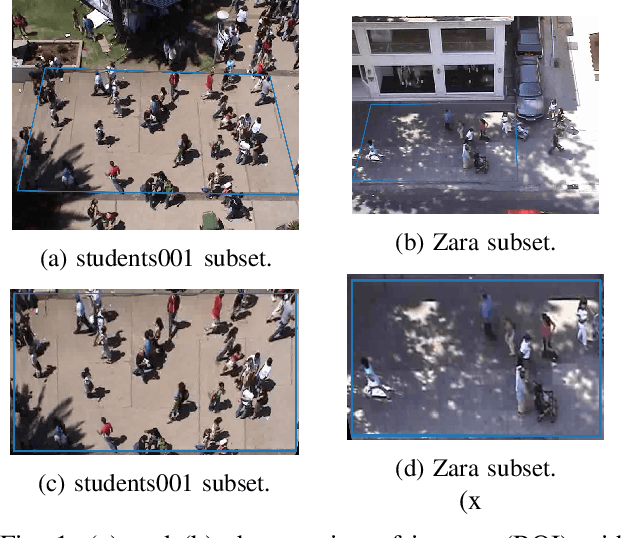



Abstract:In this paper, we present an algorithm to efficiently learn socially-compliant navigation policies from observations of human trajectories. As mobile robots come to inhabit and traffic social spaces, they must account for social cues and behave in a socially compliant manner. We focus on learning such cues from examples. We describe an inverse reinforcement learning based algorithm which learns from human trajectory observations without knowing their specific actions. We increase the sample-efficiency of our approach over alternative methods by leveraging the notion of a replay buffer (found in many off-policy reinforcement learning methods) to eliminate the additional sample complexity associated with inverse reinforcement learning. We evaluate our method by training agents using publicly available pedestrian motion data sets and compare it to related methods. We show that our approach yields better performance while also decreasing training time and sample complexity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge