Bhavika Devnani
Learning Spatially-Aware Language and Audio Embedding
Sep 17, 2024



Abstract:Humans can picture a sound scene given an imprecise natural language description. For example, it is easy to imagine an acoustic environment given a phrase like "the lion roar came from right behind me!". For a machine to have the same degree of comprehension, the machine must know what a lion is (semantic attribute), what the concept of "behind" is (spatial attribute) and how these pieces of linguistic information align with the semantic and spatial attributes of the sound (what a roar sounds like when its coming from behind). State-of-the-art audio foundation models which learn to map between audio scenes and natural textual descriptions, are trained on non-spatial audio and text pairs, and hence lack spatial awareness. In contrast, sound event localization and detection models are limited to recognizing sounds from a fixed number of classes, and they localize the source to absolute position (e.g., 0.2m) rather than a position described using natural language (e.g., "next to me"). To address these gaps, we present ELSA a spatially aware-audio and text embedding model trained using multimodal contrastive learning. ELSA supports non-spatial audio, spatial audio, and open vocabulary text captions describing both the spatial and semantic components of sound. To train ELSA: (a) we spatially augment the audio and captions of three open-source audio datasets totaling 4,738 hours of audio, and (b) we design an encoder to capture the semantics of non-spatial audio, and the semantics and spatial attributes of spatial audio using contrastive learning. ELSA is competitive with state-of-the-art for both semantic retrieval and 3D source localization. In particular, ELSA achieves +2.8% mean audio-to-text and text-to-audio R@1 above the baseline, and outperforms by -11.6{\deg} mean-absolute-error in 3D source localization over the baseline.
ZSON: Zero-Shot Object-Goal Navigation using Multimodal Goal Embeddings
Jun 24, 2022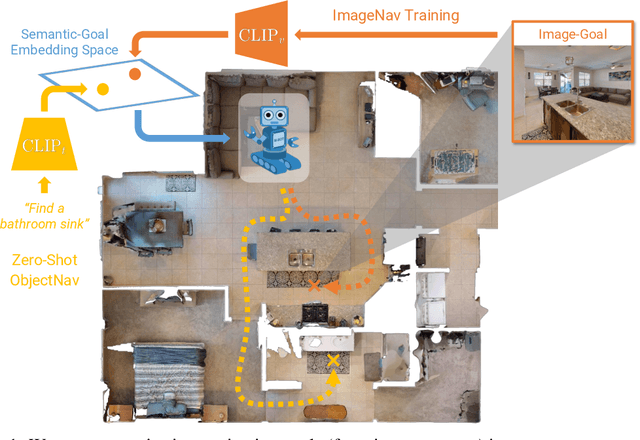
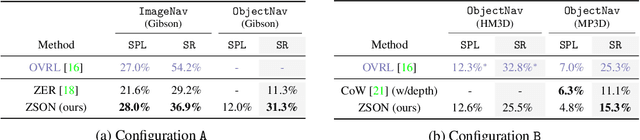
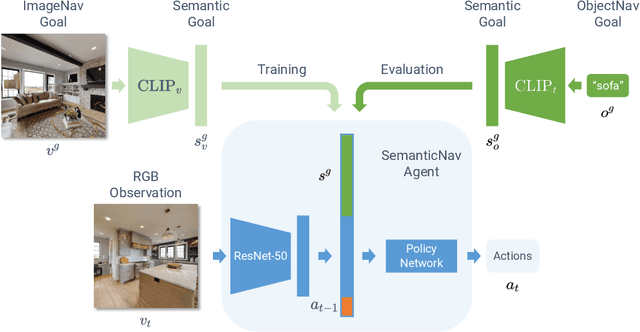
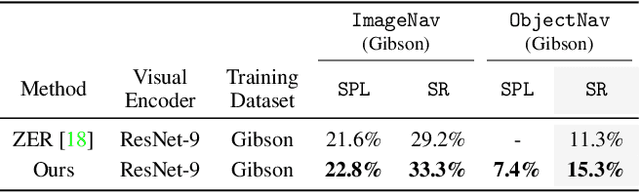
Abstract:We present a scalable approach for learning open-world object-goal navigation (ObjectNav) -- the task of asking a virtual robot (agent) to find any instance of an object in an unexplored environment (e.g., "find a sink"). Our approach is entirely zero-shot -- i.e., it does not require ObjectNav rewards or demonstrations of any kind. Instead, we train on the image-goal navigation (ImageNav) task, in which agents find the location where a picture (i.e., goal image) was captured. Specifically, we encode goal images into a multimodal, semantic embedding space to enable training semantic-goal navigation (SemanticNav) agents at scale in unannotated 3D environments (e.g., HM3D). After training, SemanticNav agents can be instructed to find objects described in free-form natural language (e.g., "sink", "bathroom sink", etc.) by projecting language goals into the same multimodal, semantic embedding space. As a result, our approach enables open-world ObjectNav. We extensively evaluate our agents on three ObjectNav datasets (Gibson, HM3D, and MP3D) and observe absolute improvements in success of 4.2% - 20.0% over existing zero-shot methods. For reference, these gains are similar or better than the 5% improvement in success between the Habitat 2020 and 2021 ObjectNav challenge winners. In an open-world setting, we discover that our agents can generalize to compound instructions with a room explicitly mentioned (e.g., "Find a kitchen sink") and when the target room can be inferred (e.g., "Find a sink and a stove").
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge