Baolei Zhang
Practical Framework for Privacy-Preserving and Byzantine-robust Federated Learning
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) allows multiple clients to collaboratively train a model without sharing their private data. However, FL is vulnerable to Byzantine attacks, where adversaries manipulate client models to compromise the federated model, and privacy inference attacks, where adversaries exploit client models to infer private data. Existing defenses against both backdoor and privacy inference attacks introduce significant computational and communication overhead, creating a gap between theory and practice. To address this, we propose ABBR, a practical framework for Byzantine-robust and privacy-preserving FL. We are the first to utilize dimensionality reduction to speed up the private computation of complex filtering rules in privacy-preserving FL. Additionally, we analyze the accuracy loss of vector-wise filtering in low-dimensional space and introduce an adaptive tuning strategy to minimize the impact of malicious models that bypass filtering on the global model. We implement ABBR with state-of-the-art Byzantine-robust aggregation rules and evaluate it on public datasets, showing that it runs significantly faster, has minimal communication overhead, and maintains nearly the same Byzantine-resilience as the baselines.
Gradient Surgery for Safe LLM Fine-Tuning
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Fine-tuning-as-a-Service introduces a critical vulnerability where a few malicious examples mixed into the user's fine-tuning dataset can compromise the safety alignment of Large Language Models (LLMs). While a recognized paradigm frames safe fine-tuning as a multi-objective optimization problem balancing user task performance with safety alignment, we find existing solutions are critically sensitive to the harmful ratio, with defenses degrading sharply as harmful ratio increases. We diagnose that this failure stems from conflicting gradients, where the user-task update directly undermines the safety objective. To resolve this, we propose SafeGrad, a novel method that employs gradient surgery. When a conflict is detected, SafeGrad nullifies the harmful component of the user-task gradient by projecting it onto the orthogonal plane of the alignment gradient, allowing the model to learn the user's task without sacrificing safety. To further enhance robustness and data efficiency, we employ a KL-divergence alignment loss that learns the rich, distributional safety profile of the well-aligned foundation model. Extensive experiments show that SafeGrad provides state-of-the-art defense across various LLMs and datasets, maintaining robust safety even at high harmful ratios without compromising task fidelity.
Benchmarking Poisoning Attacks against Retrieval-Augmented Generation
May 24, 2025



Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has proven effective in mitigating hallucinations in large language models by incorporating external knowledge during inference. However, this integration introduces new security vulnerabilities, particularly to poisoning attacks. Although prior work has explored various poisoning strategies, a thorough assessment of their practical threat to RAG systems remains missing. To address this gap, we propose the first comprehensive benchmark framework for evaluating poisoning attacks on RAG. Our benchmark covers 5 standard question answering (QA) datasets and 10 expanded variants, along with 13 poisoning attack methods and 7 defense mechanisms, representing a broad spectrum of existing techniques. Using this benchmark, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of all included attacks and defenses across the full dataset spectrum. Our findings show that while existing attacks perform well on standard QA datasets, their effectiveness drops significantly on the expanded versions. Moreover, our results demonstrate that various advanced RAG architectures, such as sequential, branching, conditional, and loop RAG, as well as multi-turn conversational RAG, multimodal RAG systems, and RAG-based LLM agent systems, remain susceptible to poisoning attacks. Notably, current defense techniques fail to provide robust protection, underscoring the pressing need for more resilient and generalizable defense strategies.
CTRAP: Embedding Collapse Trap to Safeguard Large Language Models from Harmful Fine-Tuning
May 22, 2025Abstract:Fine-tuning-as-a-service, while commercially successful for Large Language Model (LLM) providers, exposes models to harmful fine-tuning attacks. As a widely explored defense paradigm against such attacks, unlearning attempts to remove malicious knowledge from LLMs, thereby essentially preventing them from being used to perform malicious tasks. However, we highlight a critical flaw: the powerful general adaptability of LLMs allows them to easily bypass selective unlearning by rapidly relearning or repurposing their capabilities for harmful tasks. To address this fundamental limitation, we propose a paradigm shift: instead of selective removal, we advocate for inducing model collapse--effectively forcing the model to "unlearn everything"--specifically in response to updates characteristic of malicious adaptation. This collapse directly neutralizes the very general capabilities that attackers exploit, tackling the core issue unaddressed by selective unlearning. We introduce the Collapse Trap (CTRAP) as a practical mechanism to implement this concept conditionally. Embedded during alignment, CTRAP pre-configures the model's reaction to subsequent fine-tuning dynamics. If updates during fine-tuning constitute a persistent attempt to reverse safety alignment, the pre-configured trap triggers a progressive degradation of the model's core language modeling abilities, ultimately rendering it inert and useless for the attacker. Crucially, this collapse mechanism remains dormant during benign fine-tuning, ensuring the model's utility and general capabilities are preserved for legitimate users. Extensive empirical results demonstrate that CTRAP effectively counters harmful fine-tuning risks across various LLMs and attack settings, while maintaining high performance in benign scenarios. Our code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CTRAP.
Traceback of Poisoning Attacks to Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Apr 30, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) integrated with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems improve accuracy by leveraging external knowledge sources. However, recent research has revealed RAG's susceptibility to poisoning attacks, where the attacker injects poisoned texts into the knowledge database, leading to attacker-desired responses. Existing defenses, which predominantly focus on inference-time mitigation, have proven insufficient against sophisticated attacks. In this paper, we introduce RAGForensics, the first traceback system for RAG, designed to identify poisoned texts within the knowledge database that are responsible for the attacks. RAGForensics operates iteratively, first retrieving a subset of texts from the database and then utilizing a specially crafted prompt to guide an LLM in detecting potential poisoning texts. Empirical evaluations across multiple datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of RAGForensics against state-of-the-art poisoning attacks. This work pioneers the traceback of poisoned texts in RAG systems, providing a practical and promising defense mechanism to enhance their security.
Practical Poisoning Attacks against Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive natural language processing abilities but face challenges such as hallucination and outdated knowledge. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a state-of-the-art approach to mitigate these issues. While RAG enhances LLM outputs, it remains vulnerable to poisoning attacks. Recent studies show that injecting poisoned text into the knowledge database can compromise RAG systems, but most existing attacks assume that the attacker can insert a sufficient number of poisoned texts per query to outnumber correct-answer texts in retrieval, an assumption that is often unrealistic. To address this limitation, we propose CorruptRAG, a practical poisoning attack against RAG systems in which the attacker injects only a single poisoned text, enhancing both feasibility and stealth. Extensive experiments across multiple datasets demonstrate that CorruptRAG achieves higher attack success rates compared to existing baselines.
Prompt-Guided Internal States for Hallucination Detection of Large Language Models
Nov 07, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across a variety of tasks in different domains. However, they sometimes generate responses that are logically coherent but factually incorrect or misleading, which is known as LLM hallucinations. Data-driven supervised methods train hallucination detectors by leveraging the internal states of LLMs, but detectors trained on specific domains often struggle to generalize well to other domains. In this paper, we aim to enhance the cross-domain performance of supervised detectors with only in-domain data. We propose a novel framework, prompt-guided internal states for hallucination detection of LLMs, namely PRISM. By utilizing appropriate prompts to guide changes in the structure related to text truthfulness within the LLM's internal states, we make this structure more salient and consistent across texts from different domains. We integrated our framework with existing hallucination detection methods and conducted experiments on datasets from different domains. The experimental results indicate that our framework significantly enhances the cross-domain generalization of existing hallucination detection methods.
BadActs: A Universal Backdoor Defense in the Activation Space
May 18, 2024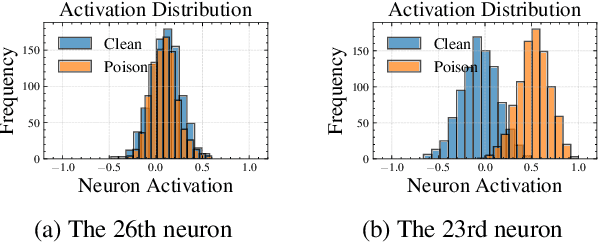
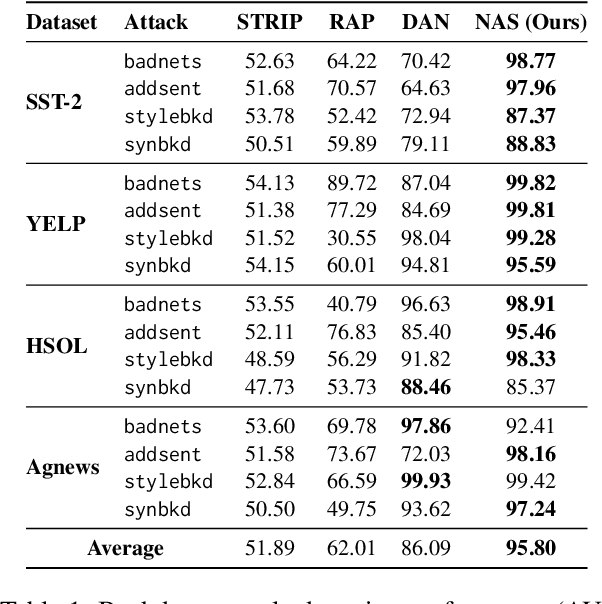
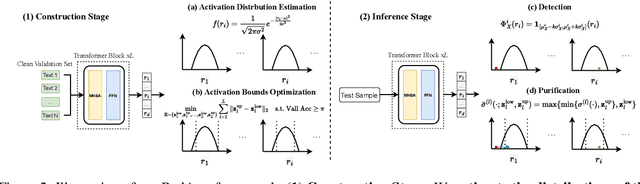
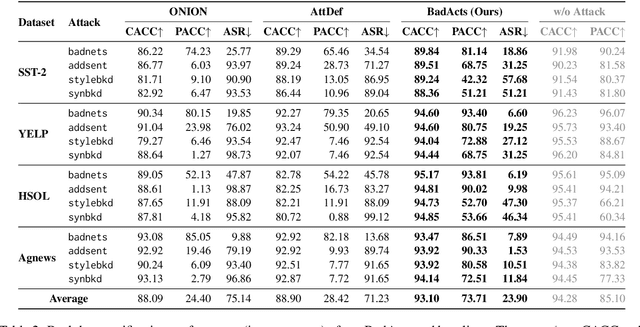
Abstract:Backdoor attacks pose an increasingly severe security threat to Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) during their development stage. In response, backdoor sample purification has emerged as a promising defense mechanism, aiming to eliminate backdoor triggers while preserving the integrity of the clean content in the samples. However, existing approaches have been predominantly focused on the word space, which are ineffective against feature-space triggers and significantly impair performance on clean data. To address this, we introduce a universal backdoor defense that purifies backdoor samples in the activation space by drawing abnormal activations towards optimized minimum clean activation distribution intervals. The advantages of our approach are twofold: (1) By operating in the activation space, our method captures from surface-level information like words to higher-level semantic concepts such as syntax, thus counteracting diverse triggers; (2) the fine-grained continuous nature of the activation space allows for more precise preservation of clean content while removing triggers. Furthermore, we propose a detection module based on statistical information of abnormal activations, to achieve a better trade-off between clean accuracy and defending performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge