Beiming Li
Learning Policy Representations for Steerable Behavior Synthesis
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Given a Markov decision process (MDP), we seek to learn representations for a range of policies to facilitate behavior steering at test time. As policies of an MDP are uniquely determined by their occupancy measures, we propose modeling policy representations as expectations of state-action feature maps with respect to occupancy measures. We show that these representations can be approximated uniformly for a range of policies using a set-based architecture. Our model encodes a set of state-action samples into a latent embedding, from which we decode both the policy and its value functions corresponding to multiple rewards. We use variational generative approach to induce a smooth latent space, and further shape it with contrastive learning so that latent distances align with differences in value functions. This geometry permits gradient-based optimization directly in the latent space. Leveraging this capability, we solve a novel behavior synthesis task, where policies are steered to satisfy previously unseen value function constraints without additional training.
Learning to Explore Indoor Environments using Autonomous Micro Aerial Vehicles
Sep 13, 2023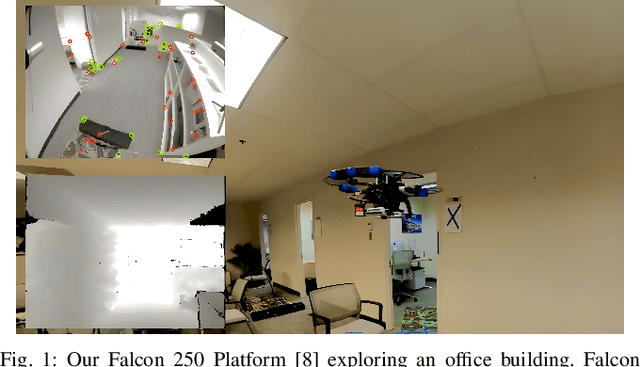

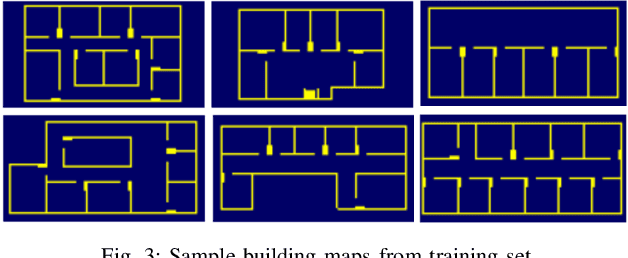
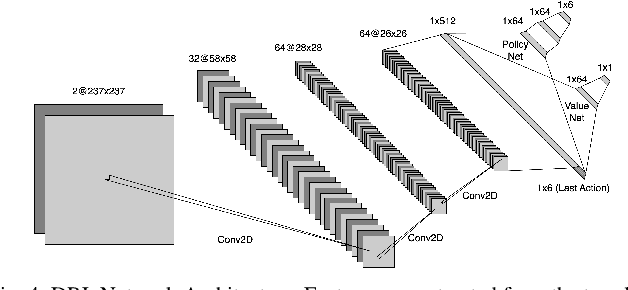
Abstract:In this paper, we address the challenge of exploring unknown indoor aerial environments using autonomous aerial robots with Size Weight and Power (SWaP) constraints. The SWaP constraints induce limits on mission time requiring efficiency in exploration. We present a novel exploration framework that uses Deep Learning (DL) to predict the most likely indoor map given the previous observations, and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) for exploration, designed to run on modern SWaP constraints neural processors. The DL-based map predictor provides a prediction of the occupancy of the unseen environment while the DRL-based planner determines the best navigation goals that can be safely reached to provide the most information. The two modules are tightly coupled and run onboard allowing the vehicle to safely map an unknown environment. Extensive experimental and simulation results show that our approach surpasses state-of-the-art methods by 50-60% in efficiency, which we measure by the fraction of the explored space as a function of the length of the trajectory traveled.
SEER: Safe Efficient Exploration for Aerial Robots using Learning to Predict Information Gain
Sep 22, 2022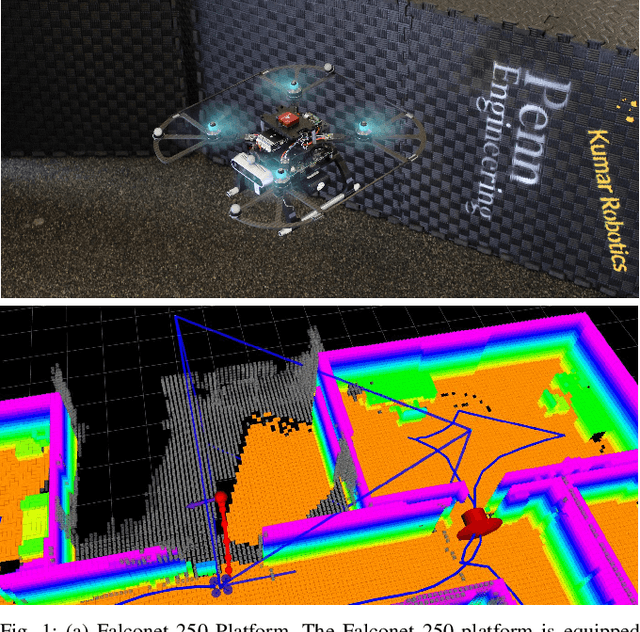
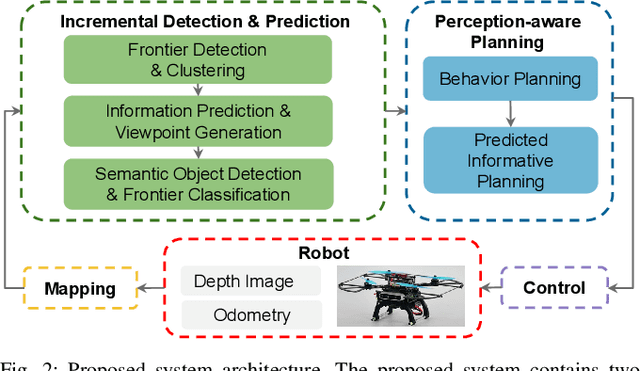
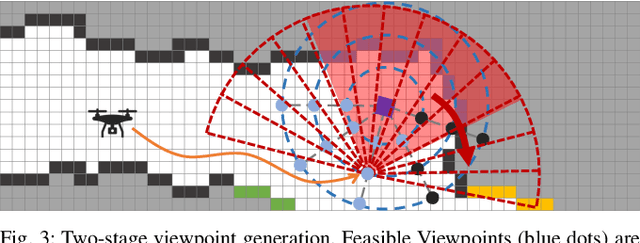
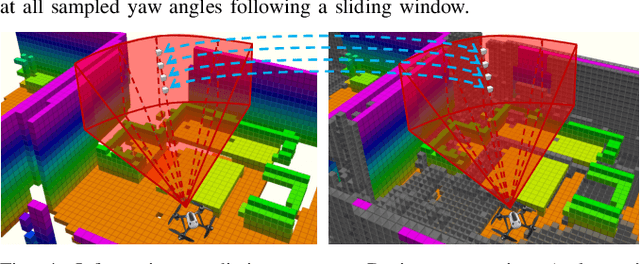
Abstract:We address the problem of efficient 3-D exploration in indoor environments for micro aerial vehicles with limited sensing capabilities and payload/power constraints. We develop an indoor exploration framework that uses learning to predict the occupancy of unseen areas, extracts semantic features, samples viewpoints to predict information gains for different exploration goals, and plans informative trajectories to enable safe and smart exploration. Extensive experimentation in simulated and real-world environments shows the proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art exploration framework by 24% in terms of the total path length in a structured indoor environment and with a higher success rate during exploration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge