Beatrice Achilli
Theory of Speciation Transitions in Diffusion Models with General Class Structure
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Models generate data by reversing a stochastic diffusion process, progressively transforming noise into structured samples drawn from a target distribution. Recent theoretical work has shown that this backward dynamics can undergo sharp qualitative transitions, known as speciation transitions, during which trajectories become dynamically committed to data classes. Existing theoretical analyses, however, are limited to settings where classes are identifiable through first moments, such as mixtures of Gaussians with well-separated means. In this work, we develop a general theory of speciation in diffusion models that applies to arbitrary target distributions admitting well-defined classes. We formalize the notion of class structure through Bayes classification and characterize speciation times in terms of free-entropy difference between classes. This criterion recovers known results in previously studied Gaussian-mixture models, while extending to situations in which classes are not distinguishable by first moments and may instead differ through higher-order or collective features. Our framework also accommodates multiple classes and predicts the existence of successive speciation times associated with increasingly fine-grained class commitment. We illustrate the theory on two analytically tractable examples: mixtures of one-dimensional Ising models at different temperatures and mixtures of zero-mean Gaussians with distinct covariance structures. In the Ising case, we obtain explicit expressions for speciation times by mapping the problem onto a random-field Ising model and solving it via the replica method. Our results provide a unified and broadly applicable description of speciation transitions in diffusion-based generative models.
Emergence of Distortions in High-Dimensional Guided Diffusion Models
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Classifier-free guidance (CFG) is the de facto standard for conditional sampling in diffusion models, yet it often leads to a loss of diversity in generated samples. We formalize this phenomenon as generative distortion, defined as the mismatch between the CFG-induced sampling distribution and the true conditional distribution. Considering Gaussian mixtures and their exact scores, and leveraging tools from statistical physics, we characterize the onset of distortion in a high-dimensional regime as a function of the number of classes. Our analysis reveals that distortions emerge through a phase transition in the effective potential governing the guided dynamics. In particular, our dynamical mean-field analysis shows that distortion persists when the number of modes grows exponentially with dimension, but vanishes in the sub-exponential regime. Consistent with prior finite-dimensional results, we further demonstrate that vanilla CFG shifts the mean and shrinks the variance of the conditional distribution. We show that standard CFG schedules are fundamentally incapable of preventing variance shrinkage. Finally, we propose a theoretically motivated guidance schedule featuring a negative-guidance window, which mitigates loss of diversity while preserving class separability.
Losing dimensions: Geometric memorization in generative diffusion
Oct 11, 2024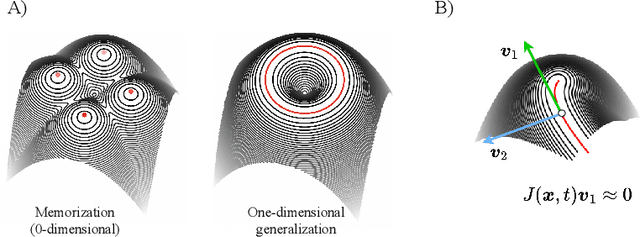

Abstract:Generative diffusion processes are state-of-the-art machine learning models deeply connected with fundamental concepts in statistical physics. Depending on the dataset size and the capacity of the network, their behavior is known to transition from an associative memory regime to a generalization phase in a phenomenon that has been described as a glassy phase transition. Here, using statistical physics techniques, we extend the theory of memorization in generative diffusion to manifold-supported data. Our theoretical and experimental findings indicate that different tangent subspaces are lost due to memorization effects at different critical times and dataset sizes, which depend on the local variance of the data along their directions. Perhaps counterintuitively, we find that, under some conditions, subspaces of higher variance are lost first due to memorization effects. This leads to a selective loss of dimensionality where some prominent features of the data are memorized without a full collapse on any individual training point. We validate our theory with a comprehensive set of experiments on networks trained both in image datasets and on linear manifolds, which result in a remarkable qualitative agreement with the theoretical predictions.
Manifolds, Random Matrices and Spectral Gaps: The geometric phases of generative diffusion
Oct 08, 2024



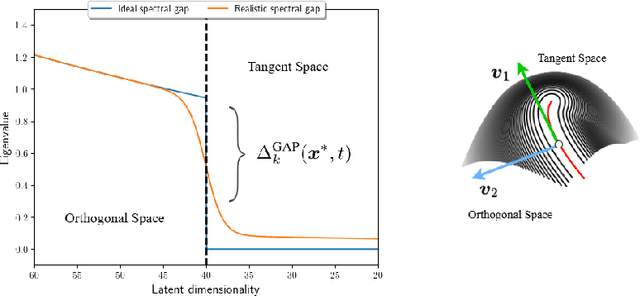
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the latent geometry of generative diffusion models under the manifold hypothesis. To this purpose, we analyze the spectrum of eigenvalues (and singular values) of the Jacobian of the score function, whose discontinuities (gaps) reveal the presence and dimensionality of distinct sub-manifolds. Using a statistical physics approach, we derive the spectral distributions and formulas for the spectral gaps under several distributional assumptions and we compare these theoretical predictions with the spectra estimated from trained networks. Our analysis reveals the existence of three distinct qualitative phases during the generative process: a trivial phase; a manifold coverage phase where the diffusion process fits the distribution internal to the manifold; a consolidation phase where the score becomes orthogonal to the manifold and all particles are projected on the support of the data. This `division of labor' between different timescales provides an elegant explanation on why generative diffusion models are not affected by the manifold overfitting phenomenon that plagues likelihood-based models, since the internal distribution and the manifold geometry are produced at different time points during generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge