Alejandro Martin
An Effective Networks Intrusion Detection Approach Based on Hybrid Harris Hawks and Multi-Layer Perceptron
Feb 21, 2024
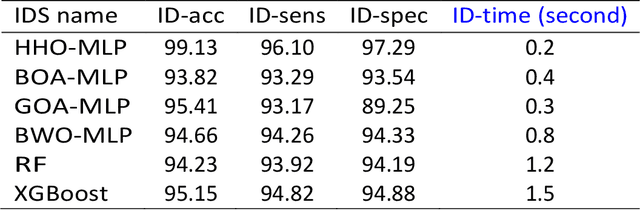
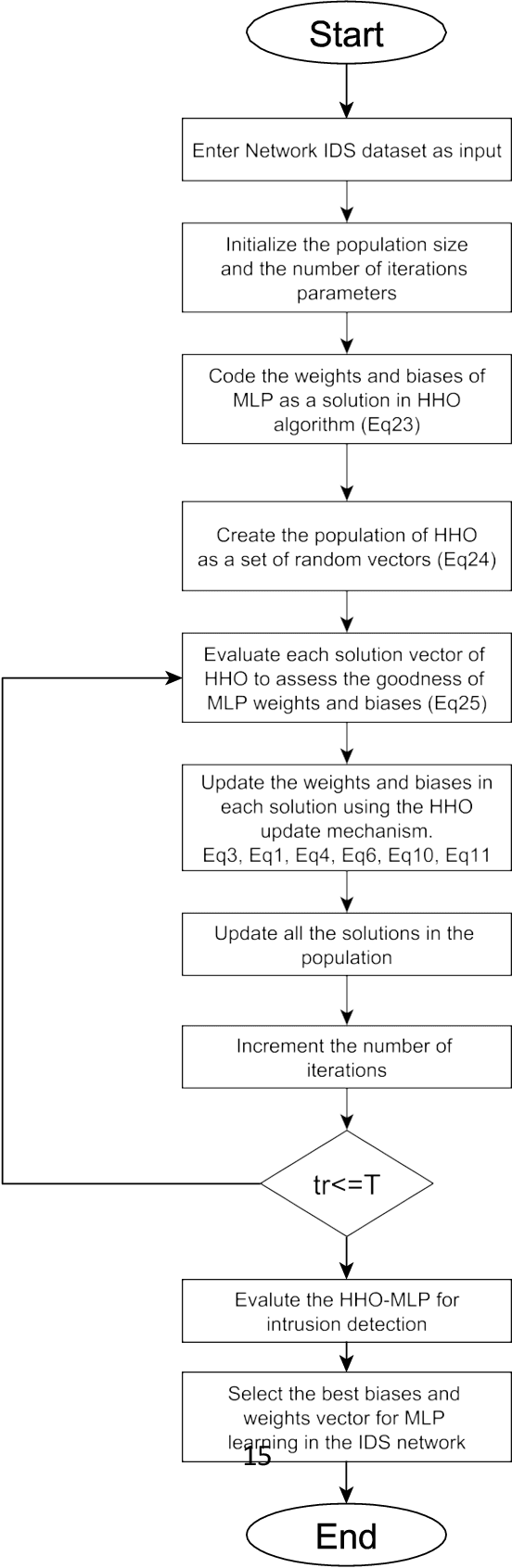
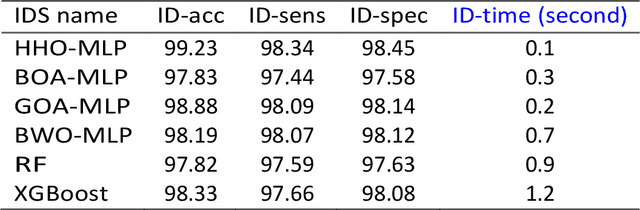
Abstract:This paper proposes an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) employing the Harris Hawks Optimization algorithm (HHO) to optimize Multilayer Perceptron learning by optimizing bias and weight parameters. HHO-MLP aims to select optimal parameters in its learning process to minimize intrusion detection errors in networks. HHO-MLP has been implemented using EvoloPy NN framework, an open-source Python tool specialized for training MLPs using evolutionary algorithms. For purposes of comparing the HHO model against other evolutionary methodologies currently available, specificity and sensitivity measures, accuracy measures, and mse and rmse measures have been calculated using KDD datasets. Experiments have demonstrated the HHO MLP method is effective at identifying malicious patterns. HHO-MLP has been tested against evolutionary algorithms like Butterfly Optimization Algorithm (BOA), Grasshopper Optimization Algorithms (GOA), and Black Widow Optimizations (BOW), with validation by Random Forest (RF), XG-Boost. HHO-MLP showed superior performance by attaining top scores with accuracy rate of 93.17%, sensitivity level of 89.25%, and specificity percentage of 95.41%.
Understanding writing style in social media with a supervised contrastively pre-trained transformer
Oct 17, 2023Abstract:Online Social Networks serve as fertile ground for harmful behavior, ranging from hate speech to the dissemination of disinformation. Malicious actors now have unprecedented freedom to misbehave, leading to severe societal unrest and dire consequences, as exemplified by events such as the Capitol assault during the US presidential election and the Antivaxx movement during the COVID-19 pandemic. Understanding online language has become more pressing than ever. While existing works predominantly focus on content analysis, we aim to shift the focus towards understanding harmful behaviors by relating content to their respective authors. Numerous novel approaches attempt to learn the stylistic features of authors in texts, but many of these approaches are constrained by small datasets or sub-optimal training losses. To overcome these limitations, we introduce the Style Transformer for Authorship Representations (STAR), trained on a large corpus derived from public sources of 4.5 x 10^6 authored texts involving 70k heterogeneous authors. Our model leverages Supervised Contrastive Loss to teach the model to minimize the distance between texts authored by the same individual. This author pretext pre-training task yields competitive performance at zero-shot with PAN challenges on attribution and clustering. Additionally, we attain promising results on PAN verification challenges using a single dense layer, with our model serving as an embedding encoder. Finally, we present results from our test partition on Reddit. Using a support base of 8 documents of 512 tokens, we can discern authors from sets of up to 1616 authors with at least 80\% accuracy. We share our pre-trained model at huggingface (https://huggingface.co/AIDA-UPM/star) and our code is available at (https://github.com/jahuerta92/star)
PART: Pre-trained Authorship Representation Transformer
Sep 30, 2022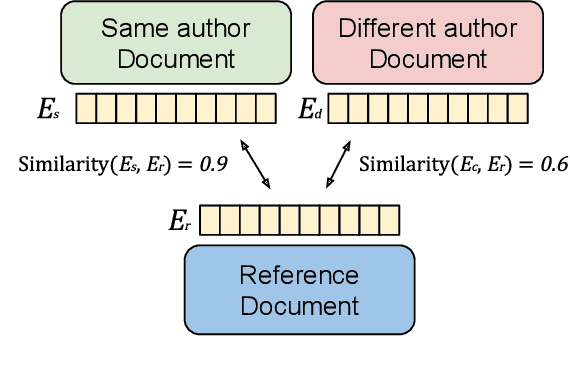
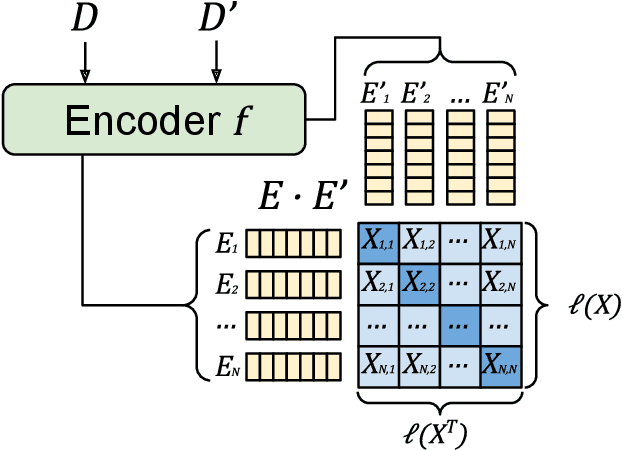

Abstract:Authors writing documents imprint identifying information within their texts: vocabulary, registry, punctuation, misspellings, or even emoji usage. Finding these details is very relevant to profile authors, relating back to their gender, occupation, age, and so on. But most importantly, repeating writing patterns can help attributing authorship to a text. Previous works use hand-crafted features or classification tasks to train their authorship models, leading to poor performance on out-of-domain authors. A better approach to this task is to learn stylometric representations, but this by itself is an open research challenge. In this paper, we propose PART: a contrastively trained model fit to learn \textbf{authorship embeddings} instead of semantics. By comparing pairs of documents written by the same author, we are able to determine the proprietary of a text by evaluating the cosine similarity of the evaluated documents, a zero-shot generalization to authorship identification. To this end, a pre-trained Transformer with an LSTM head is trained with the contrastive training method. We train our model on a diverse set of authors, from literature, anonymous blog posters and corporate emails; a heterogeneous set with distinct and identifiable writing styles. The model is evaluated on these datasets, achieving zero-shot 72.39\% and 86.73\% accuracy and top-5 accuracy respectively on the joint evaluation dataset when determining authorship from a set of 250 different authors. We qualitatively assess the representations with different data visualizations on the available datasets, profiling features such as book types, gender, age, or occupation of the author.
BERTuit: Understanding Spanish language in Twitter through a native transformer
Apr 07, 2022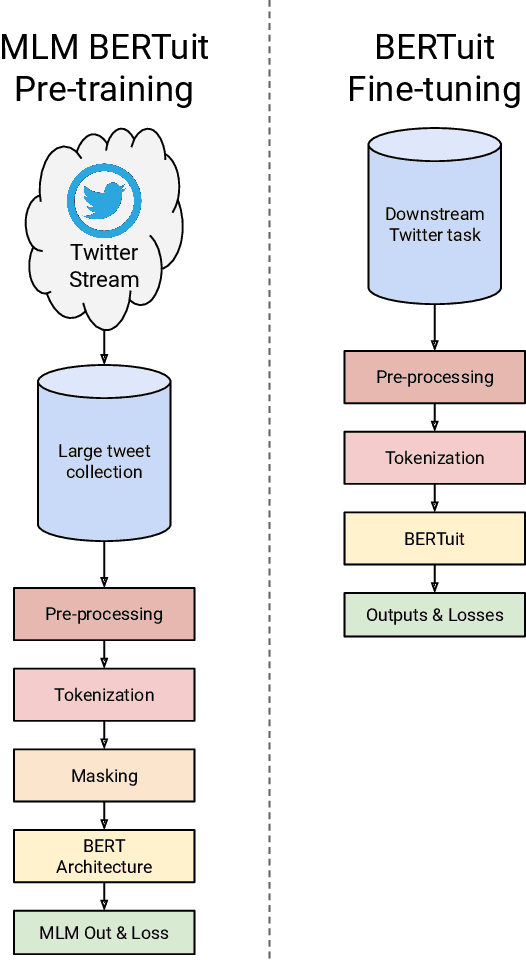

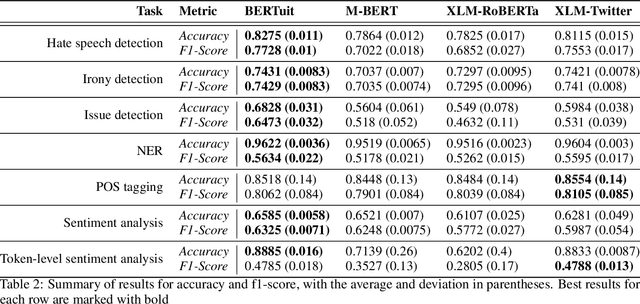
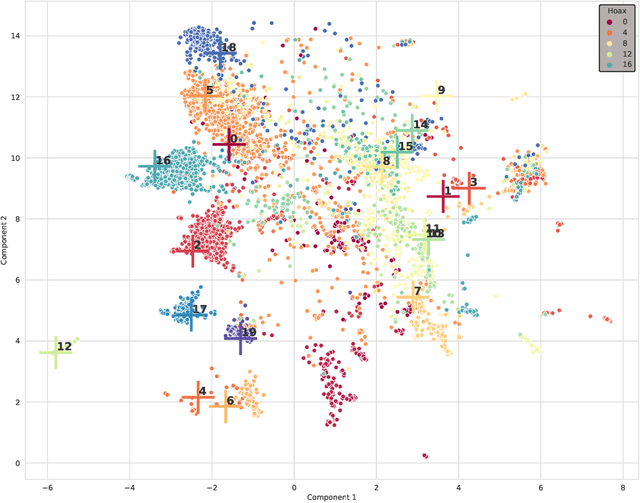
Abstract:The appearance of complex attention-based language models such as BERT, Roberta or GPT-3 has allowed to address highly complex tasks in a plethora of scenarios. However, when applied to specific domains, these models encounter considerable difficulties. This is the case of Social Networks such as Twitter, an ever-changing stream of information written with informal and complex language, where each message requires careful evaluation to be understood even by humans given the important role that context plays. Addressing tasks in this domain through Natural Language Processing involves severe challenges. When powerful state-of-the-art multilingual language models are applied to this scenario, language specific nuances use to get lost in translation. To face these challenges we present \textbf{BERTuit}, the larger transformer proposed so far for Spanish language, pre-trained on a massive dataset of 230M Spanish tweets using RoBERTa optimization. Our motivation is to provide a powerful resource to better understand Spanish Twitter and to be used on applications focused on this social network, with special emphasis on solutions devoted to tackle the spreading of misinformation in this platform. BERTuit is evaluated on several tasks and compared against M-BERT, XLM-RoBERTa and XLM-T, very competitive multilingual transformers. The utility of our approach is shown with applications, in this case: a zero-shot methodology to visualize groups of hoaxes and profiling authors spreading disinformation. Misinformation spreads wildly on platforms such as Twitter in languages other than English, meaning performance of transformers may suffer when transferred outside English speaking communities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge