Ang Liu
Boosting Large-scale Parallel Training Efficiency with C4: A Communication-Driven Approach
Jun 07, 2024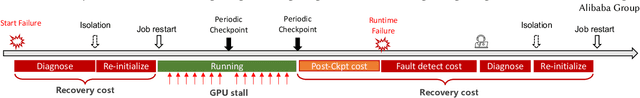

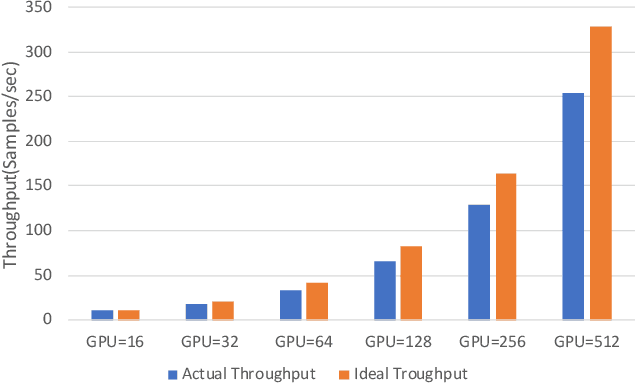

Abstract:The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has necessitated the adoption of parallel training techniques, involving the deployment of thousands of GPUs to train a single model. Unfortunately, we have found that the efficiency of current parallel training is often suboptimal, largely due to the following two main issues. Firstly, hardware failures are inevitable, leading to interruptions in the training tasks. The inability to quickly identify the faulty components results in a substantial waste of GPU resources. Secondly, since GPUs must wait for parameter synchronization to complete before proceeding to the next round of computation, network congestions can greatly increase the waiting time for GPUs. To address these challenges, this paper introduces a communication-driven solution, namely the C4. The key insights of C4 are two folds. First, in parallel training, collective communication exhibits periodic and homogeneous characteristics, so any anomalies are certainly due to some form of hardware malfunction. By leveraging this feature, C4 can rapidly identify the faulty components, swiftly isolate the anomaly, and restart the task, thereby avoiding resource wastage caused by delays in anomaly detection. Second, the predictable communication model of collective communication, involving few large flows, allows C4 to efficiently execute traffic planning, substantially reducing network congestion. C4 has been extensively implemented across our production systems, cutting error-induced overhead by roughly 30% and enhancing runtime performance by about 15% for certain applications with moderate communication costs.
Similar Data Points Identification with LLM: A Human-in-the-loop Strategy Using Summarization and Hidden State Insights
Apr 03, 2024Abstract:This study introduces a simple yet effective method for identifying similar data points across non-free text domains, such as tabular and image data, using Large Language Models (LLMs). Our two-step approach involves data point summarization and hidden state extraction. Initially, data is condensed via summarization using an LLM, reducing complexity and highlighting essential information in sentences. Subsequently, the summarization sentences are fed through another LLM to extract hidden states, serving as compact, feature-rich representations. This approach leverages the advanced comprehension and generative capabilities of LLMs, offering a scalable and efficient strategy for similarity identification across diverse datasets. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in identifying similar data points on multiple datasets. Additionally, our approach enables non-technical domain experts, such as fraud investigators or marketing operators, to quickly identify similar data points tailored to specific scenarios, demonstrating its utility in practical applications. In general, our results open new avenues for leveraging LLMs in data analysis across various domains.
Opportunities and challenges of ChatGPT for design knowledge management
Apr 06, 2023


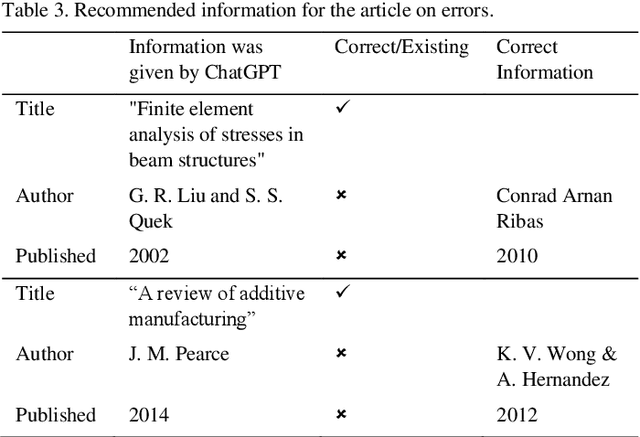
Abstract:Recent advancements in Natural Language Processing have opened up new possibilities for the development of large language models like ChatGPT, which can facilitate knowledge management in the design process by providing designers with access to a vast array of relevant information. However, integrating ChatGPT into the design process also presents new challenges. In this paper, we provide a concise review of the classification and representation of design knowledge, and past efforts to support designers in acquiring knowledge. We analyze the opportunities and challenges that ChatGPT presents for knowledge management in design and propose promising future research directions. A case study is conducted to validate the advantages and drawbacks of ChatGPT, showing that designers can acquire targeted knowledge from various domains, but the quality of the acquired knowledge is highly dependent on the prompt.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge