Aoran Gan
Retrieval Augmented Generation Evaluation in the Era of Large Language Models: A Comprehensive Survey
Apr 21, 2025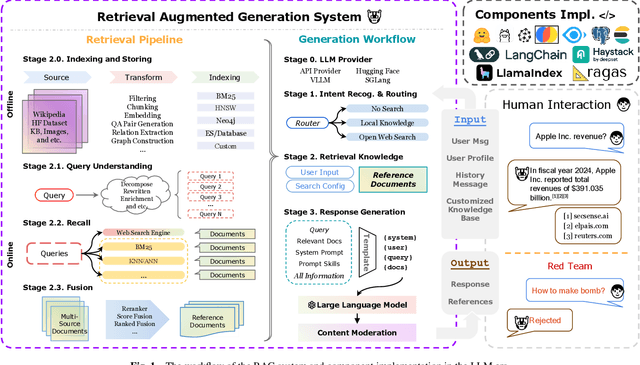
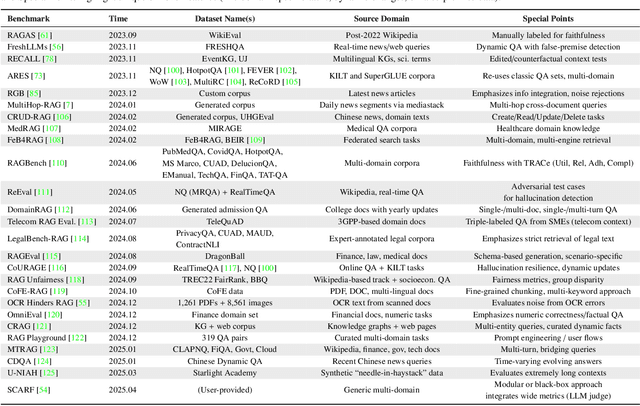

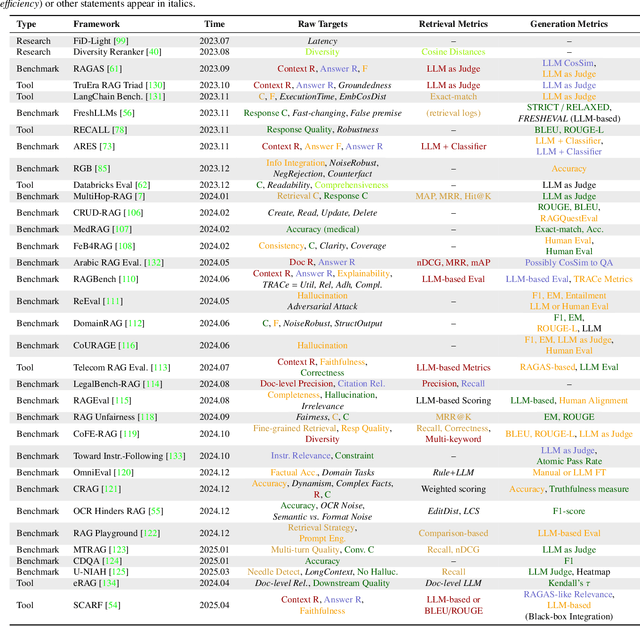
Abstract:Recent advancements in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) have revolutionized natural language processing by integrating Large Language Models (LLMs) with external information retrieval, enabling accurate, up-to-date, and verifiable text generation across diverse applications. However, evaluating RAG systems presents unique challenges due to their hybrid architecture that combines retrieval and generation components, as well as their dependence on dynamic knowledge sources in the LLM era. In response, this paper provides a comprehensive survey of RAG evaluation methods and frameworks, systematically reviewing traditional and emerging evaluation approaches, for system performance, factual accuracy, safety, and computational efficiency in the LLM era. We also compile and categorize the RAG-specific datasets and evaluation frameworks, conducting a meta-analysis of evaluation practices in high-impact RAG research. To the best of our knowledge, this work represents the most comprehensive survey for RAG evaluation, bridging traditional and LLM-driven methods, and serves as a critical resource for advancing RAG development.
Enhancing Knowledge Graph Completion with Entity Neighborhood and Relation Context
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Knowledge Graph Completion (KGC) aims to infer missing information in Knowledge Graphs (KGs) to address their inherent incompleteness. Traditional structure-based KGC methods, while effective, face significant computational demands and scalability challenges due to the need for dense embedding learning and scoring all entities in the KG for each prediction. Recent text-based approaches using language models like T5 and BERT have mitigated these issues by converting KG triples into text for reasoning. However, they often fail to fully utilize contextual information, focusing mainly on the neighborhood of the entity and neglecting the context of the relation. To address this issue, we propose KGC-ERC, a framework that integrates both types of context to enrich the input of generative language models and enhance their reasoning capabilities. Additionally, we introduce a sampling strategy to effectively select relevant context within input token constraints, which optimizes the utilization of contextual information and potentially improves model performance. Experiments on the Wikidata5M, Wiki27K, and FB15K-237-N datasets show that KGC-ERC outperforms or matches state-of-the-art baselines in predictive performance and scalability.
Empowering Few-Shot Relation Extraction with The Integration of Traditional RE Methods and Large Language Models
Jul 12, 2024Abstract:Few-Shot Relation Extraction (FSRE), a subtask of Relation Extraction (RE) that utilizes limited training instances, appeals to more researchers in Natural Language Processing (NLP) due to its capability to extract textual information in extremely low-resource scenarios. The primary methodologies employed for FSRE have been fine-tuning or prompt tuning techniques based on Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs). Recently, the emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has prompted numerous researchers to explore FSRE through In-Context Learning (ICL). However, there are substantial limitations associated with methods based on either traditional RE models or LLMs. Traditional RE models are hampered by a lack of necessary prior knowledge, while LLMs fall short in their task-specific capabilities for RE. To address these shortcomings, we propose a Dual-System Augmented Relation Extractor (DSARE), which synergistically combines traditional RE models with LLMs. Specifically, DSARE innovatively injects the prior knowledge of LLMs into traditional RE models, and conversely enhances LLMs' task-specific aptitude for RE through relation extraction augmentation. Moreover, an Integrated Prediction module is employed to jointly consider these two respective predictions and derive the final results. Extensive experiments demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed method.
Evaluation of Retrieval-Augmented Generation: A Survey
May 13, 2024Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a pivotal innovation in natural language processing, enhancing generative models by incorporating external information retrieval. Evaluating RAG systems, however, poses distinct challenges due to their hybrid structure and reliance on dynamic knowledge sources. We consequently enhanced an extensive survey and proposed an analysis framework for benchmarks of RAG systems, RAGR (Retrieval, Generation, Additional Requirement), designed to systematically analyze RAG benchmarks by focusing on measurable outputs and established truths. Specifically, we scrutinize and contrast multiple quantifiable metrics of the Retrieval and Generation component, such as relevance, accuracy, and faithfulness, of the internal links within the current RAG evaluation methods, covering the possible output and ground truth pairs. We also analyze the integration of additional requirements of different works, discuss the limitations of current benchmarks, and propose potential directions for further research to address these shortcomings and advance the field of RAG evaluation. In conclusion, this paper collates the challenges associated with RAG evaluation. It presents a thorough analysis and examination of existing methodologies for RAG benchmark design based on the proposed RGAR framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge