Bilal Abu-Salih
An Effective Networks Intrusion Detection Approach Based on Hybrid Harris Hawks and Multi-Layer Perceptron
Feb 21, 2024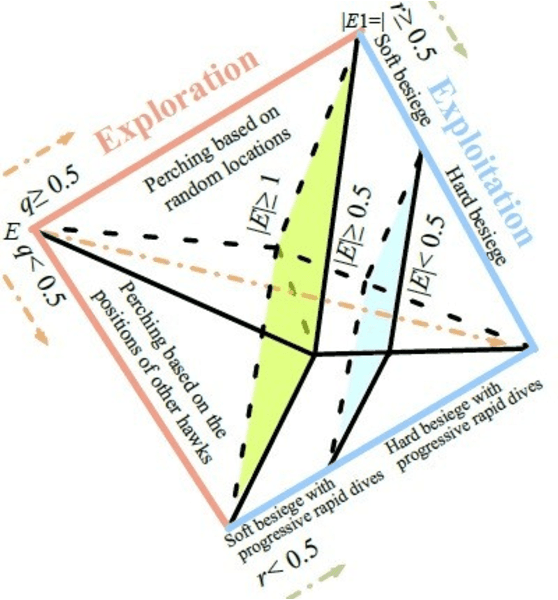
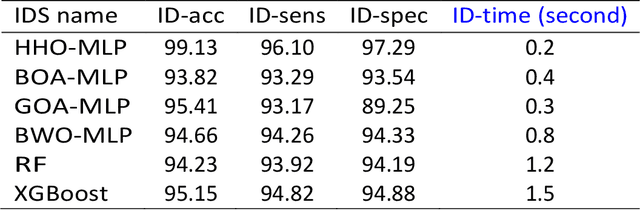
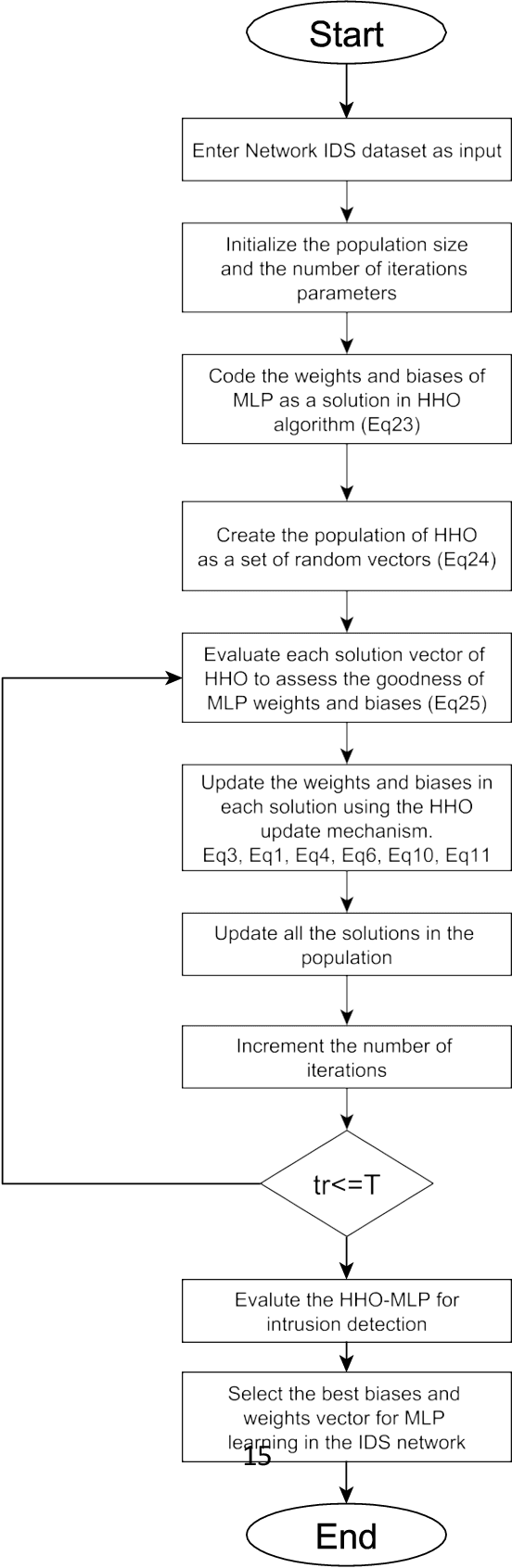
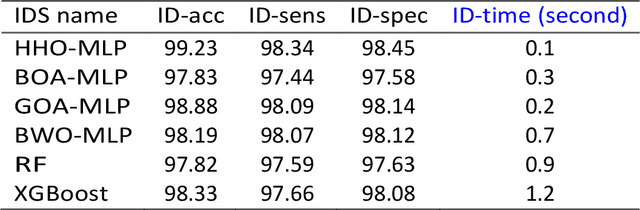
Abstract:This paper proposes an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) employing the Harris Hawks Optimization algorithm (HHO) to optimize Multilayer Perceptron learning by optimizing bias and weight parameters. HHO-MLP aims to select optimal parameters in its learning process to minimize intrusion detection errors in networks. HHO-MLP has been implemented using EvoloPy NN framework, an open-source Python tool specialized for training MLPs using evolutionary algorithms. For purposes of comparing the HHO model against other evolutionary methodologies currently available, specificity and sensitivity measures, accuracy measures, and mse and rmse measures have been calculated using KDD datasets. Experiments have demonstrated the HHO MLP method is effective at identifying malicious patterns. HHO-MLP has been tested against evolutionary algorithms like Butterfly Optimization Algorithm (BOA), Grasshopper Optimization Algorithms (GOA), and Black Widow Optimizations (BOW), with validation by Random Forest (RF), XG-Boost. HHO-MLP showed superior performance by attaining top scores with accuracy rate of 93.17%, sensitivity level of 89.25%, and specificity percentage of 95.41%.
Healthcare Knowledge Graph Construction: State-of-the-art, open issues, and opportunities
Jul 08, 2022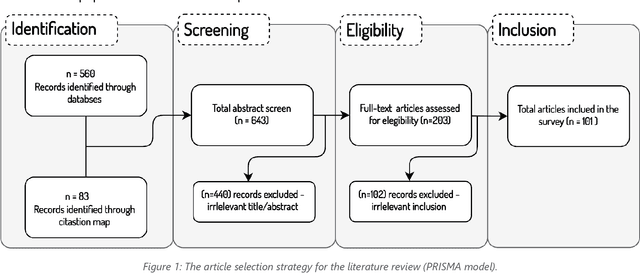
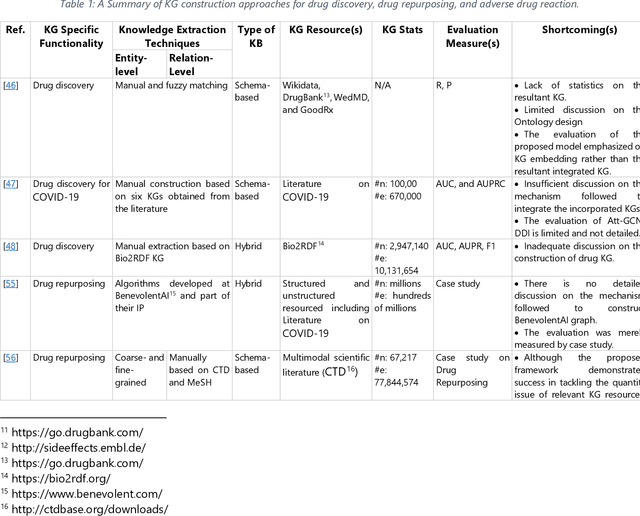
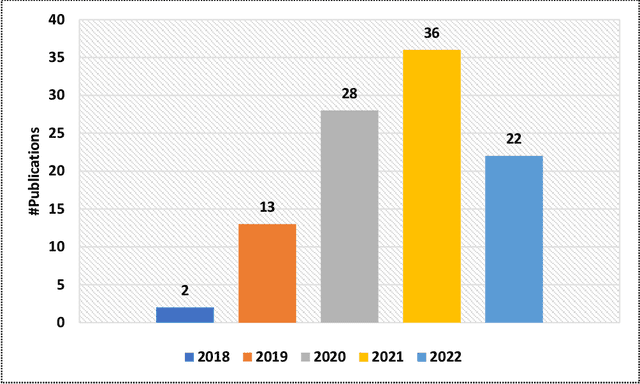
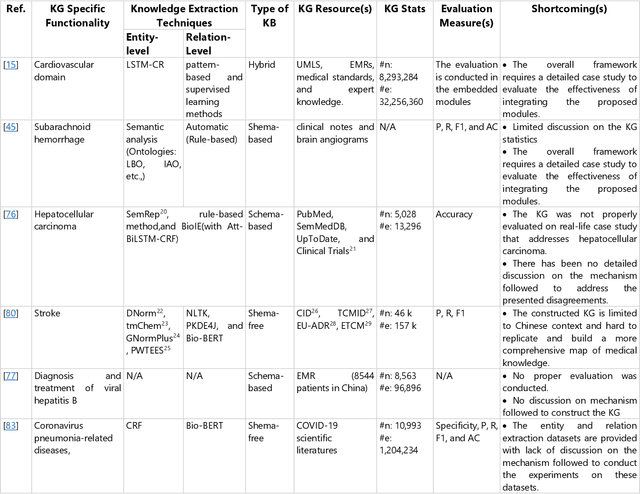
Abstract:The incorporation of data analytics in the healthcare industry has made significant progress, driven by the demand for efficient and effective big data analytics solutions. Knowledge graphs (KGs) have proven utility in this arena and are rooted in a number of healthcare applications to furnish better data representation and knowledge inference. However, in conjunction with a lack of a representative KG construction taxonomy, several existing approaches in this designated domain are inadequate and inferior. This paper is the first to provide a comprehensive taxonomy and a bird's eye view of healthcare KG construction. Additionally, a thorough examination of the current state-of-the-art techniques drawn from academic works relevant to various healthcare contexts is carried out. These techniques are critically evaluated in terms of methods used for knowledge extraction, types of the knowledge base and sources, and the incorporated evaluation protocols. Finally, several research findings and existing issues in the literature are reported and discussed, opening horizons for future research in this vibrant area.
Domain-specific Knowledge Graphs: A survey
Nov 03, 2020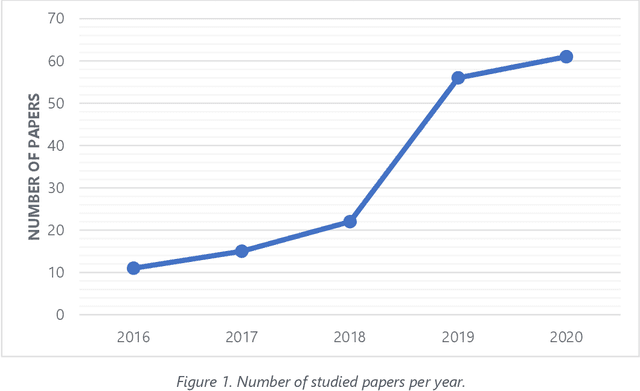
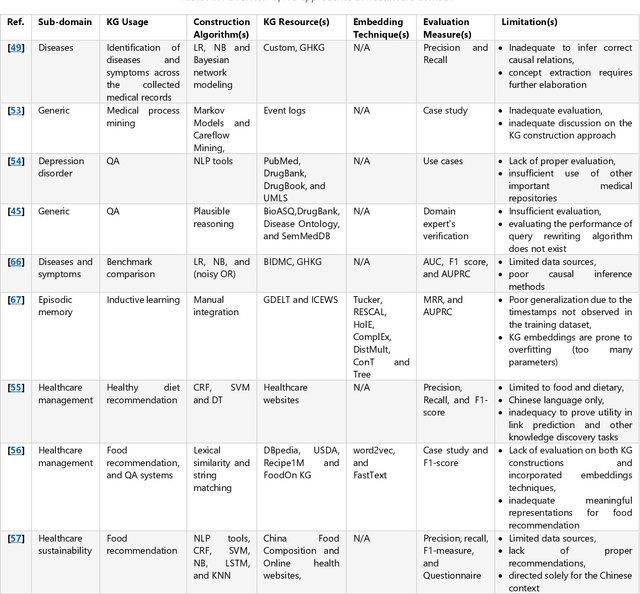
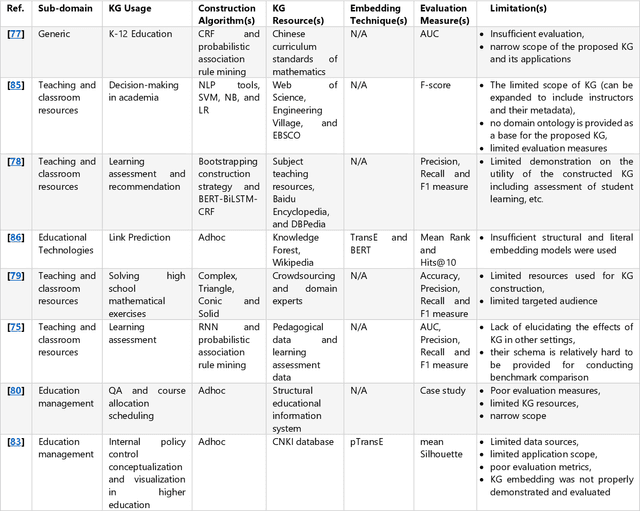
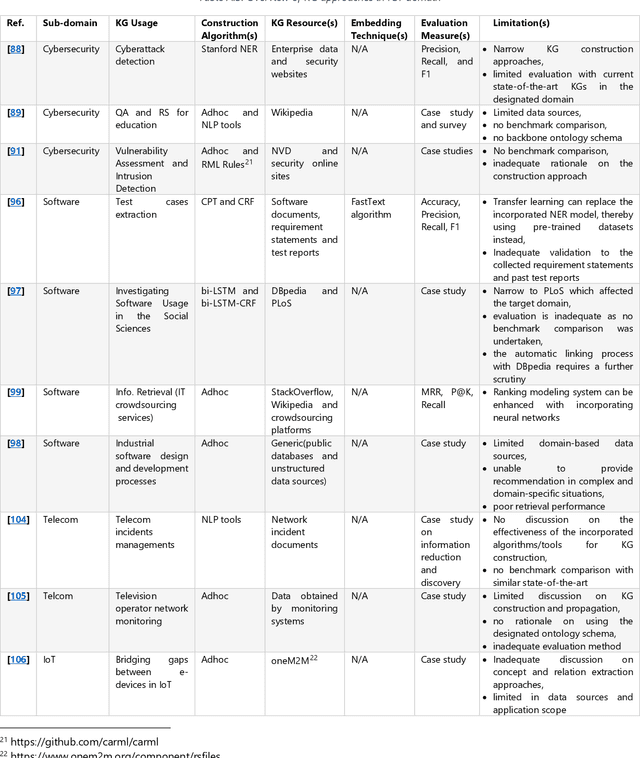
Abstract:Knowledge Graphs (KGs) have made a qualitative leap and effected a real revolution in knowledge representation. This is leveraged by the underlying structure of the KG which underpins a better comprehension, reasoning and interpreting of knowledge for both human and machine. Therefore, KGs continue to be used as a main driver to tackle a plethora of real-life problems in dissimilar domains. However, there is no consensus on a plausible and definition to domain KG. Further, in conjunction with several limitations and deficiencies, various domain KG construction approaches are far from perfection. This survey is the first to provide an inclusive definition to the notion of domain KG. Also, a comprehensive review of the state-of-the-art approaches drawn from academic works relevant to seven dissimilar domains of knowledge is provided. The scrutiny of the current approaches reveals a correlated array of limitations and deficiencies. The set of improvements made to address the limitations of the current approaches are introduced followed by recommendations and opportunities for future research directions.
Relational Learning Analysis of Social Politics using Knowledge Graph Embedding
Jun 02, 2020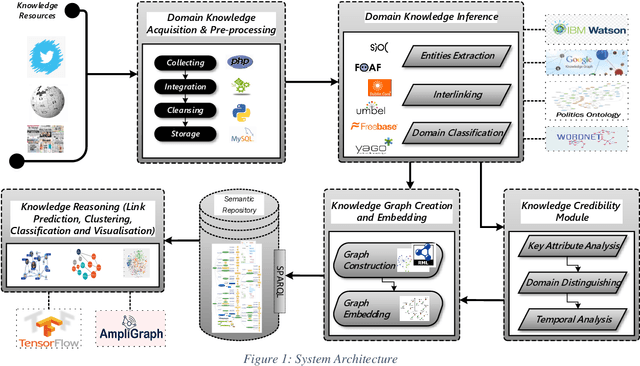
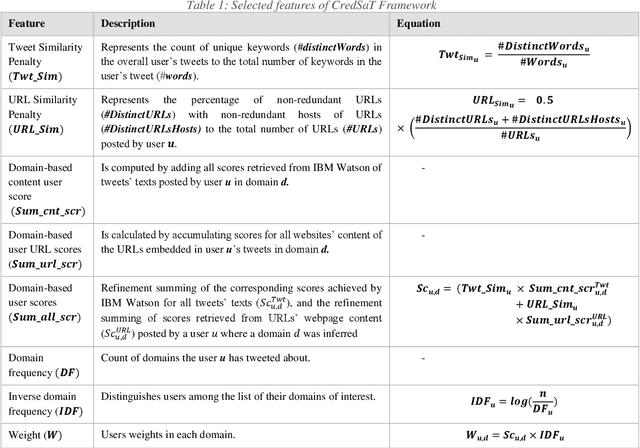
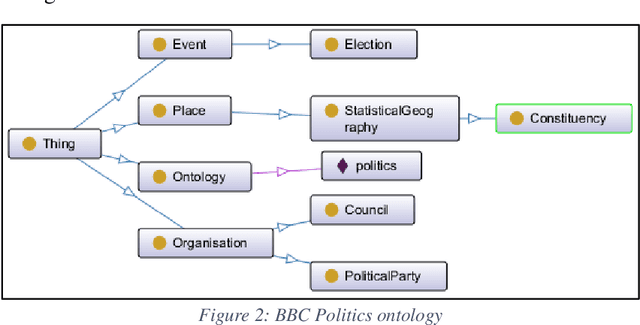
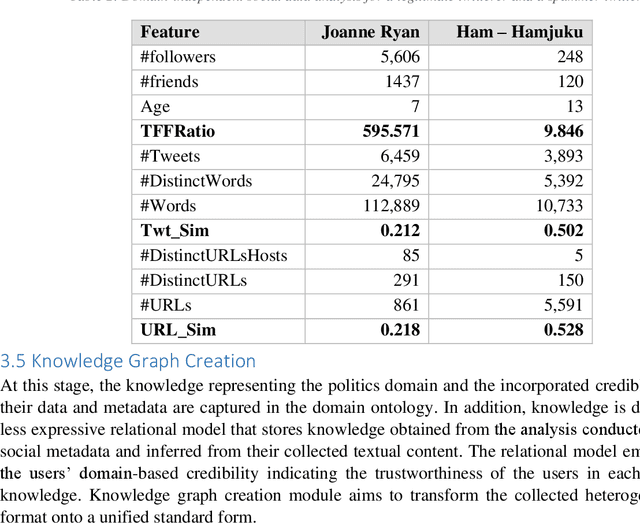
Abstract:Knowledge Graphs (KGs) have gained considerable attention recently from both academia and industry. In fact, incorporating graph technology and the copious of various graph datasets have led the research community to build sophisticated graph analytics tools. Therefore, the application of KGs has extended to tackle a plethora of real-life problems in dissimilar domains. Despite the abundance of the currently proliferated generic KGs, there is a vital need to construct domain-specific KGs. Further, quality and credibility should be assimilated in the process of constructing and augmenting KGs, particularly those propagated from mixed-quality resources such as social media data. This paper presents a novel credibility domain-based KG Embedding framework. This framework involves capturing a fusion of data obtained from heterogeneous resources into a formal KG representation depicted by a domain ontology. The proposed approach makes use of various knowledge-based repositories to enrich the semantics of the textual contents, thereby facilitating the interoperability of information. The proposed framework also embodies a credibility module to ensure data quality and trustworthiness. The constructed KG is then embedded in a low-dimension semantically-continuous space using several embedding techniques. The utility of the constructed KG and its embeddings is demonstrated and substantiated on link prediction, clustering, and visualisation tasks.
An Approach for Time-aware Domain-based Social Influence Prediction
Jan 19, 2020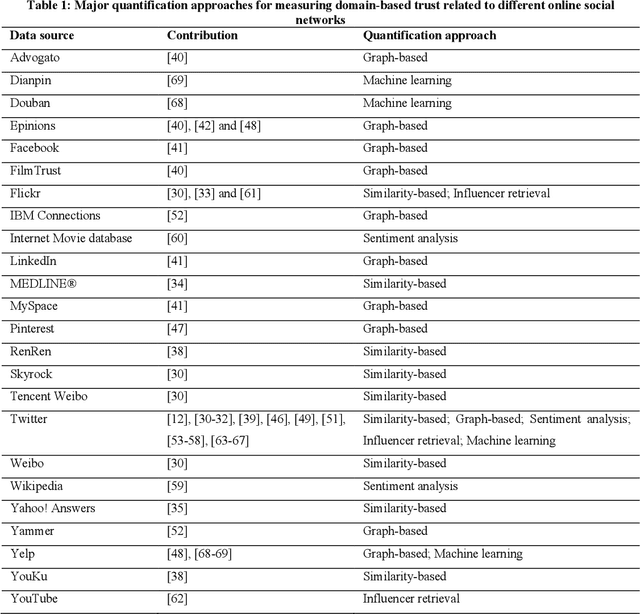
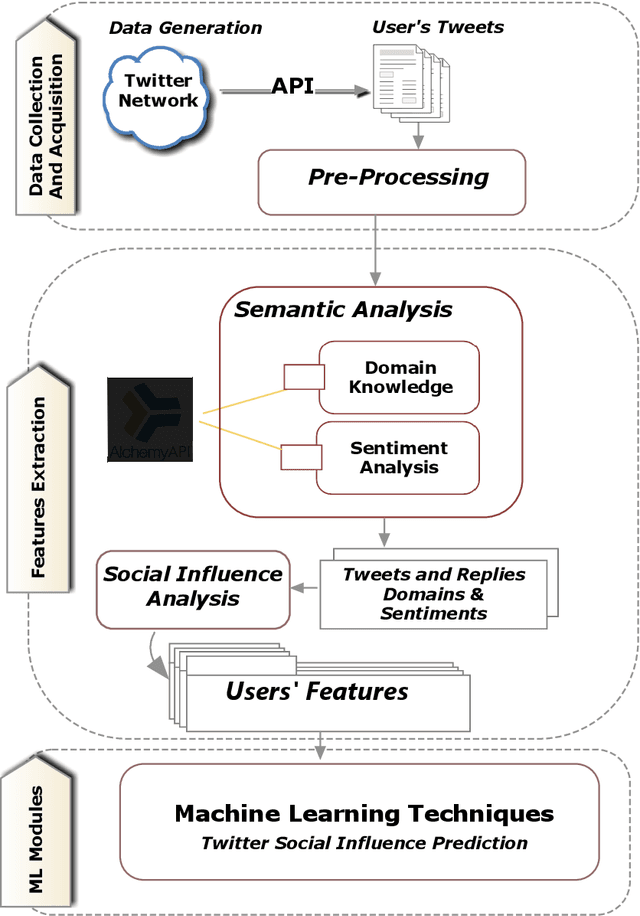
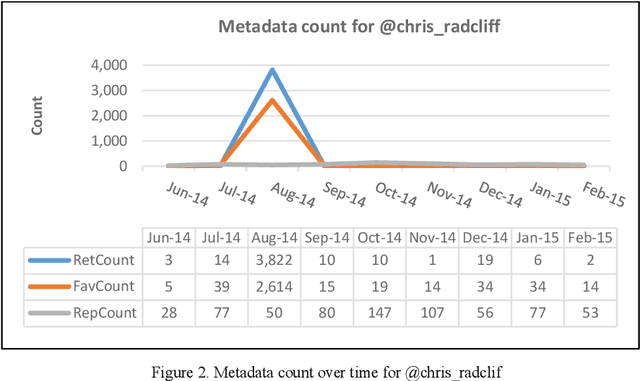
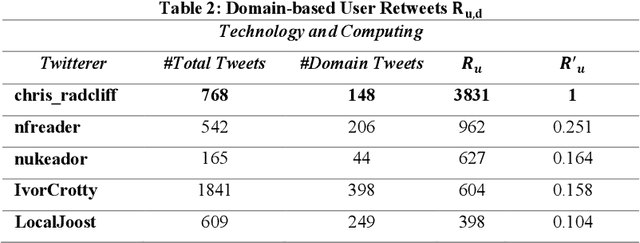
Abstract:Online Social Networks(OSNs) have established virtual platforms enabling people to express their opinions, interests and thoughts in a variety of contexts and domains, allowing legitimate users as well as spammers and other untrustworthy users to publish and spread their content. Hence, the concept of social trust has attracted the attention of information processors/data scientists and information consumers/business firms. One of the main reasons for acquiring the value of Social Big Data (SBD) is to provide frameworks and methodologies using which the credibility of OSNs users can be evaluated. These approaches should be scalable to accommodate large-scale social data. Hence, there is a need for well comprehending of social trust to improve and expand the analysis process and inferring the credibility of SBD. Given the exposed environment's settings and fewer limitations related to OSNs, the medium allows legitimate and genuine users as well as spammers and other low trustworthy users to publish and spread their content. Hence, this paper presents an approach incorporates semantic analysis and machine learning modules to measure and predict users' trustworthiness in numerous domains in different time periods. The evaluation of the conducted experiment validates the applicability of the incorporated machine learning techniques to predict highly trustworthy domain-based users.
Social Credibility Incorporating Semantic Analysis and Machine Learning: A Survey of the State-of-the-Art and Future Research Directions
Feb 27, 2019Abstract:The wealth of Social Big Data (SBD) represents a unique opportunity for organisations to obtain the excessive use of such data abundance to increase their revenues. Hence, there is an imperative need to capture, load, store, process, analyse, transform, interpret, and visualise such manifold social datasets to develop meaningful insights that are specific to an application domain. This paper lays the theoretical background by introducing the state-of-the-art literature review of the research topic. This is associated with a critical evaluation of the current approaches, and fortified with certain recommendations indicated to bridge the research gap.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge