Biprateep Dey
Interpretable Uncertainty Quantification in AI for HEP
Aug 08, 2022Abstract:Estimating uncertainty is at the core of performing scientific measurements in HEP: a measurement is not useful without an estimate of its uncertainty. The goal of uncertainty quantification (UQ) is inextricably linked to the question, "how do we physically and statistically interpret these uncertainties?" The answer to this question depends not only on the computational task we aim to undertake, but also on the methods we use for that task. For artificial intelligence (AI) applications in HEP, there are several areas where interpretable methods for UQ are essential, including inference, simulation, and control/decision-making. There exist some methods for each of these areas, but they have not yet been demonstrated to be as trustworthy as more traditional approaches currently employed in physics (e.g., non-AI frequentist and Bayesian methods). Shedding light on the questions above requires additional understanding of the interplay of AI systems and uncertainty quantification. We briefly discuss the existing methods in each area and relate them to tasks across HEP. We then discuss recommendations for avenues to pursue to develop the necessary techniques for reliable widespread usage of AI with UQ over the next decade.
Calibrated Predictive Distributions via Diagnostics for Conditional Coverage
May 29, 2022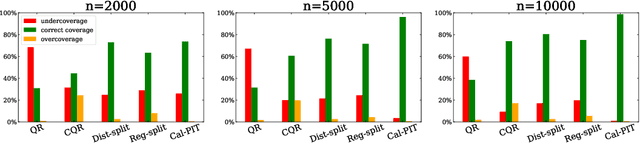
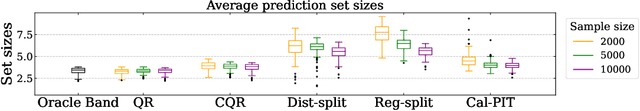
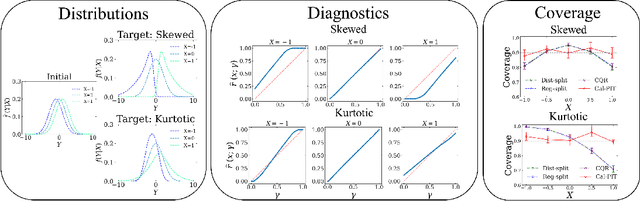
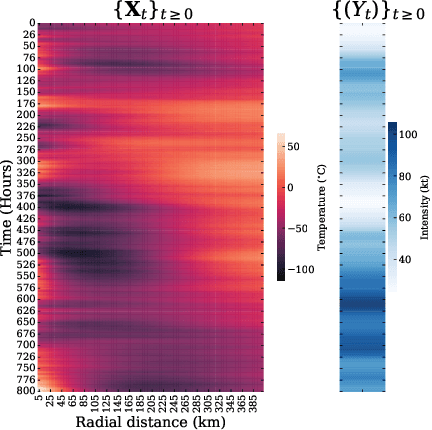
Abstract:Uncertainty quantification is crucial for assessing the predictive ability of AI algorithms. A large body of work (including normalizing flows and Bayesian neural networks) has been devoted to describing the entire predictive distribution (PD) of a target variable Y given input features $\mathbf{X}$. However, off-the-shelf PDs are usually far from being conditionally calibrated; i.e., the probability of occurrence of an event given input $\mathbf{X}$ can be significantly different from the predicted probability. Most current research on predictive inference (such as conformal prediction) concerns constructing prediction sets, that do not only provide correct uncertainties on average over the entire population (that is, averaging over $\mathbf{X}$), but that are also approximately conditionally calibrated with accurate uncertainties for individual instances. It is often believed that the problem of obtaining and assessing entire conditionally calibrated PDs is too challenging to approach. In this work, we show that recalibration as well as validation are indeed attainable goals in practice. Our proposed method relies on the idea of regressing probability integral transform (PIT) scores against $\mathbf{X}$. This regression gives full diagnostics of conditional coverage across the entire feature space and can be used to recalibrate misspecified PDs. We benchmark our corrected prediction bands against oracle bands and state-of-the-art predictive inference algorithms for synthetic data, including settings with distributional shift and dependent high-dimensional sequence data. Finally, we demonstrate an application to the physical sciences in which we assess and produce calibrated PDs for measurements of galaxy distances using imaging data (i.e., photometric redshifts).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge