Armaghan Moemeni
Ensemble Foreground Management for Unsupervised Object Discovery
Jul 28, 2025



Abstract:Unsupervised object discovery (UOD) aims to detect and segment objects in 2D images without handcrafted annotations. Recent progress in self-supervised representation learning has led to some success in UOD algorithms. However, the absence of ground truth provides existing UOD methods with two challenges: 1) determining if a discovered region is foreground or background, and 2) knowing how many objects remain undiscovered. To address these two problems, previous solutions rely on foreground priors to distinguish if the discovered region is foreground, and conduct one or fixed iterations of discovery. However, the existing foreground priors are heuristic and not always robust, and a fixed number of discoveries leads to under or over-segmentation, since the number of objects in images varies. This paper introduces UnionCut, a robust and well-grounded foreground prior based on min-cut and ensemble methods that detects the union of foreground areas of an image, allowing UOD algorithms to identify foreground objects and stop discovery once the majority of the foreground union in the image is segmented. In addition, we propose UnionSeg, a distilled transformer of UnionCut that outputs the foreground union more efficiently and accurately. Our experiments show that by combining with UnionCut or UnionSeg, previous state-of-the-art UOD methods witness an increase in the performance of single object discovery, saliency detection and self-supervised instance segmentation on various benchmarks. The code is available at https://github.com/YFaris/UnionCut.
Dealing with Distribution Mismatch in Semi-supervised Deep Learning for Covid-19 Detection Using Chest X-ray Images: A Novel Approach Using Feature Densities
Aug 17, 2021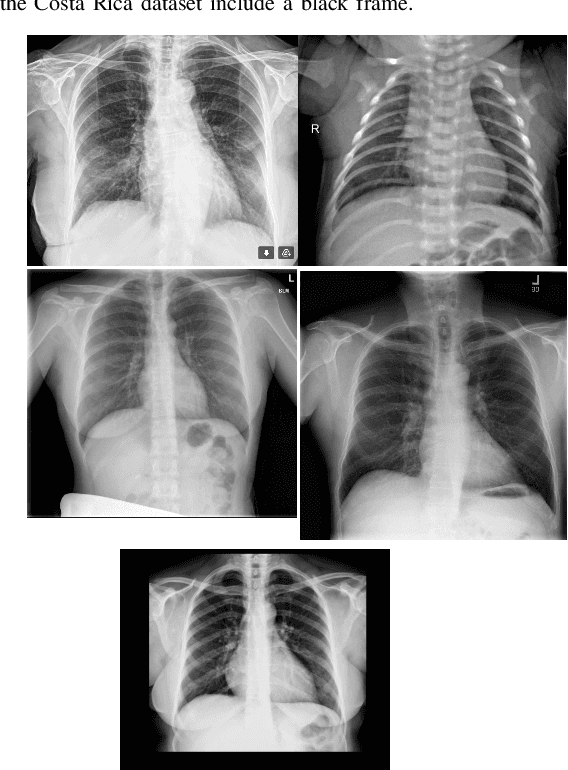
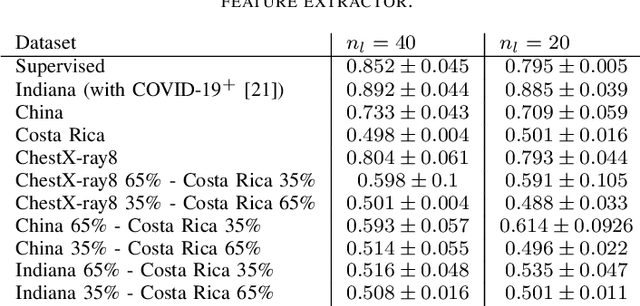
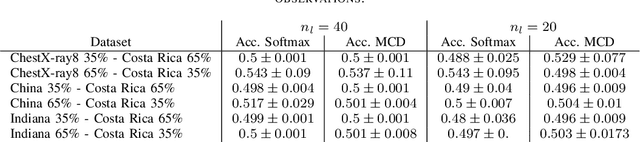
Abstract:In the context of the global coronavirus pandemic, different deep learning solutions for infected subject detection using chest X-ray images have been proposed. However, deep learning models usually need large labelled datasets to be effective. Semi-supervised deep learning is an attractive alternative, where unlabelled data is leveraged to improve the overall model's accuracy. However, in real-world usage settings, an unlabelled dataset might present a different distribution than the labelled dataset (i.e. the labelled dataset was sampled from a target clinic and the unlabelled dataset from a source clinic). This results in a distribution mismatch between the unlabelled and labelled datasets. In this work, we assess the impact of the distribution mismatch between the labelled and the unlabelled datasets, for a semi-supervised model trained with chest X-ray images, for COVID-19 detection. Under strong distribution mismatch conditions, we found an accuracy hit of almost 30\%, suggesting that the unlabelled dataset distribution has a strong influence in the behaviour of the model. Therefore, we propose a straightforward approach to diminish the impact of such distribution mismatch. Our proposed method uses a density approximation of the feature space. It is built upon the target dataset to filter out the observations in the source unlabelled dataset that might harm the accuracy of the semi-supervised model. It assumes that a small labelled source dataset is available together with a larger source unlabelled dataset. Our proposed method does not require any model training, it is simple and computationally cheap. We compare our proposed method against two popular state of the art out-of-distribution data detectors, which are also cheap and simple to implement. In our tests, our method yielded accuracy gains of up to 32\%, when compared to the previous state of the art methods.
Correcting Data Imbalance for Semi-Supervised Covid-19 Detection Using X-ray Chest Images
Aug 20, 2020
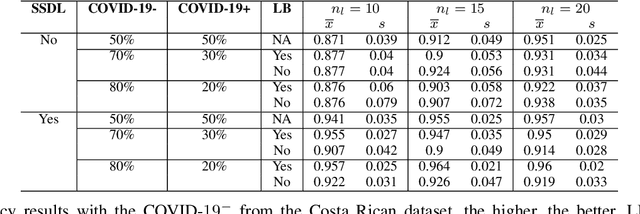
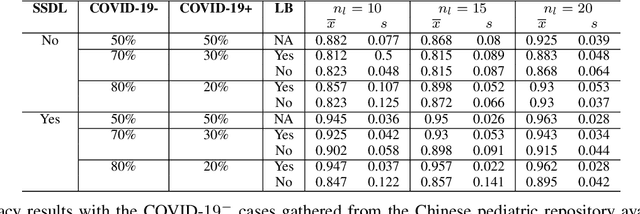
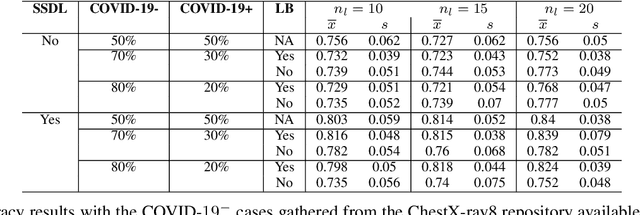
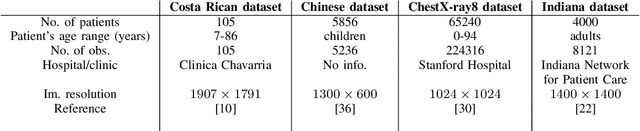
Abstract:The Corona Virus (COVID-19) is an internationalpandemic that has quickly propagated throughout the world. The application of deep learning for image classification of chest X-ray images of Covid-19 patients, could become a novel pre-diagnostic detection methodology. However, deep learning architectures require large labelled datasets. This is often a limitation when the subject of research is relatively new as in the case of the virus outbreak, where dealing with small labelled datasets is a challenge. Moreover, in the context of a new highly infectious disease, the datasets are also highly imbalanced,with few observations from positive cases of the new disease. In this work we evaluate the performance of the semi-supervised deep learning architecture known as MixMatch using a very limited number of labelled observations and highly imbalanced labelled dataset. We propose a simple approach for correcting data imbalance, re-weight each observationin the loss function, giving a higher weight to the observationscorresponding to the under-represented class. For unlabelled observations, we propose the usage of the pseudo and augmentedlabels calculated by MixMatch to choose the appropriate weight. The MixMatch method combined with the proposed pseudo-label based balance correction improved classification accuracy by up to 10%, with respect to the non balanced MixMatch algorithm, with statistical significance. We tested our proposed approach with several available datasets using 10, 15 and 20 labelledobservations. Additionally, a new dataset is included among thetested datasets, composed of chest X-ray images of Costa Rican adult patients
MixMOOD: A systematic approach to class distribution mismatch in semi-supervised learning using deep dataset dissimilarity measures
Jun 14, 2020



Abstract:In this work, we propose MixMOOD - a systematic approach to mitigate effect of class distribution mismatch in semi-supervised deep learning (SSDL) with MixMatch. This work is divided into two components: (i) an extensive out of distribution (OOD) ablation test bed for SSDL and (ii) a quantitative unlabelled dataset selection heuristic referred to as MixMOOD. In the first part, we analyze the sensitivity of MixMatch accuracy under 90 different distribution mismatch scenarios across three multi-class classification tasks. These are designed to systematically understand how OOD unlabelled data affects MixMatch performance. In the second part, we propose an efficient and effective method, called deep dataset dissimilarity measures (DeDiMs), to compare labelled and unlabelled datasets. The proposed DeDiMs are quick to evaluate and model agnostic. They use the feature space of a generic Wide-ResNet and can be applied prior to learning. Our test results reveal that supposed semantic similarity between labelled and unlabelled data is not a good heuristic for unlabelled data selection. In contrast, strong correlation between MixMatch accuracy and the proposed DeDiMs allow us to quantitatively rank different unlabelled datasets ante hoc according to expected MixMatch accuracy. This is what we call MixMOOD. Furthermore, we argue that the MixMOOD approach can aid to standardize the evaluation of different semi-supervised learning techniques under real world scenarios involving out of distribution data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge