Simon Colreavy-Donnelly
Direct deduction of chemical class from NMR spectra
Nov 06, 2022

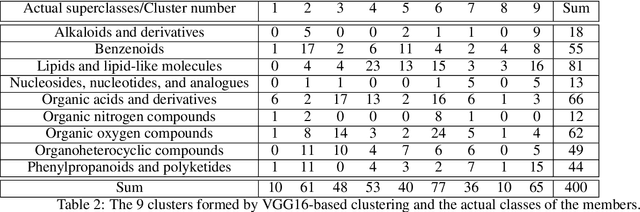

Abstract:This paper presents a proof-of-concept method for classifying chemical compounds directly from NMR data without doing structure elucidation. This can help to reduce time in finding good structure candidates, as in most cases matching must be done by a human engineer, or at the very least a process for matching must be meaningfully interpreted by one. Therefore, for a long time automation in the area of NMR has been actively sought. The method identified as suitable for the classification is a convolutional neural network (CNN). Other methods, including clustering and image registration, have not been found suitable for the task in a comparative analysis. The result shows that deep learning can offer solutions to automation problems in cheminformatics.
A Pilot Study For Fragment Identification Using 2D NMR and Deep Learning
Mar 18, 2021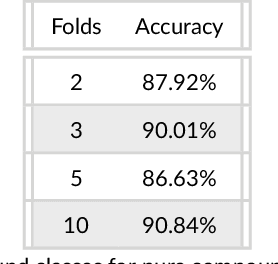
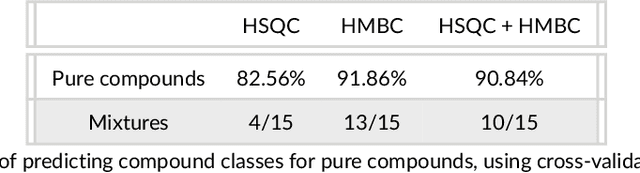
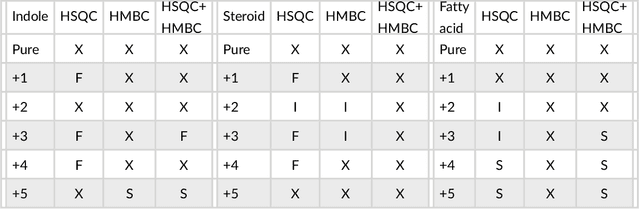
Abstract:This paper presents a method to identify substructures in NMR spectra of mixtures, specifically 2D spectra, using a bespoke image-based Convolutional Neural Network application. This is done using HSQC and HMBC spectra separately and in combination. The application can reliably detect substructures in pure compounds, using a simple network. It can work for mixtures when trained on pure compounds only. HMBC data and the combination of HMBC and HSQC show better results than HSQC alone.
Correcting Data Imbalance for Semi-Supervised Covid-19 Detection Using X-ray Chest Images
Aug 20, 2020
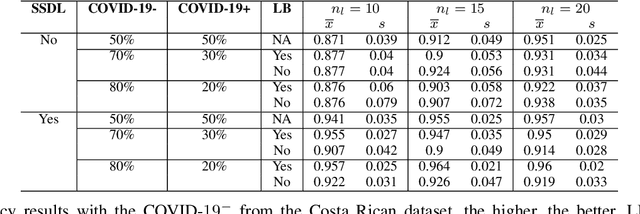
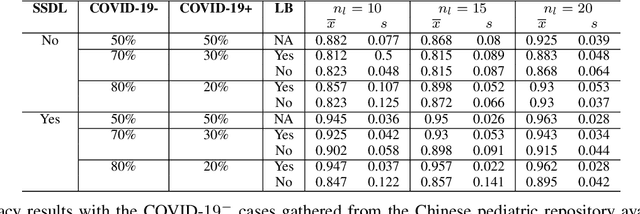
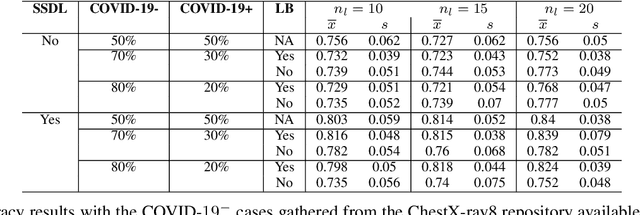
Abstract:The Corona Virus (COVID-19) is an internationalpandemic that has quickly propagated throughout the world. The application of deep learning for image classification of chest X-ray images of Covid-19 patients, could become a novel pre-diagnostic detection methodology. However, deep learning architectures require large labelled datasets. This is often a limitation when the subject of research is relatively new as in the case of the virus outbreak, where dealing with small labelled datasets is a challenge. Moreover, in the context of a new highly infectious disease, the datasets are also highly imbalanced,with few observations from positive cases of the new disease. In this work we evaluate the performance of the semi-supervised deep learning architecture known as MixMatch using a very limited number of labelled observations and highly imbalanced labelled dataset. We propose a simple approach for correcting data imbalance, re-weight each observationin the loss function, giving a higher weight to the observationscorresponding to the under-represented class. For unlabelled observations, we propose the usage of the pseudo and augmentedlabels calculated by MixMatch to choose the appropriate weight. The MixMatch method combined with the proposed pseudo-label based balance correction improved classification accuracy by up to 10%, with respect to the non balanced MixMatch algorithm, with statistical significance. We tested our proposed approach with several available datasets using 10, 15 and 20 labelledobservations. Additionally, a new dataset is included among thetested datasets, composed of chest X-ray images of Costa Rican adult patients
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge