Aran Mohammad
Fast Contact Detection via Fusion of Joint and Inertial Sensors for Parallel Robots in Human-Robot Collaboration
May 13, 2025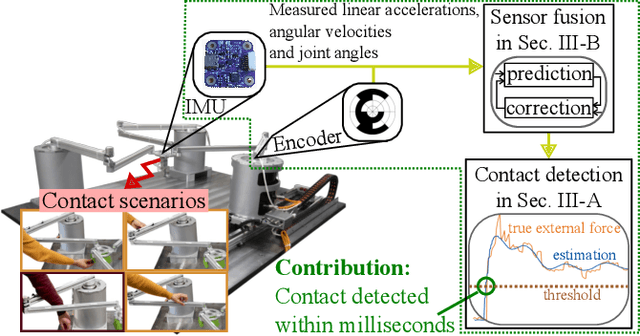
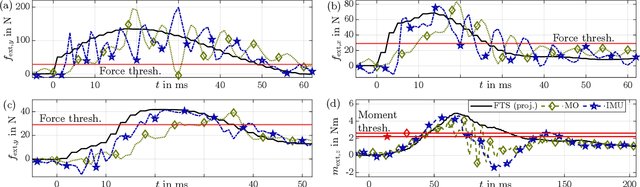
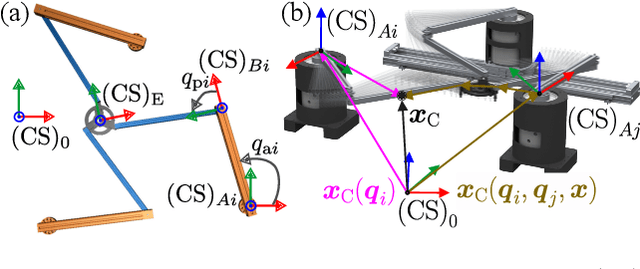
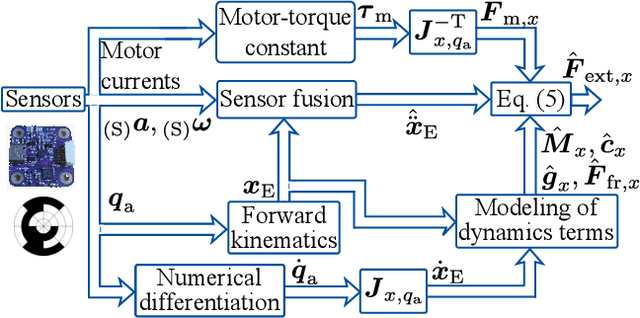
Abstract:Fast contact detection is crucial for safe human-robot collaboration. Observers based on proprioceptive information can be used for contact detection but have first-order error dynamics, which results in delays. Sensor fusion based on inertial measurement units (IMUs) consisting of accelerometers and gyroscopes is advantageous for reducing delays. The acceleration estimation enables the direct calculation of external forces. For serial robots, the installation of multiple accelerometers and gyroscopes is required for dynamics modeling since the joint coordinates are the minimal coordinates. Alternatively, parallel robots (PRs) offer the potential to use only one IMU on the end-effector platform, which already presents the minimal coordinates of the PR. This work introduces a sensor-fusion method for contact detection using encoders and only one low-cost, consumer-grade IMU for a PR. The end-effector accelerations are estimated by an extended Kalman filter and incorporated into the dynamics to calculate external forces. In real-world experiments with a planar PR, we demonstrate that this approach reduces the detection duration by up to 50% compared to a momentum observer and enables the collision and clamping detection within 3-39ms.
Generalizable and Fast Surrogates: Model Predictive Control of Articulated Soft Robots using Physics-Informed Neural Networks
Feb 04, 2025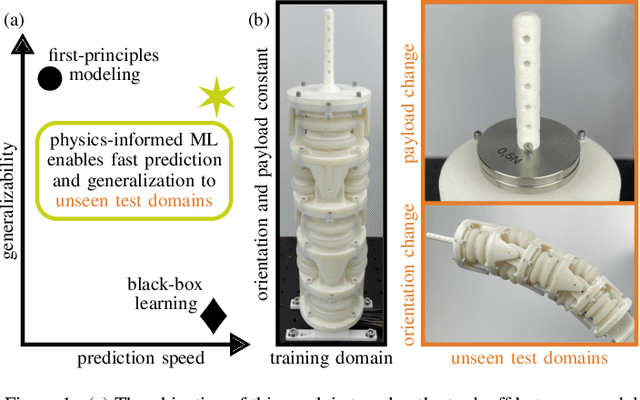
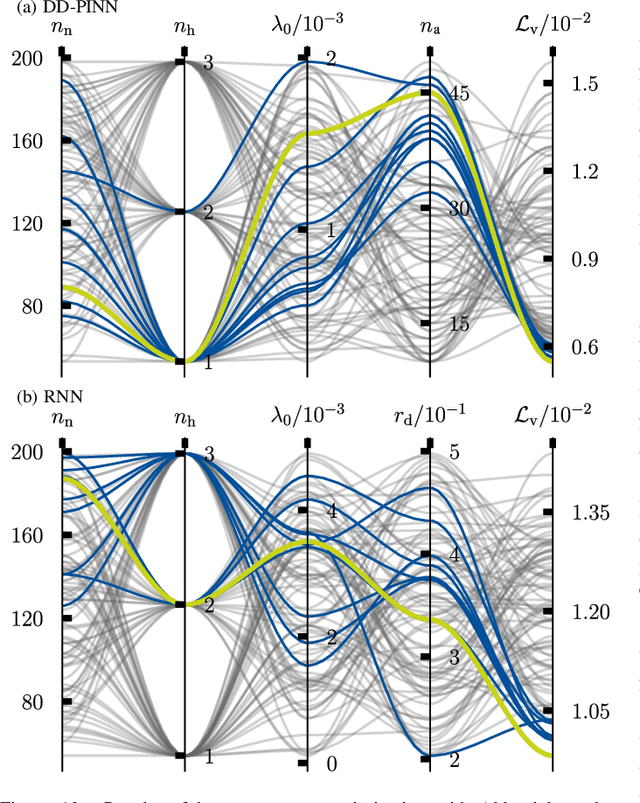
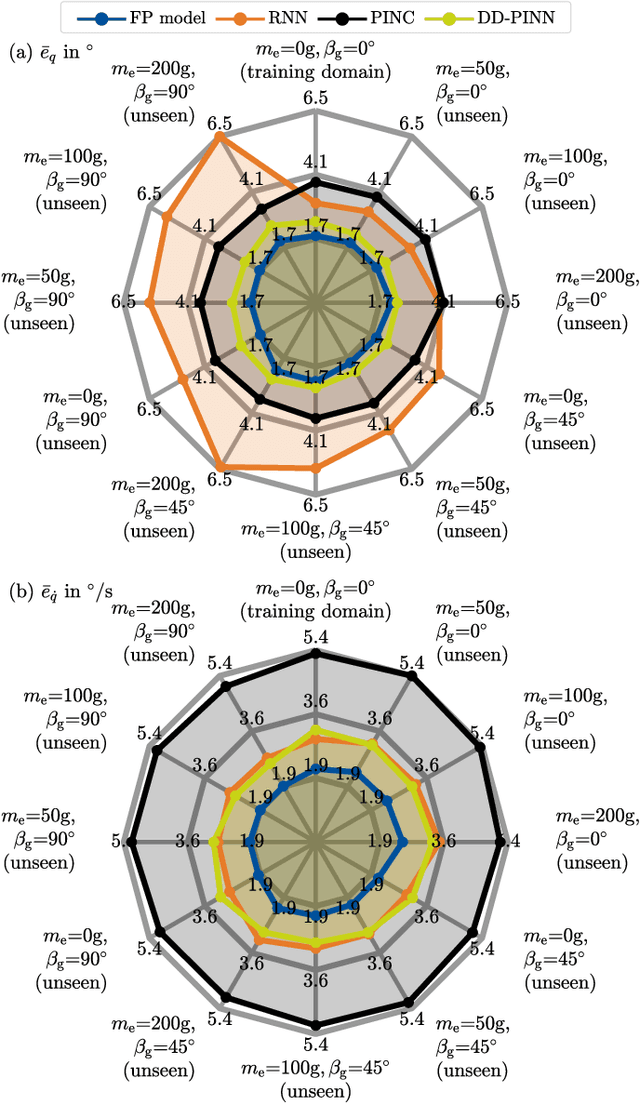
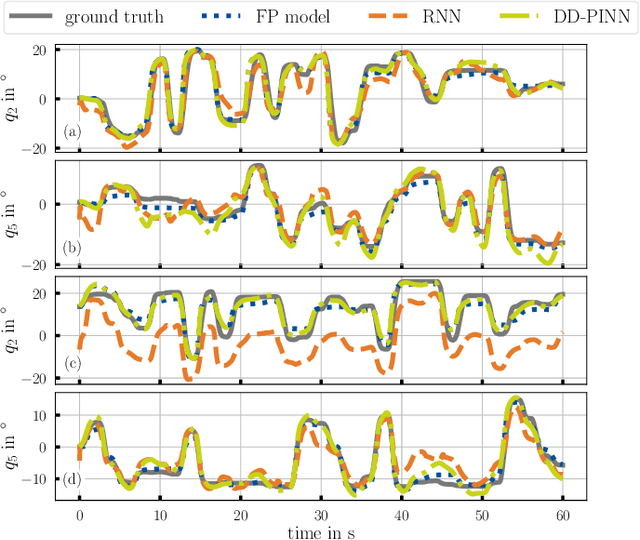
Abstract:Soft robots can revolutionize several applications with high demands on dexterity and safety. When operating these systems, real-time estimation and control require fast and accurate models. However, prediction with first-principles (FP) models is slow, and learned black-box models have poor generalizability. Physics-informed machine learning offers excellent advantages here, but it is currently limited to simple, often simulated systems without considering changes after training. We propose physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) for articulated soft robots (ASRs) with a focus on data efficiency. The amount of expensive real-world training data is reduced to a minimum - one dataset in one system domain. Two hours of data in different domains are used for a comparison against two gold-standard approaches: In contrast to a recurrent neural network, the PINN provides a high generalizability. The prediction speed of an accurate FP model is improved with the PINN by up to a factor of 466 at slightly reduced accuracy. This enables nonlinear model predictive control (MPC) of the pneumatic ASR. In nine dynamic MPC experiments, an average joint-tracking error of 1.3{\deg} is achieved.
SafePR: Unified Approach for Safe Parallel Robots by Contact Detection and Reaction with Redundancy Resolution
Jan 29, 2025



Abstract:Fast and safe motion is crucial for the successful deployment of physically interactive robots. Parallel robots (PRs) offer the potential for higher speeds while maintaining the same energy limits due to their low moving masses. However, they require methods for contact detection and reaction while avoiding singularities and self-collisions. We address this issue and present SafePR - a unified approach for the detection and localization, including the distinction between collision and clamping to perform a reaction that is safe for humans and feasible for PRs. Our approach uses information from the encoders and motor currents to estimate forces via a generalized-momentum observer. Neural networks and particle filters classify and localize the contacts. We introduce reactions with redundancy resolution to avoid type-II singularities and self-collisions. Our approach detected and terminated 72 real-world collision and clamping contacts with end-effector speeds of up to 1.5 m/s, each within 25-275 ms. The forces were below the thresholds from ISO/TS 15066. By using built-in sensors, SafePR enables safe interaction with already assembled PRs without the need for new hardware components.
Towards Optimized Parallel Robots for Human-Robot Collaboration by Combined Structural and Dimensional Synthesis
Aug 28, 2024Abstract:Parallel robots (PR) offer potential for human-robot collaboration (HRC) due to their lower moving masses and higher speeds. However, the parallel leg chains increase the risks of collision and clamping. In this work, these hazards are described by kinematics and kinetostatics models to minimize them as objective functions by a combined structural and dimensional synthesis in a particle-swarm optimization. In addition to the risk of clamping within and between kinematic chains, the back-drivability is quantified to theoretically guarantee detectability via motor current. Another HRC-relevant objective function is the largest eigenvalue of the mass matrix formulated in the operational-space coordinates to consider collision effects. Multi-objective optimization leads to different Pareto-optimal PR structures. The results show that the optimization leads to significant improvement of the HRC criteria and that a Hexa structure (6-RUS) is to be favored concerning the objective functions and due to its simpler joint structure.
Towards Human-Robot Collaboration with Parallel Robots by Kinetostatic Analysis, Impedance Control and Contact Detection
Aug 18, 2023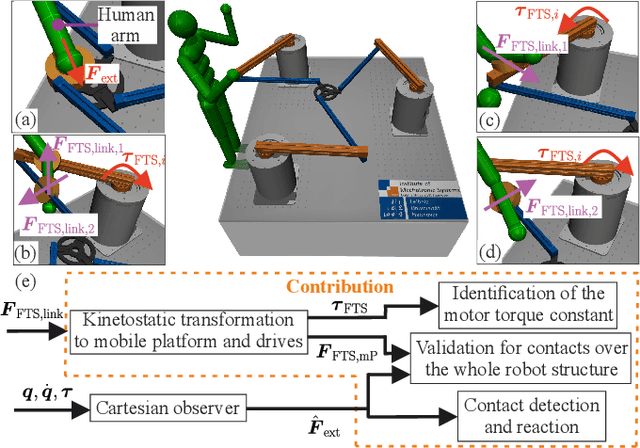
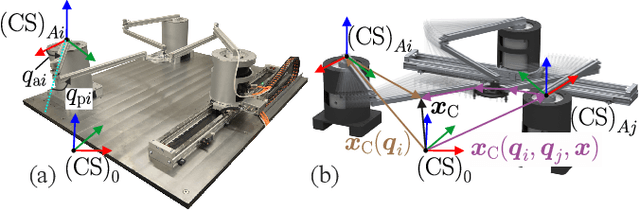
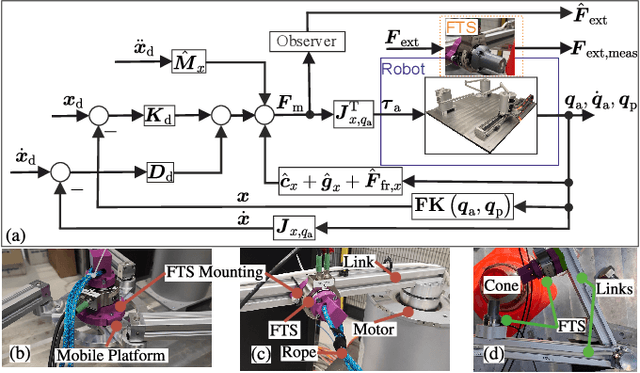
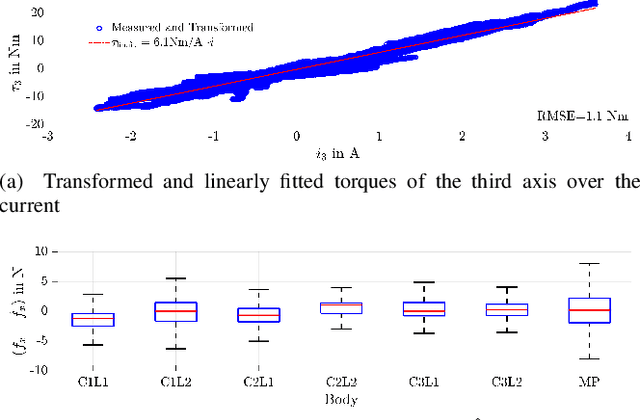
Abstract:Parallel robots provide the potential to be leveraged for human-robot collaboration (HRC) due to low collision energies even at high speeds resulting from their reduced moving masses. However, the risk of unintended contact with the leg chains increases compared to the structure of serial robots. As a first step towards HRC, contact cases on the whole parallel robot structure are investigated and a disturbance observer based on generalized momenta and measurements of motor current is applied. In addition, a Kalman filter and a second-order sliding-mode observer based on generalized momenta are compared in terms of error and detection time. Gearless direct drives with low friction improve external force estimation and enable low impedance. The experimental validation is performed with two force-torque sensors and a kinetostatic model. This allows a new identification method of the motor torque constant of an assembled parallel robot to estimate external forces from the motor current and via a dynamics model. A Cartesian impedance control scheme for compliant robot-environmental dynamics with stiffness from 0.1-2N/mm and the force observation for low forces over the entire structure are validated. The observers are used for collisions and clamping at velocities of 0.4-0.9m/s for detection within 9-58ms and a reaction in the form of a zero-g mode.
Safe Collision and Clamping Reaction for Parallel Robots During Human-Robot Collaboration
Aug 18, 2023Abstract:Parallel robots (PRs) offer the potential for safe human-robot collaboration because of their low moving masses. Due to the in-parallel kinematic chains, the risk of contact in the form of collisions and clamping at a chain increases. Ensuring safety is investigated in this work through various contact reactions on a real planar PR. External forces are estimated based on proprioceptive information and a dynamics model, which allows contact detection. Retraction along the direction of the estimated line of action provides an instantaneous response to limit the occurring contact forces within the experiment to 70N at a maximum velocity 0.4m/s. A reduction in the stiffness of a Cartesian impedance control is investigated as a further strategy. For clamping, a feedforward neural network (FNN) is trained and tested in different joint angle configurations to classify whether a collision or clamping occurs with an accuracy of 80%. A second FNN classifies the clamping kinematic chain to enable a subsequent kinematic projection of the clamping joint angle onto the rotational platform coordinates. In this way, a structure opening is performed in addition to the softer retraction movement. The reaction strategies are compared in real-world experiments at different velocities and controller stiffnesses to demonstrate their effectiveness. The results show that in all collision and clamping experiments the PR terminates the contact in less than 130ms.
Collision Isolation and Identification Using Proprioceptive Sensing for Parallel Robots to Enable Human-Robot Collaboration
Aug 18, 2023Abstract:Parallel robots (PRs) allow for higher speeds in human-robot collaboration due to their lower moving masses but are more prone to unintended contact. For a safe reaction, knowledge of the location and force of a collision is useful. A novel algorithm for collision isolation and identification with proprioceptive information for a real PR is the scope of this work. To classify the collided body, the effects of contact forces at the links and platform of the PR are analyzed using a kinetostatic projection. This insight enables the derivation of features from the line of action of the estimated external force. The significance of these features is confirmed in experiments for various load cases. A feedforward neural network (FNN) classifies the collided body based on these physically modeled features. Generalization with the FNN to 300k load cases on the whole robot structure in other joint angle configurations is successfully performed with a collision-body classification accuracy of 84% in the experiments. Platform collisions are isolated and identified with an explicit solution, while a particle filter estimates the location and force of a contact on a kinematic chain. Updating the particle filter with estimated external joint torques leads to an isolation error of less than 3cm and an identification error of 4N in a real-world experiment.
Quantifying Uncertainties of Contact Classifications in a Human-Robot Collaboration with Parallel Robots
Aug 18, 2023Abstract:In human-robot collaboration, unintentional physical contacts occur in the form of collisions and clamping, which must be detected and classified separately for a reaction. If certain collision or clamping situations are misclassified, reactions might occur that make the true contact case more dangerous. This work analyzes data-driven modeling based on physically modeled features like estimated external forces for clamping and collision classification with a real parallel robot. The prediction reliability of a feedforward neural network is investigated. Quantification of the classification uncertainty enables the distinction between safe versus unreliable classifications and optimal reactions like a retraction movement for collisions, structure opening for the clamping joint, and a fallback reaction in the form of a zero-g mode. This hypothesis is tested with experimental data of clamping and collision cases by analyzing dangerous misclassifications and then reducing them by the proposed uncertainty quantification. Finally, it is investigated how the approach of this work influences correctly classified clamping and collision scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge