Anthony D. Rollett
Equilibrium Conserving Neural Operators for Super-Resolution Learning
Apr 18, 2025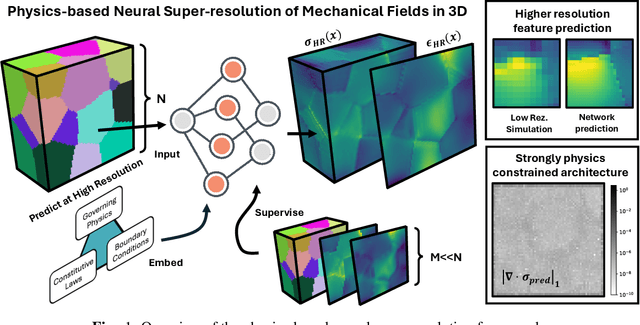
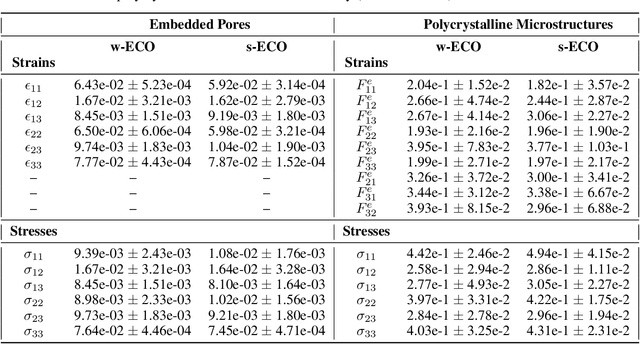
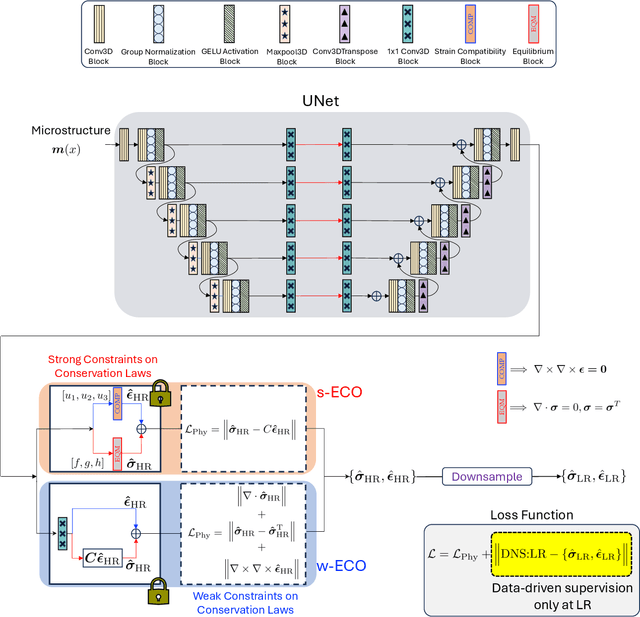
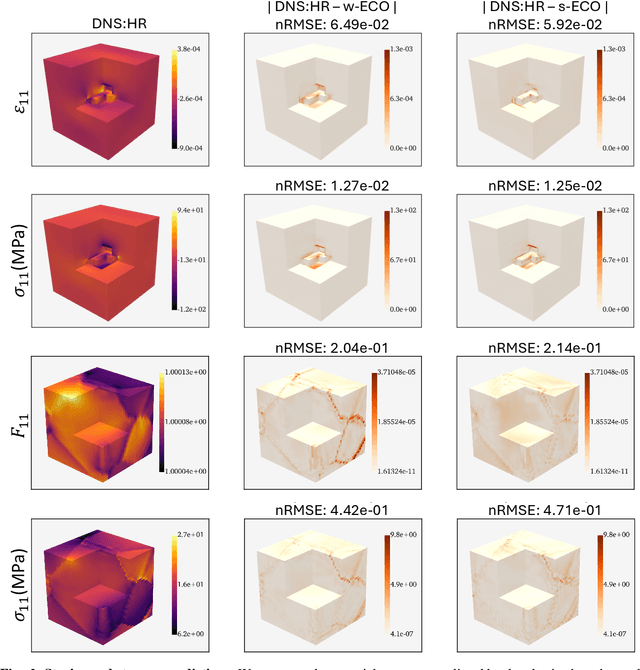
Abstract:Neural surrogate solvers can estimate solutions to partial differential equations in physical problems more efficiently than standard numerical methods, but require extensive high-resolution training data. In this paper, we break this limitation; we introduce a framework for super-resolution learning in solid mechanics problems. Our approach allows one to train a high-resolution neural network using only low-resolution data. Our Equilibrium Conserving Operator (ECO) architecture embeds known physics directly into the network to make up for missing high-resolution information during training. We evaluate this ECO-based super-resolution framework that strongly enforces conservation-laws in the predicted solutions on two working examples: embedded pores in a homogenized matrix and randomly textured polycrystalline materials. ECO eliminates the reliance on high-fidelity data and reduces the upfront cost of data collection by two orders of magnitude, offering a robust pathway for resource-efficient surrogate modeling in materials modeling. ECO is readily generalizable to other physics-based problems.
Microstructure Generation via Generative Adversarial Network for Heterogeneous, Topologically Complex 3D Materials
Jun 22, 2020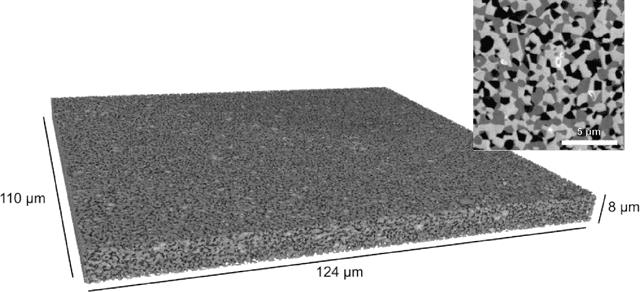
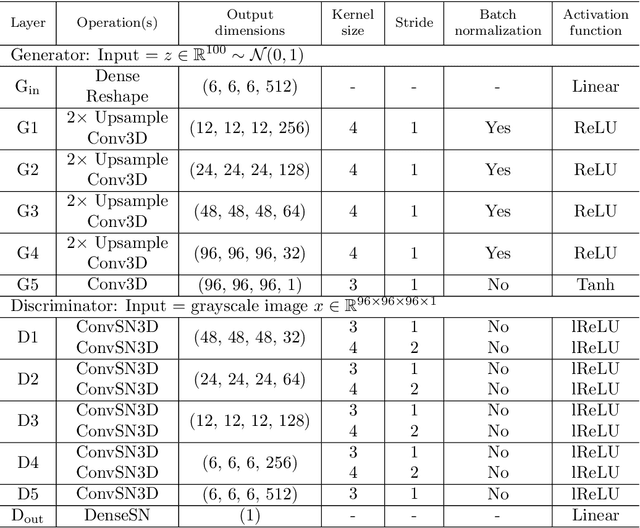
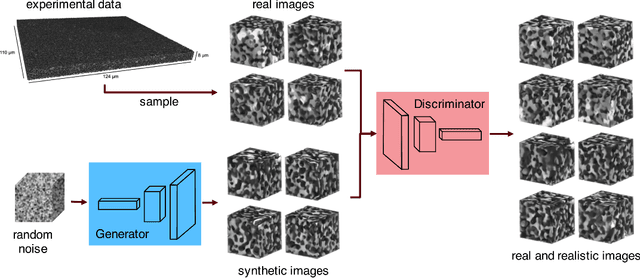

Abstract:Using a large-scale, experimentally captured 3D microstructure dataset, we implement the generative adversarial network (GAN) framework to learn and generate 3D microstructures of solid oxide fuel cell electrodes. The generated microstructures are visually, statistically, and topologically realistic, with distributions of microstructural parameters, including volume fraction, particle size, surface area, tortuosity, and triple phase boundary density, being highly similar to those of the original microstructure. These results are compared and contrasted with those from an established, grain-based generation algorithm (DREAM.3D). Importantly, simulations of electrochemical performance, using a locally resolved finite element model, demonstrate that the GAN generated microstructures closely match the performance distribution of the original, while DREAM.3D leads to significant differences. The ability of the generative machine learning model to recreate microstructures with high fidelity suggests that the essence of complex microstructures may be captured and represented in a compact and manipulatable form.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge