Arnhav Datar
LIC-GAN: Language Information Conditioned Graph Generative GAN Model
Jun 02, 2023Abstract:Deep generative models for Natural Language data offer a new angle on the problem of graph synthesis: by optimizing differentiable models that directly generate graphs, it is possible to side-step expensive search procedures in the discrete and vast space of possible graphs. We introduce LIC-GAN, an implicit, likelihood-free generative model for small graphs that circumvents the need for expensive graph matching procedures. Our method takes as input a natural language query and using a combination of language modelling and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and returns a graph that closely matches the description of the query. We combine our approach with a reward network to further enhance the graph generation with desired properties. Our experiments, show that LIC-GAN does well on metrics such as PropMatch and Closeness getting scores of 0.36 and 0.48. We also show that LIC-GAN performs as good as ChatGPT, with ChatGPT getting scores of 0.40 and 0.42. We also conduct a few experiments to demonstrate the robustness of our method, while also highlighting a few interesting caveats of the model.
Byzantine Spectral Ranking
Nov 15, 2022



Abstract:We study the problem of rank aggregation where the goal is to obtain a global ranking by aggregating pair-wise comparisons of voters over a set of items. We consider an adversarial setting where the voters are partitioned into two sets. The first set votes in a stochastic manner according to the popular score-based Bradley-Terry-Luce (BTL) model for pairwise comparisons. The second set comprises malicious Byzantine voters trying to deteriorate the ranking. We consider a strongly-adversarial scenario where the Byzantine voters know the BTL scores, the votes of the good voters, the algorithm, and can collude with each other. We first show that the popular spectral ranking based Rank-Centrality algorithm, though optimal for the BTL model, does not perform well even when a small constant fraction of the voters are Byzantine. We introduce the Byzantine Spectral Ranking Algorithm (and a faster variant of it), which produces a reliable ranking when the number of good voters exceeds the number of Byzantine voters. We show that no algorithm can produce a satisfactory ranking with probability > 1/2 for all BTL weights when there are more Byzantine voters than good voters, showing that our algorithm works for all possible population fractions. We support our theoretical results with experimental results on synthetic and real datasets to demonstrate the failure of the Rank-Centrality algorithm under several adversarial scenarios and how the proposed Byzantine Spectral Ranking algorithm is robust in obtaining good rankings.
Multi-Modal Detection of Alzheimer's Disease from Speech and Text
Nov 30, 2020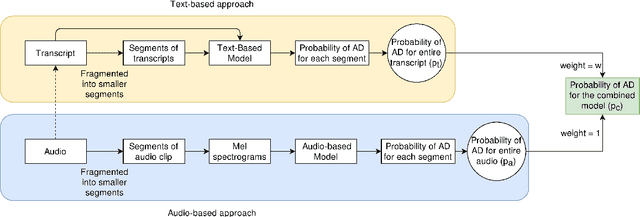
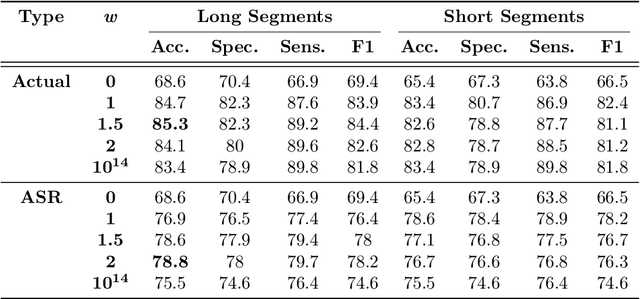
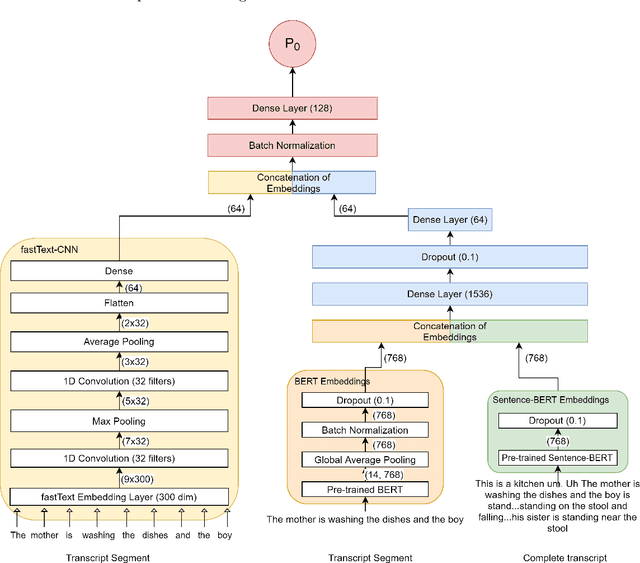
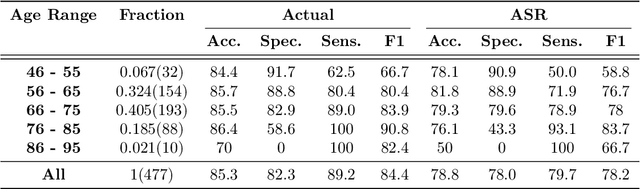
Abstract:Reliable detection of the prodromal stages of Alzheimer's disease (AD) remains difficult even today because, unlike other neurocognitive impairments, there is no definitive diagnosis of AD in vivo. In this context, existing research has shown that patients often develop language impairment even in mild AD conditions. We propose a multimodal deep learning method that utilizes speech and the corresponding transcript simultaneously to detect AD. For audio signals, the proposed audio-based network, a convolutional neural network (CNN) based model, predicts the diagnosis for multiple speech segments, which are combined for the final prediction. Similarly, we use contextual embedding extracted from BERT concatenated with a CNN-generated embedding for classifying the transcript. The individual predictions of the two models are then combined to make the final classification. We also perform experiments to analyze the model performance when Automated Speech Recognition (ASR) system generated transcripts are used instead of manual transcription in the text-based model. The proposed method achieves 85.3% 10-fold cross-validation accuracy when trained and evaluated on the Dementiabank Pitt corpus.
Depression Status Estimation by Deep Learning based Hybrid Multi-Modal Fusion Model
Nov 30, 2020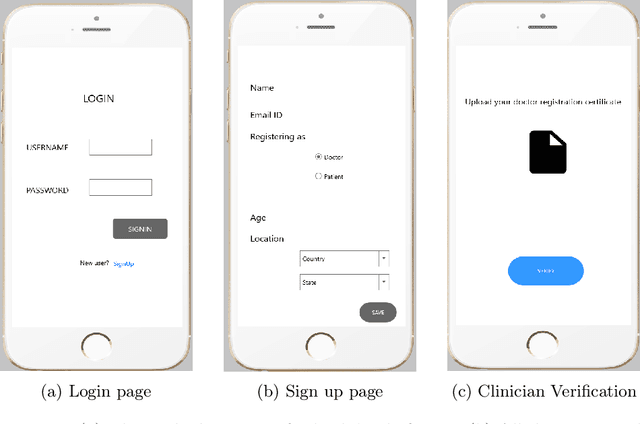
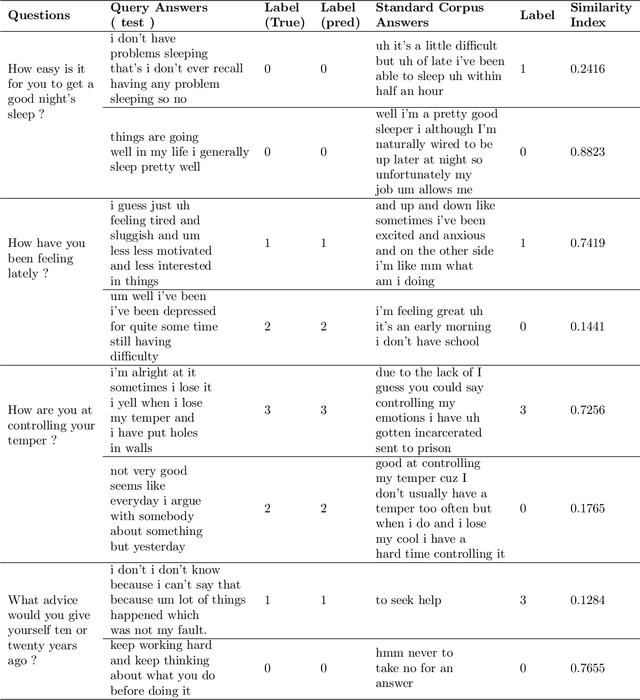
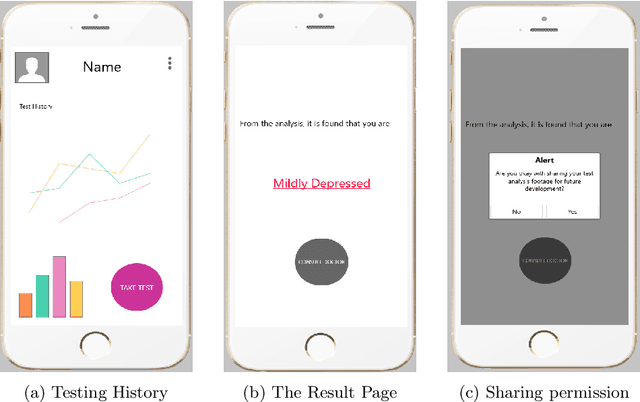
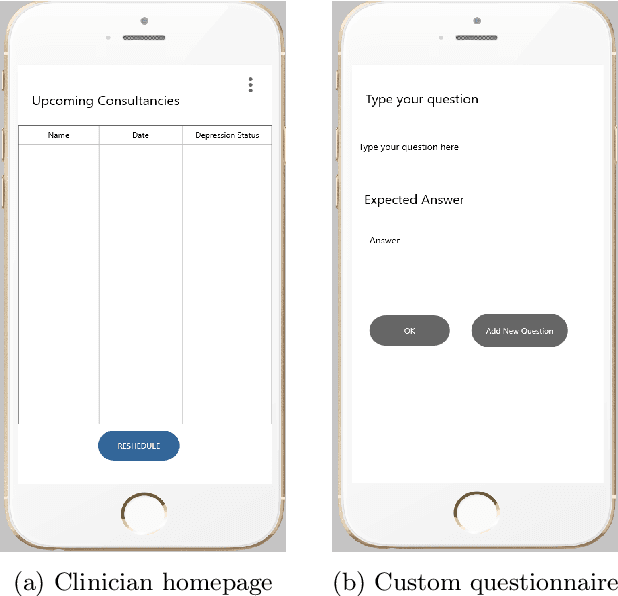
Abstract:Preliminary detection of mild depression could immensely help in effective treatment of the common mental health disorder. Due to the lack of proper awareness and the ample mix of stigmas and misconceptions present within the society, mental health status estimation has become a truly difficult task. Due to the immense variations in character level traits from person to person, traditional deep learning methods fail to generalize in a real world setting. In our study we aim to create a human allied AI workflow which could efficiently adapt to specific users and effectively perform in real world scenarios. We propose a Hybrid deep learning approach that combines the essence of one shot learning, classical supervised deep learning methods and human allied interactions for adaptation. In order to capture maximum information and make efficient diagnosis video, audio, and text modalities are utilized. Our Hybrid Fusion model achieved a high accuracy of 96.3% on the Dataset; and attained an AUC of 0.9682 which proves its robustness in discriminating classes in complex real-world scenarios making sure that no cases of mild depression are missed during diagnosis. The proposed method is deployed in a cloud-based smartphone application for robust testing. With user-specific adaptations and state of the art methodologies, we present a state-of-the-art model with user friendly experience.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge