Ashok Deb
Detecting Social Media Manipulation in Low-Resource Languages
Nov 10, 2020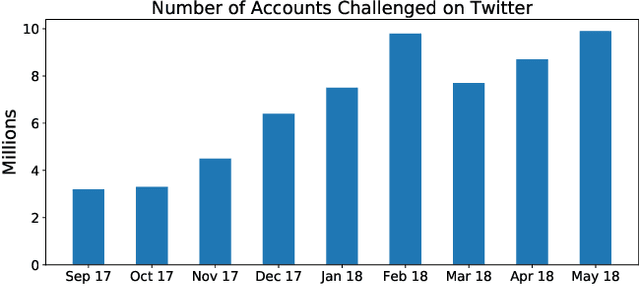
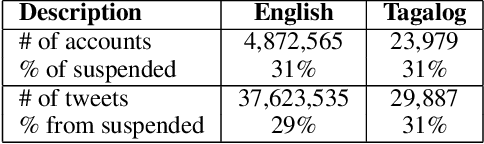
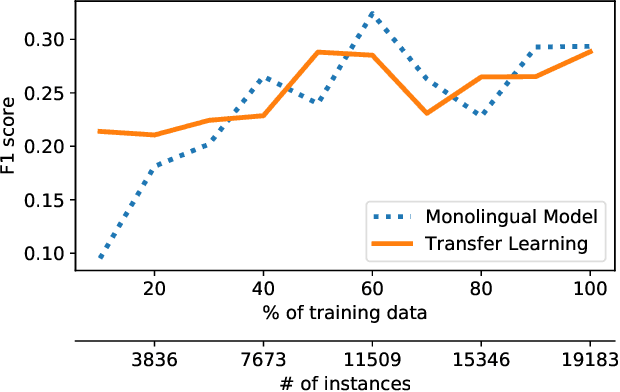
Abstract:Social media have been deliberately used for malicious purposes, including political manipulation and disinformation. Most research focuses on high-resource languages. However, malicious actors share content across countries and languages, including low-resource ones. Here, we investigate whether and to what extent malicious actors can be detected in low-resource language settings. We discovered that a high number of accounts posting in Tagalog were suspended as part of Twitter's crackdown on interference operations after the 2016 US Presidential election. By combining text embedding and transfer learning, our framework can detect, with promising accuracy, malicious users posting in Tagalog without any prior knowledge or training on malicious content in that language. We first learn an embedding model for each language, namely a high-resource language (English) and a low-resource one (Tagalog), independently. Then, we learn a mapping between the two latent spaces to transfer the detection model. We demonstrate that the proposed approach significantly outperforms state-of-the-art models, including BERT, and yields marked advantages in settings with very limited training data-the norm when dealing with detecting malicious activity in online platforms.
Discovering Signals from Web Sources to Predict Cyber Attacks
Jun 08, 2018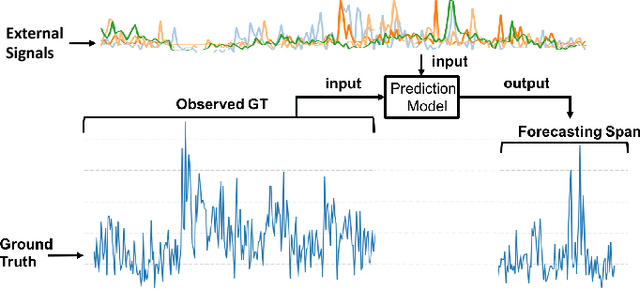
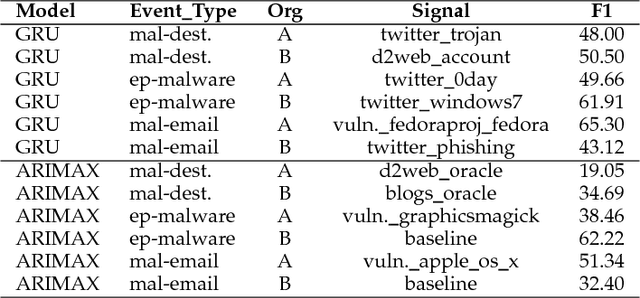
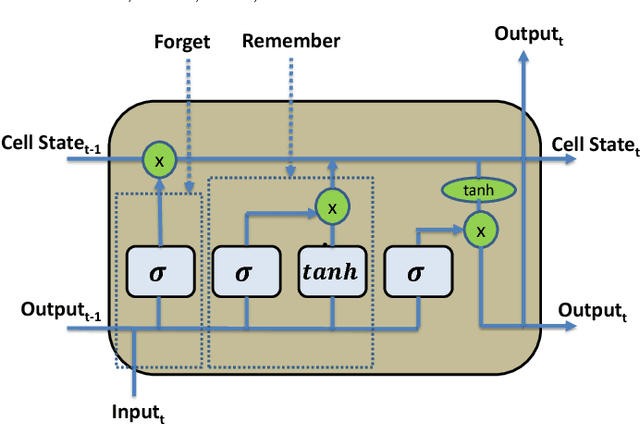
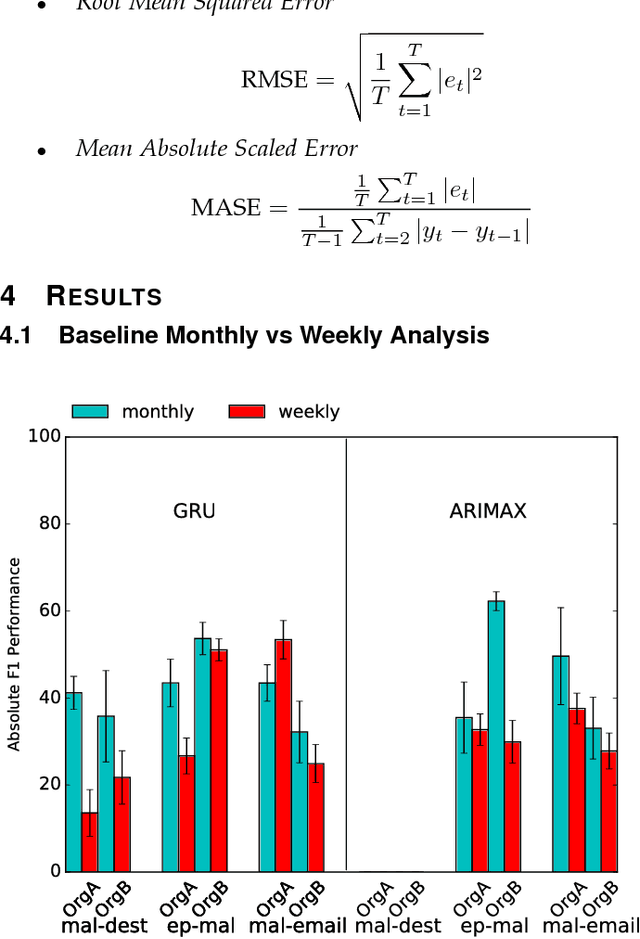
Abstract:Cyber attacks are growing in frequency and severity. Over the past year alone we have witnessed massive data breaches that stole personal information of millions of people and wide-scale ransomware attacks that paralyzed critical infrastructure of several countries. Combating the rising cyber threat calls for a multi-pronged strategy, which includes predicting when these attacks will occur. The intuition driving our approach is this: during the planning and preparation stages, hackers leave digital traces of their activities on both the surface web and dark web in the form of discussions on platforms like hacker forums, social media, blogs and the like. These data provide predictive signals that allow anticipating cyber attacks. In this paper, we describe machine learning techniques based on deep neural networks and autoregressive time series models that leverage external signals from publicly available Web sources to forecast cyber attacks. Performance of our framework across ground truth data over real-world forecasting tasks shows that our methods yield a significant lift or increase of F1 for the top signals on predicted cyber attacks. Our results suggest that, when deployed, our system will be able to provide an effective line of defense against various types of targeted cyber attacks.
Predicting Cyber Events by Leveraging Hacker Sentiment
Apr 14, 2018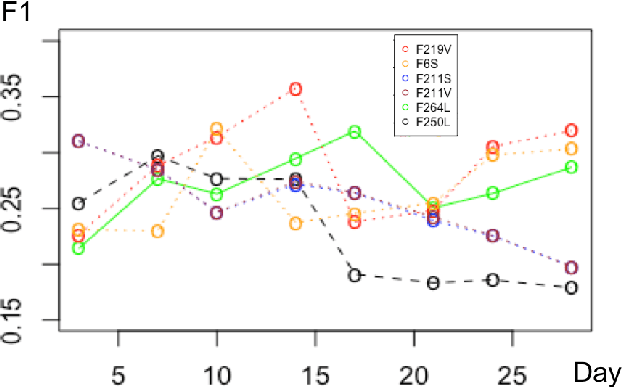
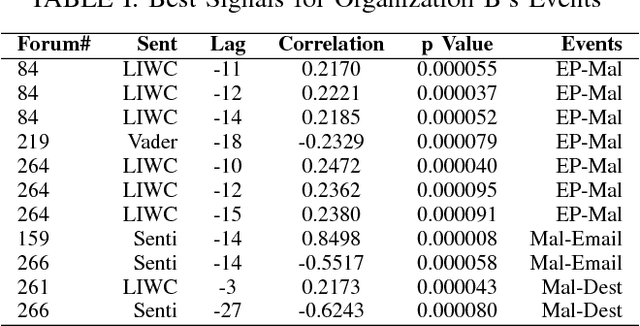
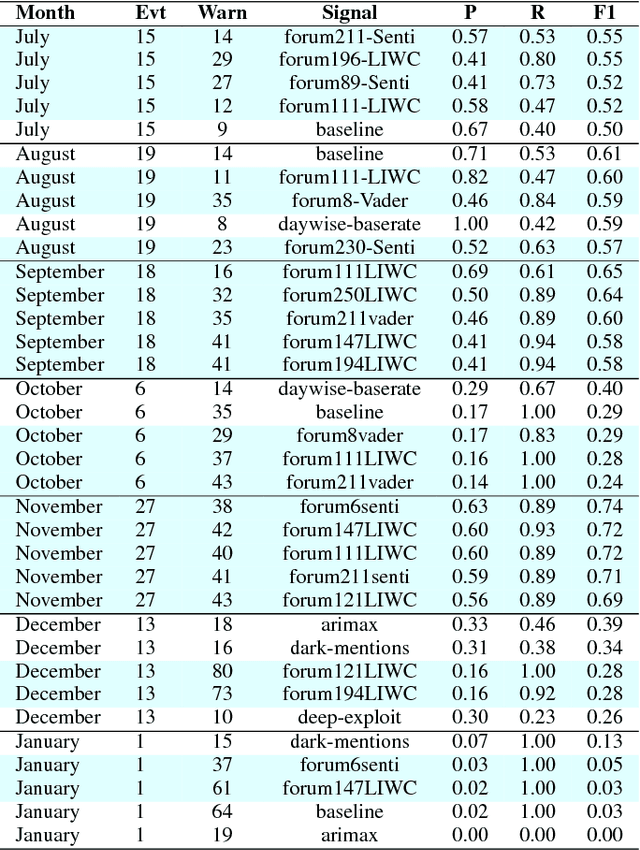
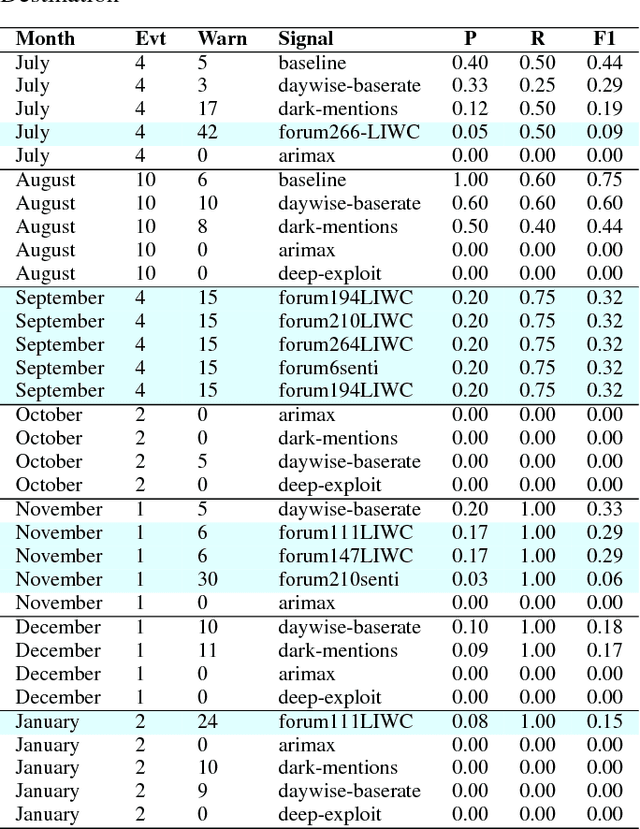
Abstract:Recent high-profile cyber attacks exemplify why organizations need better cyber defenses. Cyber threats are hard to accurately predict because attackers usually try to mask their traces. However, they often discuss exploits and techniques on hacking forums. The community behavior of the hackers may provide insights into groups' collective malicious activity. We propose a novel approach to predict cyber events using sentiment analysis. We test our approach using cyber attack data from 2 major business organizations. We consider 3 types of events: malicious software installation, malicious destination visits, and malicious emails that surpassed the target organizations' defenses. We construct predictive signals by applying sentiment analysis on hacker forum posts to better understand hacker behavior. We analyze over 400K posts generated between January 2016 and January 2018 on over 100 hacking forums both on surface and Dark Web. We find that some forums have significantly more predictive power than others. Sentiment-based models that leverage specific forums can outperform state-of-the-art deep learning and time-series models on forecasting cyber attacks weeks ahead of the events.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge