Behrouz Maham
RIS-Assisted D2D Communication in the Presence of Interference: Outage Performance Analysis and DNN-Based Prediction
Oct 09, 2024Abstract:This paper analyses the performance of reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-assisted device-to-device (D2D) communication systems, focusing on addressing co-channel interference, a prevalent issue due to the frequency reuse of sidelink in the underlay in-band D2D communications. In contrast to previous studies that either neglect interference or consider it only at the user, our research investigates a performance analysis in terms of outage probability (OP) for RIS-assisted D2D communication systems considering the presence of interference at both the user and the RIS. More specifically, we introduce a novel integral-form expression for an exact analysis of OP. Additionally, we present a new accurate approximation expression for OP, using the gamma distributions to approximate the fading of both desired and interference links, thereby yielding a closed-form expression. Nevertheless, both derived expressions, i.e., the exact integral-form and the approximate closed-form, contain special functions, such as Meijer's G-function and the parabolic cylinder function, which complicate real-time OP analysis. To circumvent this, we employ a deep neural network (DNN) for real-time OP prediction, trained with data generated by the exact expression. Moreover, we present a tight upper bound that quantifies the impact of interference on achievable diversity order and coding gain. We validate the derived expressions through Monte Carlo simulations. Our analysis reveals that while interference does not affect the system's diversity order, it significantly degrades the performance by reducing the coding gain. The results further demonstrate that increasing the number of RIS's reflecting elements is an effective strategy to mitigate the adverse effects of the interference on the system performance.
Federated Learning: A Cutting-Edge Survey of the Latest Advancements and Applications
Oct 15, 2023Abstract:In the realm of machine learning (ML) systems featuring client-host connections, the enhancement of privacy security can be effectively achieved through federated learning (FL) as a secure distributed ML methodology. FL effectively integrates cloud infrastructure to transfer ML models onto edge servers using blockchain technology. Through this mechanism, it guarantees the streamlined processing and data storage requirements of both centralized and decentralized systems, with an emphasis on scalability, privacy considerations, and cost-effective communication. In current FL implementations, data owners locally train their models, and subsequently upload the outcomes in the form of weights, gradients, and parameters to the cloud for overall model aggregation. This innovation obviates the necessity of engaging Internet of Things (IoT) clients and participants to communicate raw and potentially confidential data directly with a cloud center. This not only reduces the costs associated with communication networks but also enhances the protection of private data. This survey conducts an analysis and comparison of recent FL applications, aiming to assess their efficiency, accuracy, and privacy protection. However, in light of the complex and evolving nature of FL, it becomes evident that additional research is imperative to address lingering knowledge gaps and effectively confront the forthcoming challenges in this field. In this study, we categorize recent literature into the following clusters: privacy protection, resource allocation, case study analysis, and applications. Furthermore, at the end of each section, we tabulate the open areas and future directions presented in the referenced literature, affording researchers and scholars an insightful view of the evolution of the field.
Modeling RIS Empowered Outdoor-to-Indoor Communication in mmWave Cellular Networks
Jan 04, 2021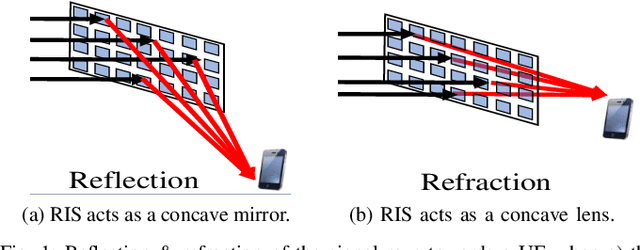
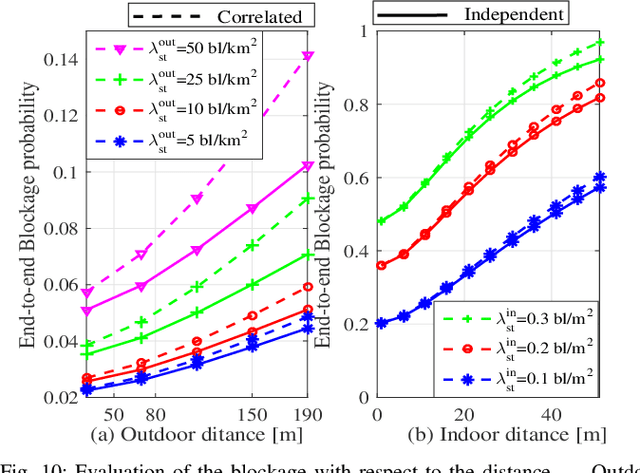
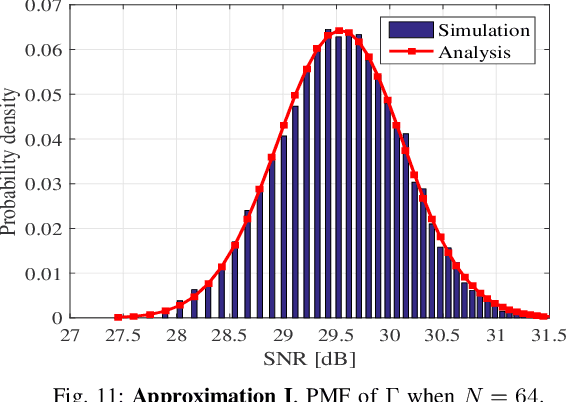
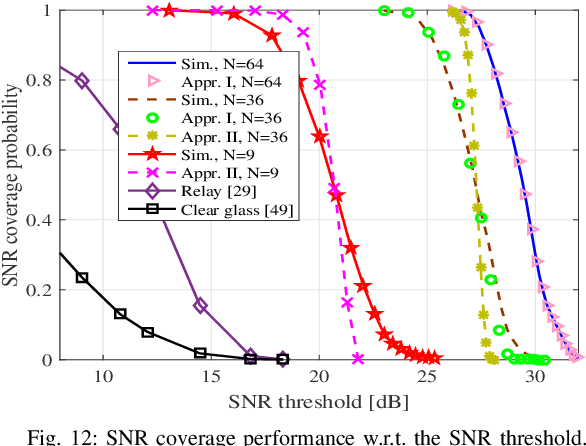
Abstract:With the increasing adoption of millimeter-waves (mmWave) over cellular networks, outdoor-to-indoor (O2I) communication has been one of the challenging research problems due to high penetration loss of buildings. To address this, we investigate the practicability of utilizing reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) for assisting such O2I communication. We propose a new notion of prefabricated RIS-empowered wall consisting of a large number of chipless radio frequency identification (RFID) sensors. Each sensor maintains its own bank of delay lines. These sensors which are built within the building walls can potentially be controlled by a main integrated circuit (IC) to regulate the phase of impinging signals. To evaluate our idea, we develop a thorough performance analysis of the RIS-based O2I communication in the mmWave network using stochastic-geometry tools for blockage models. Our analysis facilitates two closed-form approximations of the downlink signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) coverage probability for RIS-based O2I communication. We perform extensive simulations to evaluate the accuracy of the derived expressions, thus providing new observations and findings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge