Benedikt Boenninghoff
RubCSG at SemEval-2022 Task 5: Ensemble learning for identifying misogynous MEMEs
Apr 08, 2022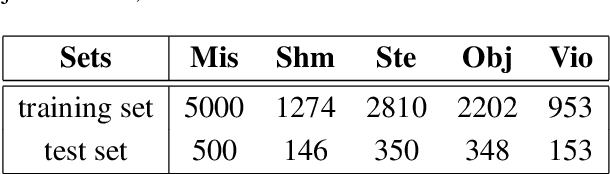
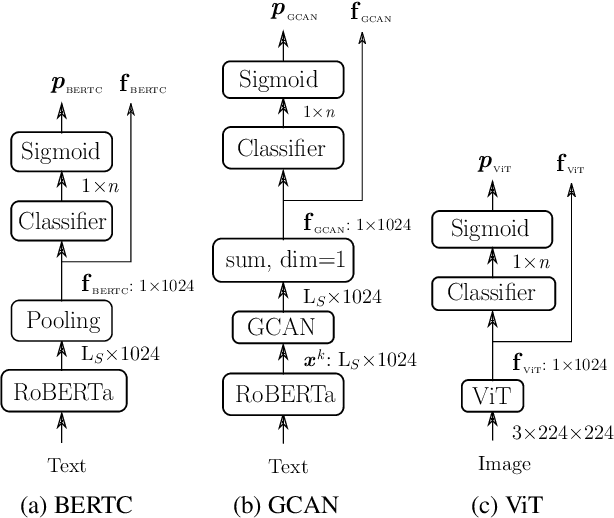
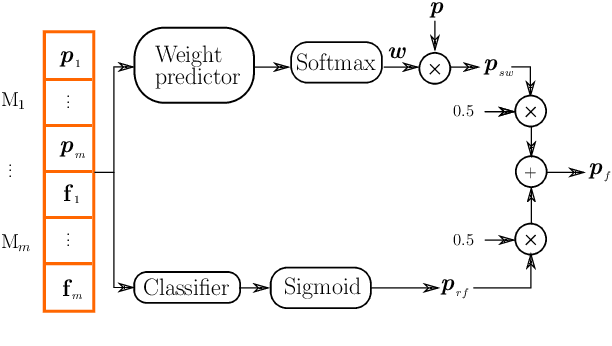
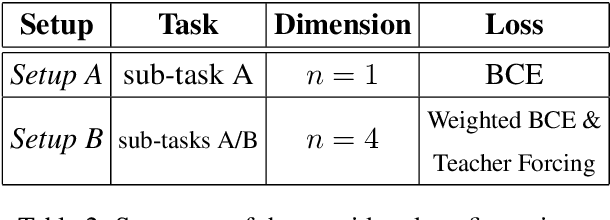
Abstract:This work presents an ensemble system based on various uni-modal and bi-modal model architectures developed for the SemEval 2022 Task 5: MAMI-Multimedia Automatic Misogyny Identification. The challenge organizers provide an English meme dataset to develop and train systems for identifying and classifying misogynous memes. More precisely, the competition is separated into two sub-tasks: sub-task A asks for a binary decision as to whether a meme expresses misogyny, while sub-task B is to classify misogynous memes into the potentially overlapping sub-categories of stereotype, shaming, objectification, and violence. For our submission, we implement a new model fusion network and employ an ensemble learning approach for better performance. With this structure, we achieve a 0.755 macroaverage F1-score (11th) in sub-task A and a 0.709 weighted-average F1-score (10th) in sub-task B.
Data Science Kitchen at GermEval 2021: A Fine Selection of Hand-Picked Features, Delivered Fresh from the Oven
Sep 06, 2021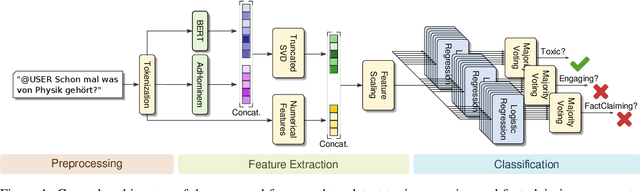
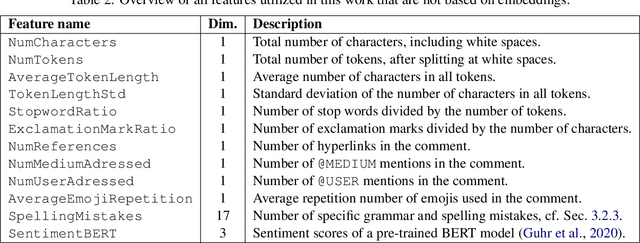
Abstract:This paper presents the contribution of the Data Science Kitchen at GermEval 2021 shared task on the identification of toxic, engaging, and fact-claiming comments. The task aims at extending the identification of offensive language, by including additional subtasks that identify comments which should be prioritized for fact-checking by moderators and community managers. Our contribution focuses on a feature-engineering approach with a conventional classification backend. We combine semantic and writing style embeddings derived from pre-trained deep neural networks with additional numerical features, specifically designed for this task. Ensembles of Logistic Regression classifiers and Support Vector Machines are used to derive predictions for each subtask via a majority voting scheme. Our best submission achieved macro-averaged F1-scores of 66.8%, 69.9% and 72.5% for the identification of toxic, engaging, and fact-claiming comments.
O2D2: Out-Of-Distribution Detector to Capture Undecidable Trials in Authorship Verification
Jul 30, 2021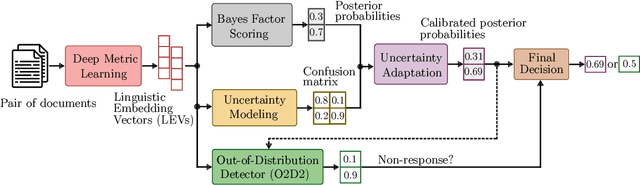
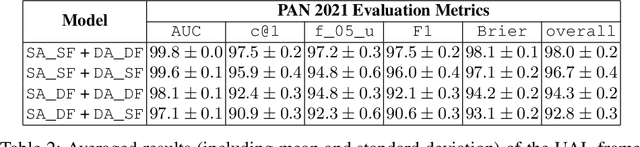
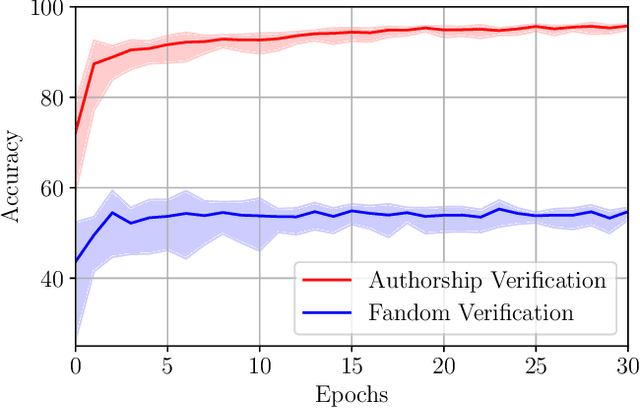
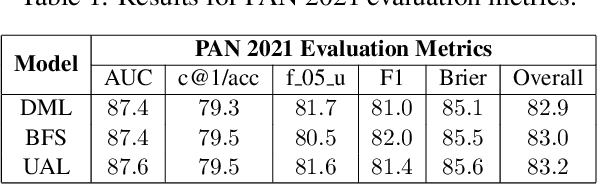
Abstract:The PAN 2021 authorship verification (AV) challenge is part of a three-year strategy, moving from a cross-topic/closed-set AV task to a cross-topic/open-set AV task over a collection of fanfiction texts. In this work, we present a novel hybrid neural-probabilistic framework that is designed to tackle the challenges of the 2021 task. Our system is based on our 2020 winning submission, with updates to significantly reduce sensitivities to topical variations and to further improve the system's calibration by means of an uncertainty-adaptation layer. Our framework additionally includes an out-of-distribution detector (O2D2) for defining non-responses. Our proposed system outperformed all other systems that participated in the PAN 2021 AV task.
Self-Calibrating Neural-Probabilistic Model for Authorship Verification Under Covariate Shift
Jun 21, 2021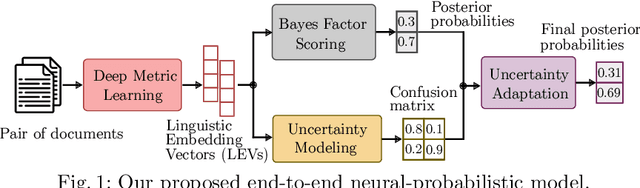
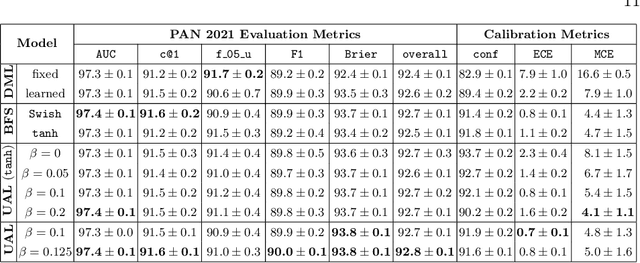
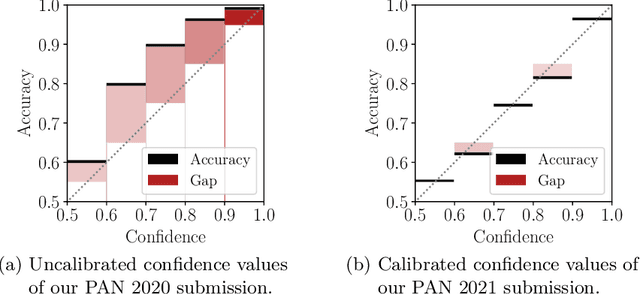
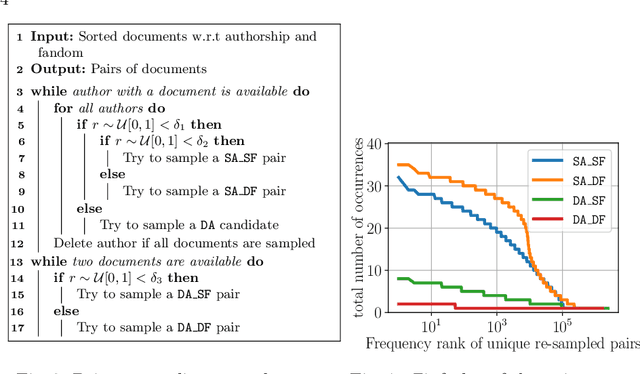
Abstract:We are addressing two fundamental problems in authorship verification (AV): Topic variability and miscalibration. Variations in the topic of two disputed texts are a major cause of error for most AV systems. In addition, it is observed that the underlying probability estimates produced by deep learning AV mechanisms oftentimes do not match the actual case counts in the respective training data. As such, probability estimates are poorly calibrated. We are expanding our framework from PAN 2020 to include Bayes factor scoring (BFS) and an uncertainty adaptation layer (UAL) to address both problems. Experiments with the 2020/21 PAN AV shared task data show that the proposed method significantly reduces sensitivities to topical variations and significantly improves the system's calibration.
Unsupervised Classification of Voiced Speech and Pitch Tracking Using Forward-Backward Kalman Filtering
Mar 01, 2021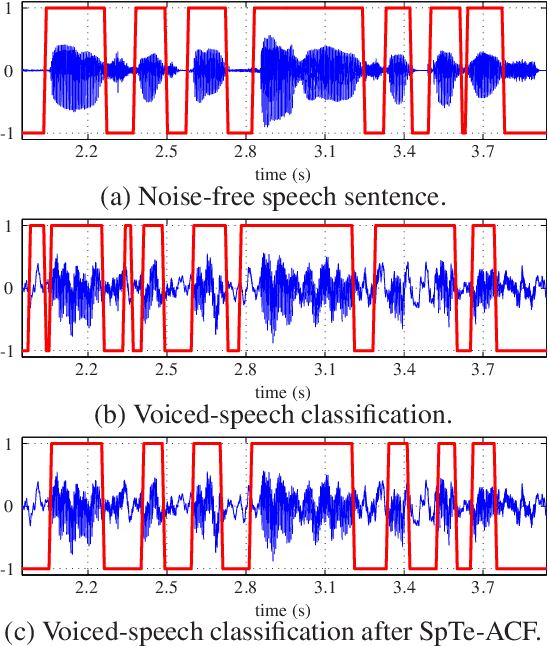
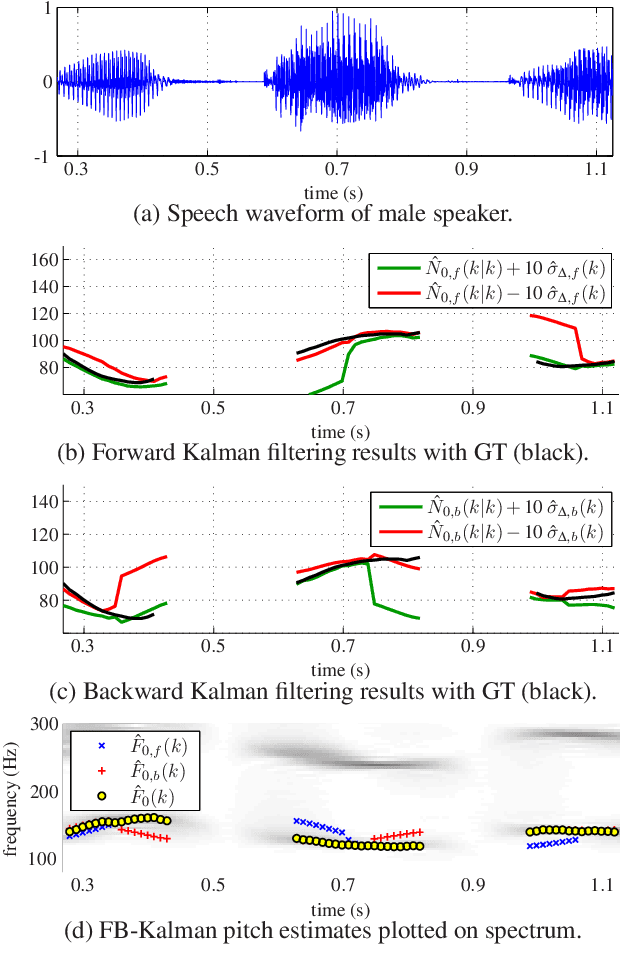
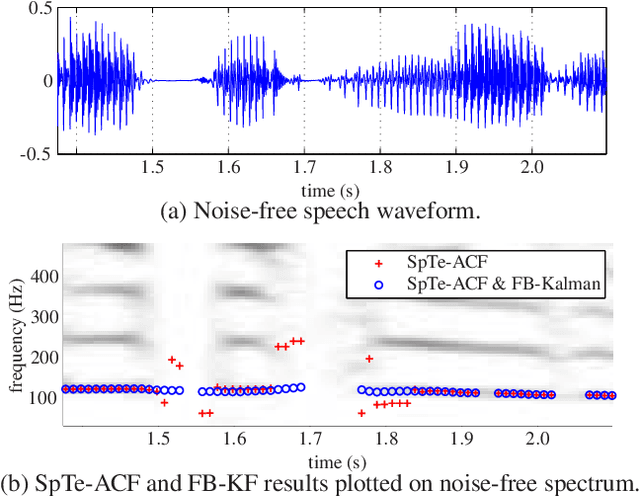
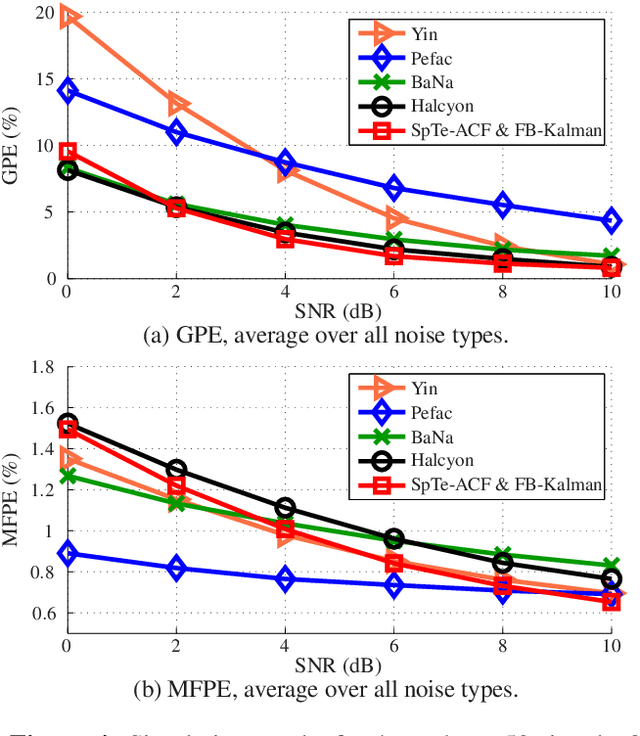
Abstract:The detection of voiced speech, the estimation of the fundamental frequency, and the tracking of pitch values over time are crucial subtasks for a variety of speech processing techniques. Many different algorithms have been developed for each of the three subtasks. We present a new algorithm that integrates the three subtasks into a single procedure. The algorithm can be applied to pre-recorded speech utterances in the presence of considerable amounts of background noise. We combine a collection of standard metrics, such as the zero-crossing rate, for example, to formulate an unsupervised voicing classifier. The estimation of pitch values is accomplished with a hybrid autocorrelation-based technique. We propose a forward-backward Kalman filter to smooth the estimated pitch contour. In experiments, we are able to show that the proposed method compares favorably with current, state-of-the-art pitch detection algorithms.
Data Fusion for Audiovisual Speaker Localization: Extending Dynamic Stream Weights to the Spatial Domain
Feb 24, 2021
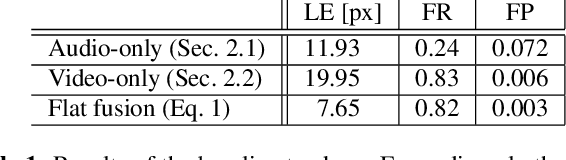
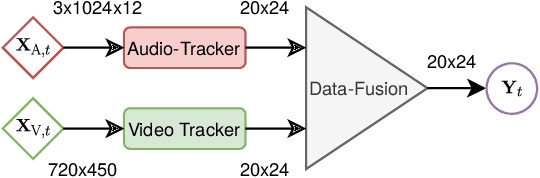
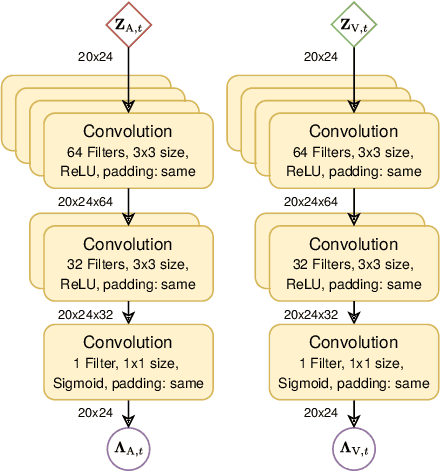
Abstract:Estimating the positions of multiple speakers can be helpful for tasks like automatic speech recognition or speaker diarization. Both applications benefit from a known speaker position when, for instance, applying beamforming or assigning unique speaker identities. Recently, several approaches utilizing acoustic signals augmented with visual data have been proposed for this task. However, both the acoustic and the visual modality may be corrupted in specific spatial regions, for instance due to poor lighting conditions or to the presence of background noise. This paper proposes a novel audiovisual data fusion framework for speaker localization by assigning individual dynamic stream weights to specific regions in the localization space. This fusion is achieved via a neural network, which combines the predictions of individual audio and video trackers based on their time- and location-dependent reliability. A performance evaluation using audiovisual recordings yields promising results, with the proposed fusion approach outperforming all baseline models.
Deep Bayes Factor Scoring for Authorship Verification
Aug 23, 2020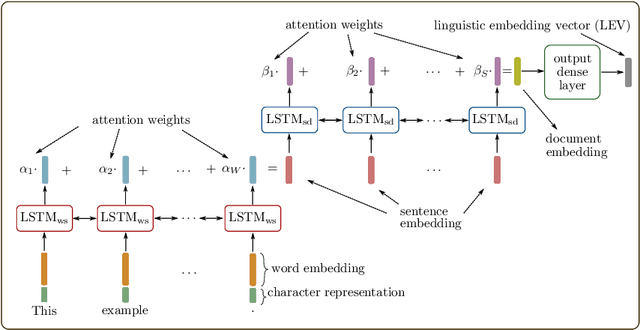
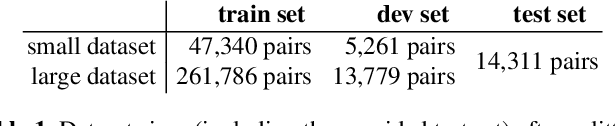
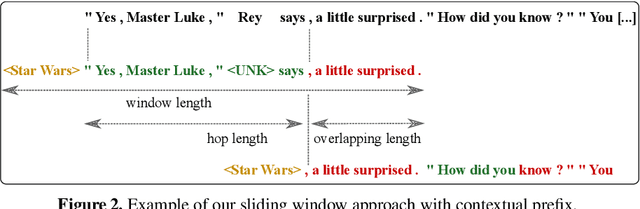
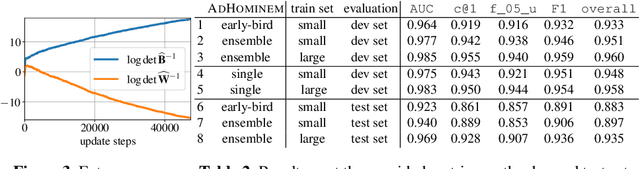
Abstract:The PAN 2020 authorship verification (AV) challenge focuses on a cross-topic/closed-set AV task over a collection of fanfiction texts. Fanfiction is a fan-written extension of a storyline in which a so-called fandom topic describes the principal subject of the document. The data provided in the PAN 2020 AV task is quite challenging because authors of texts across multiple/different fandom topics are included. In this work, we present a hierarchical fusion of two well-known approaches into a single end-to-end learning procedure: A deep metric learning framework at the bottom aims to learn a pseudo-metric that maps a document of variable length onto a fixed-sized feature vector. At the top, we incorporate a probabilistic layer to perform Bayes factor scoring in the learned metric space. We also provide text preprocessing strategies to deal with the cross-topic issue.
Variational Autoencoder with Embedded Student-$t$ Mixture Model for Authorship Attribution
May 28, 2020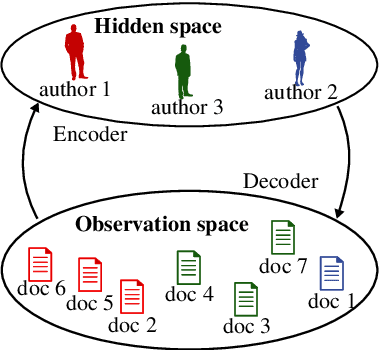
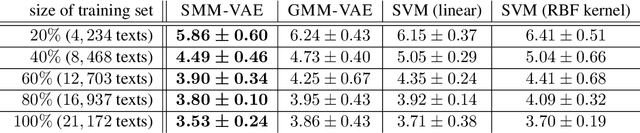
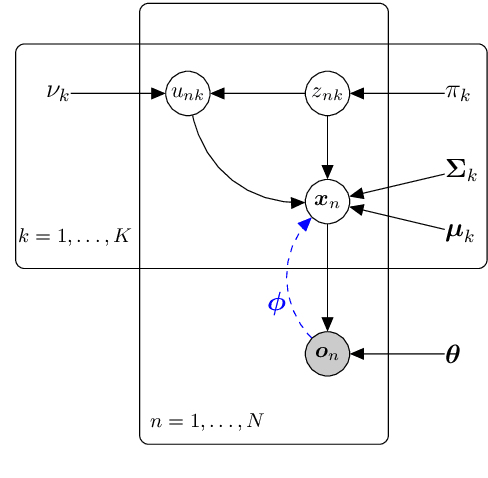
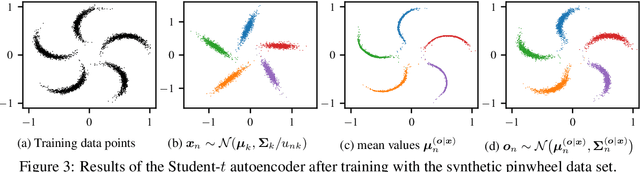
Abstract:Traditional computational authorship attribution describes a classification task in a closed-set scenario. Given a finite set of candidate authors and corresponding labeled texts, the objective is to determine which of the authors has written another set of anonymous or disputed texts. In this work, we propose a probabilistic autoencoding framework to deal with this supervised classification task. More precisely, we are extending a variational autoencoder (VAE) with embedded Gaussian mixture model to a Student-$t$ mixture model. Autoencoders have had tremendous success in learning latent representations. However, existing VAEs are currently still bound by limitations imposed by the assumed Gaussianity of the underlying probability distributions in the latent space. In this work, we are extending the Gaussian model for the VAE to a Student-$t$ model, which allows for an independent control of the "heaviness" of the respective tails of the implied probability densities. Experiments over an Amazon review dataset indicate superior performance of the proposed method.
Explainable Authorship Verification in Social Media via Attention-based Similarity Learning
Nov 19, 2019
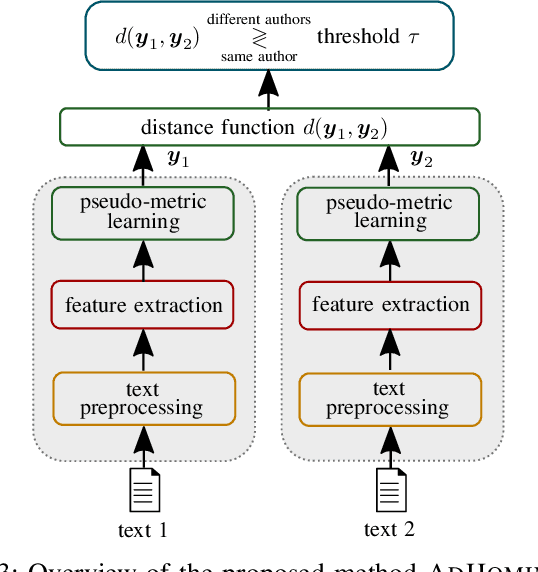
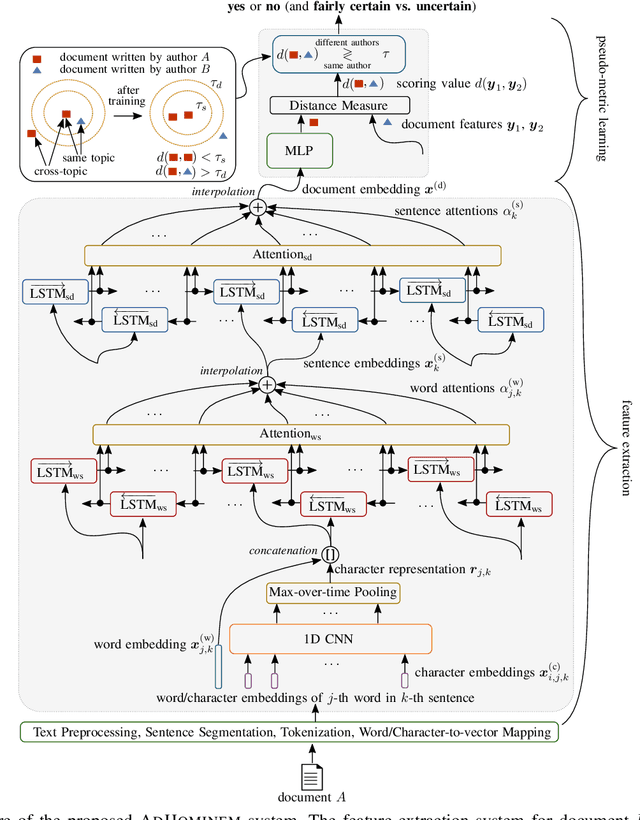
Abstract:Authorship verification is the task of analyzing the linguistic patterns of two or more texts to determine whether they were written by the same author or not. The analysis is traditionally performed by experts who consider linguistic features, which include spelling mistakes, grammatical inconsistencies, and stylistics for example. Machine learning algorithms, on the other hand, can be trained to accomplish the same, but have traditionally relied on so-called stylometric features. The disadvantage of such features is that their reliability is greatly diminished for short and topically varied social media texts. In this interdisciplinary work, we propose a substantial extension of a recently published hierarchical Siamese neural network approach, with which it is feasible to learn neural features and to visualize the decision-making process. For this purpose, a new large-scale corpus of short Amazon reviews for text comparison research is compiled and we show that the Siamese network topologies outperform state-of-the-art approaches that were built up on stylometric features. Our linguistic analysis of the internal attention weights of the network shows that the proposed method is indeed able to latch on to some traditional linguistic categories.
Similarity Learning for Authorship Verification in Social Media
Aug 20, 2019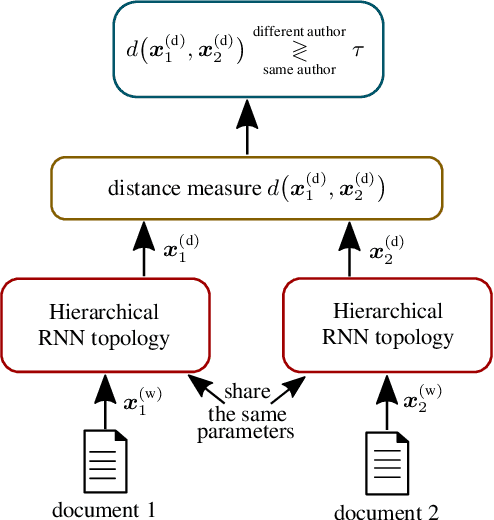
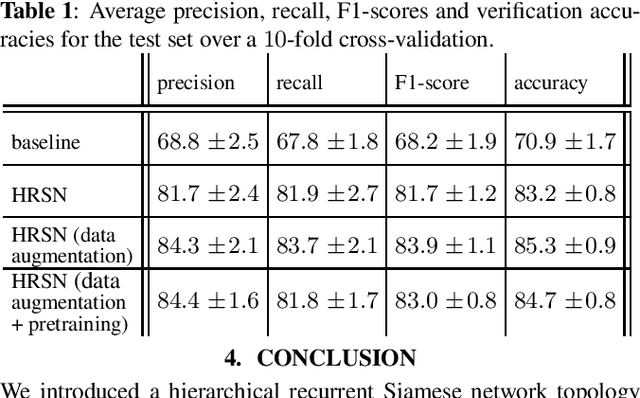
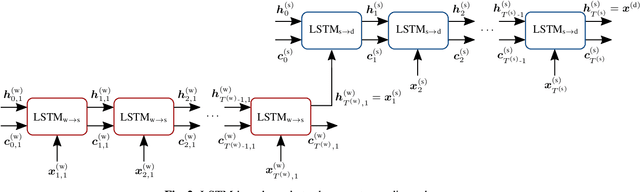
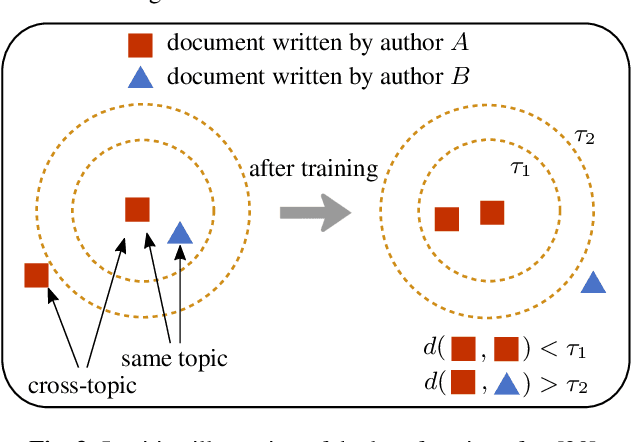
Abstract:Authorship verification tries to answer the question if two documents with unknown authors were written by the same author or not. A range of successful technical approaches has been proposed for this task, many of which are based on traditional linguistic features such as n-grams. These algorithms achieve good results for certain types of written documents like books and novels. Forensic authorship verification for social media, however, is a much more challenging task since messages tend to be relatively short, with a large variety of different genres and topics. At this point, traditional methods based on features like n-grams have had limited success. In this work, we propose a new neural network topology for similarity learning that significantly improves the performance on the author verification task with such challenging data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge