Angel M. Gomez
ASASVIcomtech: The Vicomtech-UGR Speech Deepfake Detection and SASV Systems for the ASVspoof5 Challenge
Aug 19, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents the work carried out by the ASASVIcomtech team, made up of researchers from Vicomtech and University of Granada, for the ASVspoof5 Challenge. The team has participated in both Track 1 (speech deepfake detection) and Track 2 (spoofing-aware speaker verification). This work started with an analysis of the challenge available data, which was regarded as an essential step to avoid later potential biases of the trained models, and whose main conclusions are presented here. With respect to the proposed approaches, a closed-condition system employing a deep complex convolutional recurrent architecture was developed for Track 1, although, unfortunately, no noteworthy results were achieved. On the other hand, different possibilities of open-condition systems, based on leveraging self-supervised models, augmented training data from previous challenges, and novel vocoders, were explored for both tracks, finally achieving very competitive results with an ensemble system.
PANACEA cough sound-based diagnosis of COVID-19 for the DiCOVA 2021 Challenge
Jun 07, 2021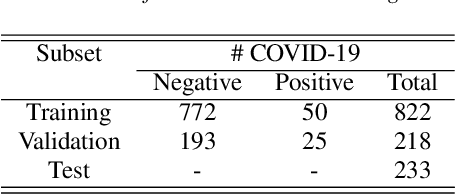
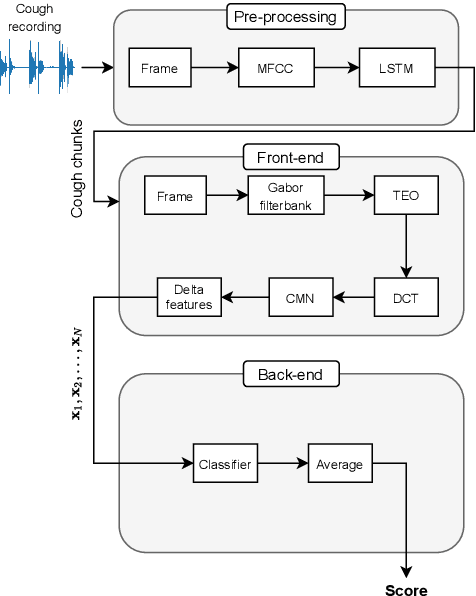
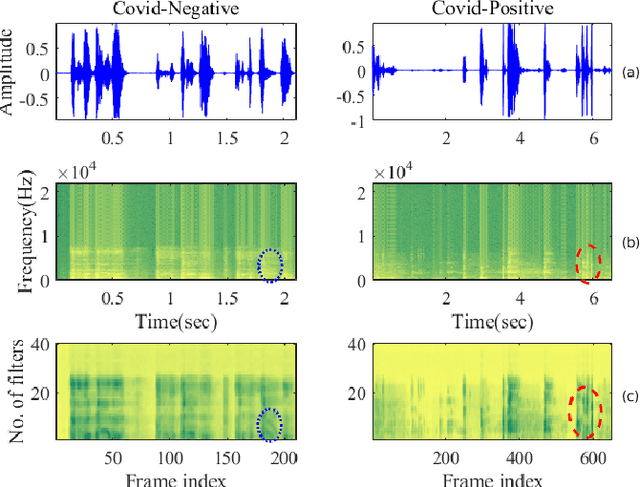
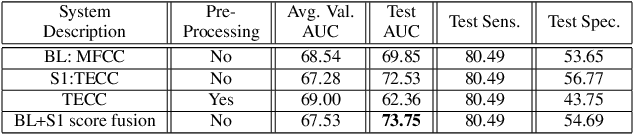
Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic has led to the saturation of public health services worldwide. In this scenario, the early diagnosis of SARS-Cov-2 infections can help to stop or slow the spread of the virus and to manage the demand upon health services. This is especially important when resources are also being stretched by heightened demand linked to other seasonal diseases, such as the flu. In this context, the organisers of the DiCOVA 2021 challenge have collected a database with the aim of diagnosing COVID-19 through the use of coughing audio samples. This work presents the details of the automatic system for COVID-19 detection from cough recordings presented by team PANACEA. This team consists of researchers from two European academic institutions and one company: EURECOM (France), University of Granada (Spain), and Biometric Vox S.L. (Spain). We developed several systems based on established signal processing and machine learning methods. Our best system employs a Teager energy operator cepstral coefficients (TECCs) based frontend and Light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM) backend. The AUC obtained by this system on the test set is 76.31% which corresponds to a 10% improvement over the official baseline.
Silent Speech Interfaces for Speech Restoration: A Review
Sep 27, 2020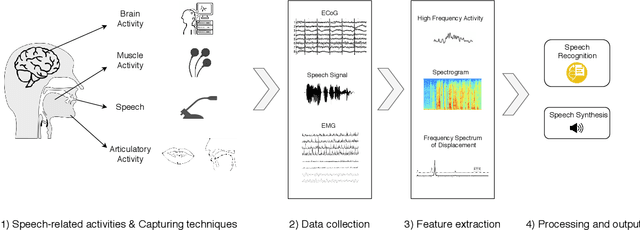
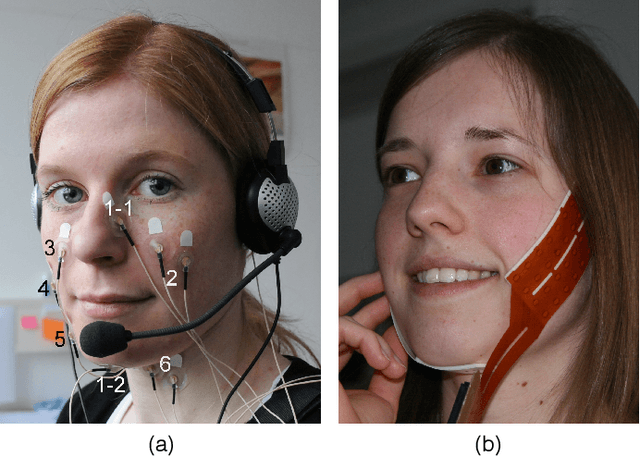
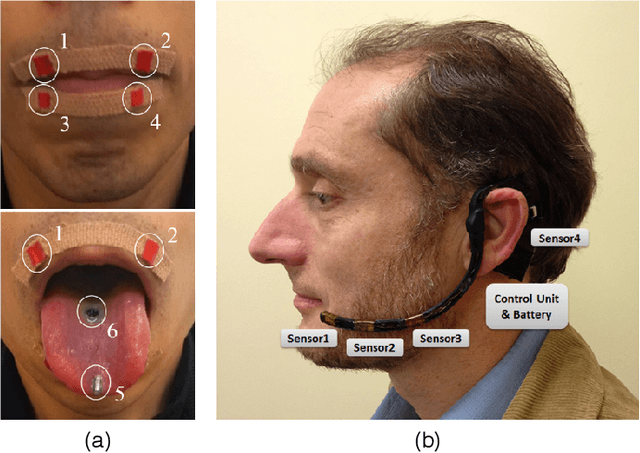

Abstract:This review summarises the status of silent speech interface (SSI) research. SSIs rely on non-acoustic biosignals generated by the human body during speech production to enable communication whenever normal verbal communication is not possible or not desirable. In this review, we focus on the first case and present latest SSI research aimed at providing new alternative and augmentative communication methods for persons with severe speech disorders. SSIs can employ a variety of biosignals to enable silent communication, such as electrophysiological recordings of neural activity, electromyographic (EMG) recordings of vocal tract movements or the direct tracking of articulator movements using imaging techniques. Depending on the disorder, some sensing techniques may be better suited than others to capture speech-related information. For instance, EMG and imaging techniques are well suited for laryngectomised patients, whose vocal tract remains almost intact but are unable to speak after the removal of the vocal folds, but fail for severely paralysed individuals. From the biosignals, SSIs decode the intended message, using automatic speech recognition or speech synthesis algorithms. Despite considerable advances in recent years, most present-day SSIs have only been validated in laboratory settings for healthy users. Thus, as discussed in this paper, a number of challenges remain to be addressed in future research before SSIs can be promoted to real-world applications. If these issues can be addressed successfully, future SSIs will improve the lives of persons with severe speech impairments by restoring their communication capabilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge