Bhargav Ghanekar
Video-based Surgical Tool-tip and Keypoint Tracking using Multi-frame Context-driven Deep Learning Models
Jan 30, 2025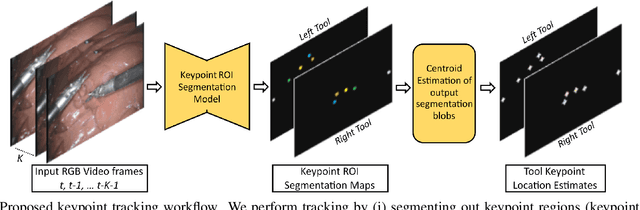
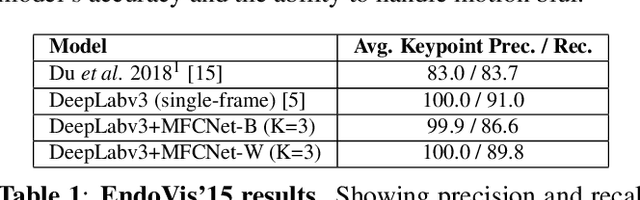
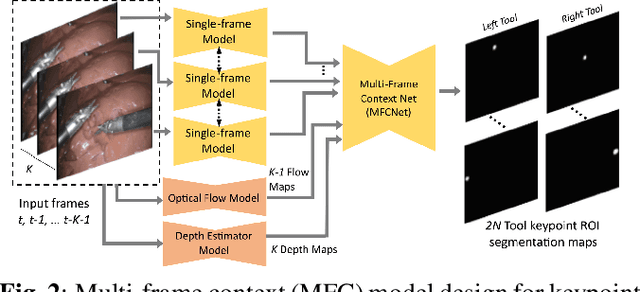
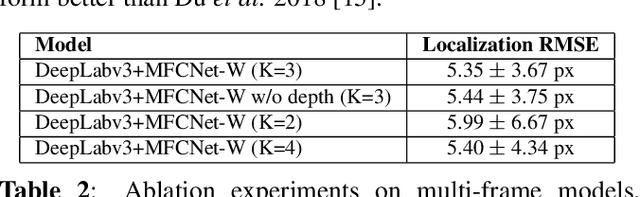
Abstract:Automated tracking of surgical tool keypoints in robotic surgery videos is an essential task for various downstream use cases such as skill assessment, expertise assessment, and the delineation of safety zones. In recent years, the explosion of deep learning for vision applications has led to many works in surgical instrument segmentation, while lesser focus has been on tracking specific tool keypoints, such as tool tips. In this work, we propose a novel, multi-frame context-driven deep learning framework to localize and track tool keypoints in surgical videos. We train and test our models on the annotated frames from the 2015 EndoVis Challenge dataset, resulting in state-of-the-art performance. By leveraging sophisticated deep learning models and multi-frame context, we achieve 90\% keypoint detection accuracy and a localization RMS error of 5.27 pixels. Results on a self-annotated JIGSAWS dataset with more challenging scenarios also show that the proposed multi-frame models can accurately track tool-tip and tool-base keypoints, with ${<}4.2$-pixel RMS error overall. Such a framework paves the way for accurately tracking surgical instrument keypoints, enabling further downstream use cases. Project and dataset webpage: https://tinyurl.com/mfc-tracker
Passive Snapshot Coded Aperture Dual-Pixel RGB-D Imaging
Feb 28, 2024



Abstract:Passive, compact, single-shot 3D sensing is useful in many application areas such as microscopy, medical imaging, surgical navigation, and autonomous driving where form factor, time, and power constraints can exist. Obtaining RGB-D scene information over a short imaging distance, in an ultra-compact form factor, and in a passive, snapshot manner is challenging. Dual-pixel (DP) sensors are a potential solution to achieve the same. DP sensors collect light rays from two different halves of the lens in two interleaved pixel arrays, thus capturing two slightly different views of the scene, like a stereo camera system. However, imaging with a DP sensor implies that the defocus blur size is directly proportional to the disparity seen between the views. This creates a trade-off between disparity estimation vs. deblurring accuracy. To improve this trade-off effect, we propose CADS (Coded Aperture Dual-Pixel Sensing), in which we use a coded aperture in the imaging lens along with a DP sensor. In our approach, we jointly learn an optimal coded pattern and the reconstruction algorithm in an end-to-end optimization setting. Our resulting CADS imaging system demonstrates improvement of $>$1.5dB PSNR in all-in-focus (AIF) estimates and 5-6% in depth estimation quality over naive DP sensing for a wide range of aperture settings. Furthermore, we build the proposed CADS prototypes for DSLR photography settings and in an endoscope and a dermoscope form factor. Our novel coded dual-pixel sensing approach demonstrates accurate RGB-D reconstruction results in simulations and real-world experiments in a passive, snapshot, and compact manner.
PS$^2$F: Polarized Spiral Point Spread Function for Single-Shot 3D Sensing
Jul 03, 2022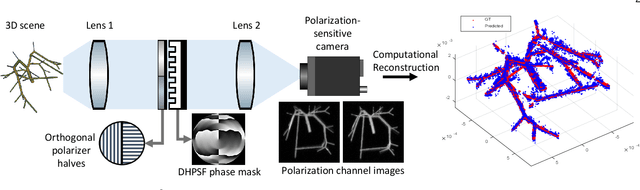
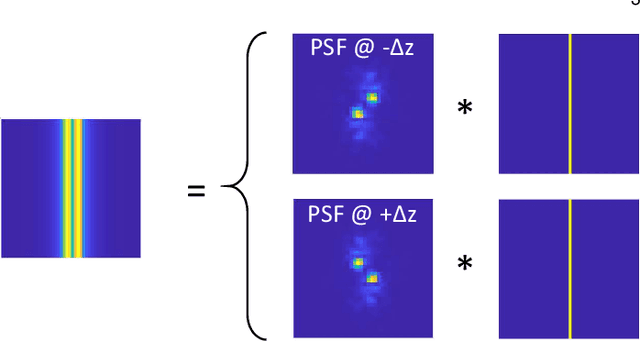
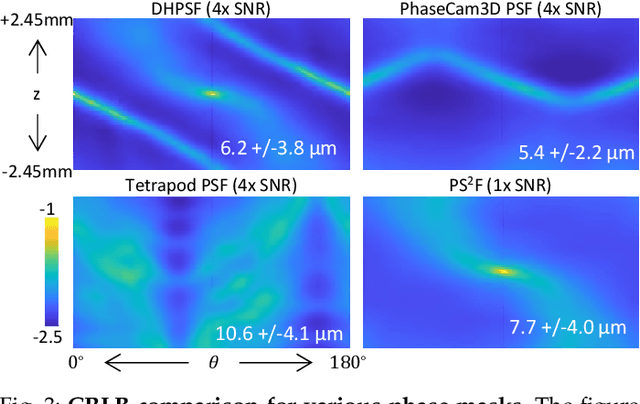
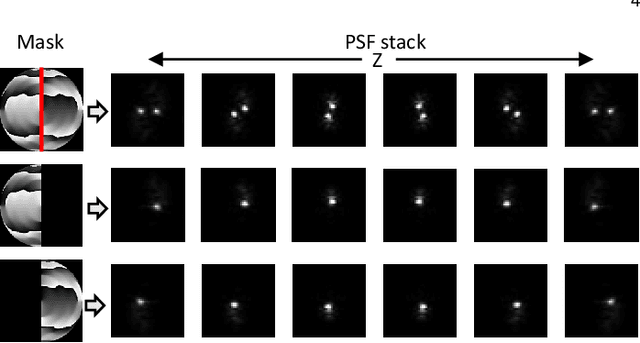
Abstract:We propose a compact snapshot monocular depth estimation technique that relies on an engineered point spread function (PSF). Traditional approaches used in microscopic super-resolution imaging, such as the Double-Helix PSF (DHPSF), are ill-suited for scenes that are more complex than a sparse set of point light sources. We show, using the Cram\'er-Rao lower bound (CRLB), that separating the two lobes of the DHPSF and thereby capturing two separate images leads to a dramatic increase in depth accuracy. A unique property of the phase mask used for generating the DHPSF is that a separation of the phase mask into two halves leads to a spatial separation of the two lobes. We leverage this property to build a compact polarization-based optical setup, where we place two orthogonal linear polarizers on each half of the DHPSF phase mask and then capture the resulting image with a polarization sensitive camera. Results from simulations and a lab prototype demonstrate that our technique achieves up to $50\%$ lower depth error compared to state-of-the-art designs including the DHPSF, and the Tetrapod PSF, with little to no loss in spatial resolution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge