Biwei Yan
Don't believe everything you read: Understanding and Measuring MCP Behavior under Misleading Tool Descriptions
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:The Model Context Protocol (MCP) enables large language models to invoke external tools through natural-language descriptions, forming the foundation of many AI agent applications. However, MCP does not enforce consistency between documented tool behavior and actual code execution, even though MCP Servers often run with broad system privileges. This gap introduces a largely unexplored security risk. We study how mismatches between externally presented tool descriptions and underlying implementations systematically shape the mental models and decision-making behavior of intelligent agents. Specifically, we present the first large-scale study of description-code inconsistency in the MCP ecosystem. We design an automated static analysis framework and apply it to 10,240 real-world MCP Servers across 36 categories. Our results show that while most servers are highly consistent, approximately 13% exhibit substantial mismatches that can enable undocumented privileged operations, hidden state mutations, or unauthorized financial actions. We further observe systematic differences across application categories, popularity levels, and MCP marketplaces. Our findings demonstrate that description-code inconsistency is a concrete and prevalent attack surface in MCP-based AI agents, and motivate the need for systematic auditing and stronger transparency guarantees in future agent ecosystems.
FedRFQ: Prototype-Based Federated Learning with Reduced Redundancy, Minimal Failure, and Enhanced Quality
Jan 15, 2024


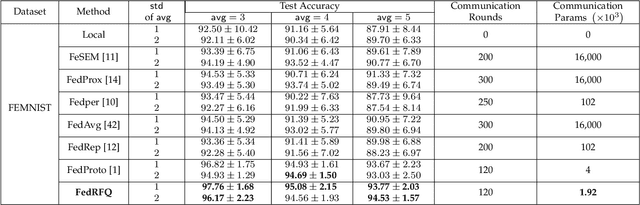
Abstract:Federated learning is a powerful technique that enables collaborative learning among different clients. Prototype-based federated learning is a specific approach that improves the performance of local models under non-IID (non-Independently and Identically Distributed) settings by integrating class prototypes. However, prototype-based federated learning faces several challenges, such as prototype redundancy and prototype failure, which limit its accuracy. It is also susceptible to poisoning attacks and server malfunctions, which can degrade the prototype quality. To address these issues, we propose FedRFQ, a prototype-based federated learning approach that aims to reduce redundancy, minimize failures, and improve \underline{q}uality. FedRFQ leverages a SoftPool mechanism, which effectively mitigates prototype redundancy and prototype failure on non-IID data. Furthermore, we introduce the BFT-detect, a BFT (Byzantine Fault Tolerance) detectable aggregation algorithm, to ensure the security of FedRFQ against poisoning attacks and server malfunctions. Finally, we conduct experiments on three different datasets, namely MNIST, FEMNIST, and CIFAR-10, and the results demonstrate that FedRFQ outperforms existing baselines in terms of accuracy when handling non-IID data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge