Bastian Epping
Graph Neural Networks Do Not Always Oversmooth
Jun 04, 2024Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have emerged as powerful tools for processing relational data in applications. However, GNNs suffer from the problem of oversmoothing, the property that the features of all nodes exponentially converge to the same vector over layers, prohibiting the design of deep GNNs. In this work we study oversmoothing in graph convolutional networks (GCNs) by using their Gaussian process (GP) equivalence in the limit of infinitely many hidden features. By generalizing methods from conventional deep neural networks (DNNs), we can describe the distribution of features at the output layer of deep GCNs in terms of a GP: as expected, we find that typical parameter choices from the literature lead to oversmoothing. The theory, however, allows us to identify a new, nonoversmoothing phase: if the initial weights of the network have sufficiently large variance, GCNs do not oversmooth, and node features remain informative even at large depth. We demonstrate the validity of this prediction in finite-size GCNs by training a linear classifier on their output. Moreover, using the linearization of the GCN GP, we generalize the concept of propagation depth of information from DNNs to GCNs. This propagation depth diverges at the transition between the oversmoothing and non-oversmoothing phase. We test the predictions of our approach and find good agreement with finite-size GCNs. Initializing GCNs near the transition to the non-oversmoothing phase, we obtain networks which are both deep and expressive.
Unified Field Theory for Deep and Recurrent Neural Networks
Jan 07, 2022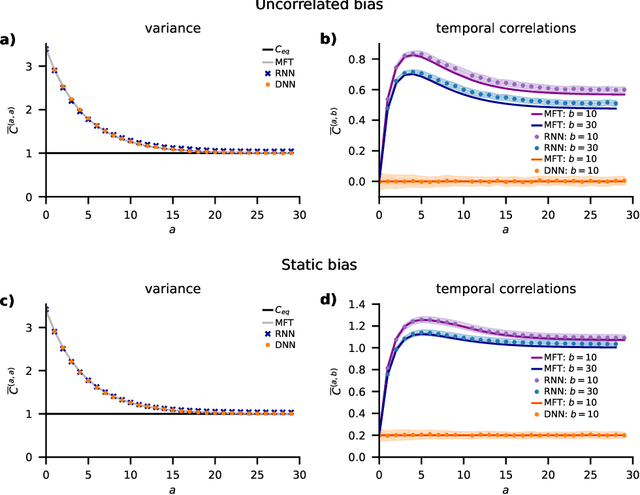
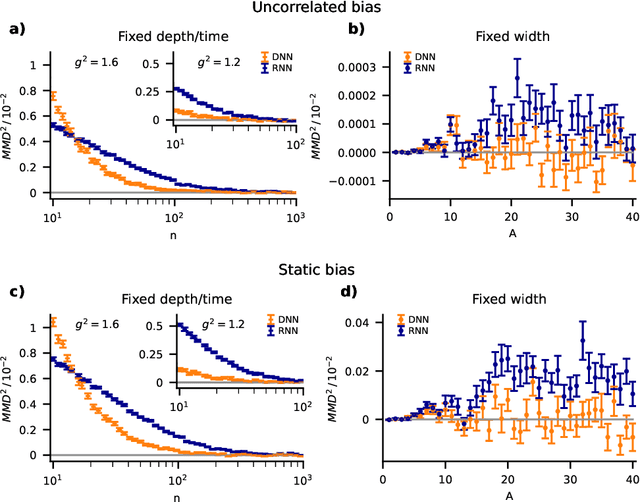
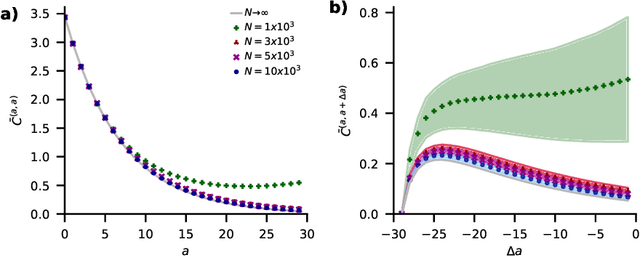
Abstract:Understanding capabilities and limitations of different network architectures is of fundamental importance to machine learning. Bayesian inference on Gaussian processes has proven to be a viable approach for studying recurrent and deep networks in the limit of infinite layer width, $n\to\infty$. Here we present a unified and systematic derivation of the mean-field theory for both architectures that starts from first principles by employing established methods from statistical physics of disordered systems. The theory elucidates that while the mean-field equations are different with regard to their temporal structure, they yet yield identical Gaussian kernels when readouts are taken at a single time point or layer, respectively. Bayesian inference applied to classification then predicts identical performance and capabilities for the two architectures. Numerically, we find that convergence towards the mean-field theory is typically slower for recurrent networks than for deep networks and the convergence speed depends non-trivially on the parameters of the weight prior as well as the depth or number of time steps, respectively. Our method exposes that Gaussian processes are but the lowest order of a systematic expansion in $1/n$. The formalism thus paves the way to investigate the fundamental differences between recurrent and deep architectures at finite widths $n$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge