Anees Peringal
Collision Detection with Analytical Derivatives of Contact Kinematics
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Differentiable contact kinematics are essential for gradient-based methods in robotics, yet the mapping from robot state to contact distance, location, and normal becomes non-smooth in degenerate configurations of shapes with zero or undefined curvature. We address this inherent limitation by selectively regularizing such geometries into strictly convex implicit representations, restoring uniqueness and smoothness of the contact map. Leveraging this geometric regularization, we develop iDCOL, an implicit differentiable collision detection and contact kinematics framework. iDCOL represents colliding bodies using strictly convex implicit surfaces and computes collision detection and contact kinematics by solving a fixed-size nonlinear system derived from a geometric scaling-based convex optimization formulation. By applying the Implicit Function Theorem to the resulting system residual, we derive analytical derivatives of the contact kinematic quantities. We develop a fast Newton-based solver for iDCOL and provide an open-source C++ implementation of the framework. The robustness of the approach is evaluated through extensive collision simulations and benchmarking, and applicability is demonstrated in gradient-based kinematic path planning and differentiable contact physics, including multi-body rigid collisions and a soft-robot interaction example.
Remaining Useful Life Prediction for Aircraft Engines using LSTM
Jan 15, 2024Abstract:This study uses a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network to predict the remaining useful life (RUL) of jet engines from time-series data, crucial for aircraft maintenance and safety. The LSTM model's performance is compared with a Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) on the C-MAPSS dataset from NASA, which contains jet engine run-to-failure events. The LSTM learns from temporal sequences of sensor data, while the MLP learns from static data snapshots. The LSTM model consistently outperforms the MLP in prediction accuracy, demonstrating its superior ability to capture temporal dependencies in jet engine degradation patterns. The software for this project is in https://github.com/AneesPeringal/rul-prediction.git.
Design of Dynamics Invariant LSTM for Touch Based Human-UAV Interaction Detection
Jul 12, 2022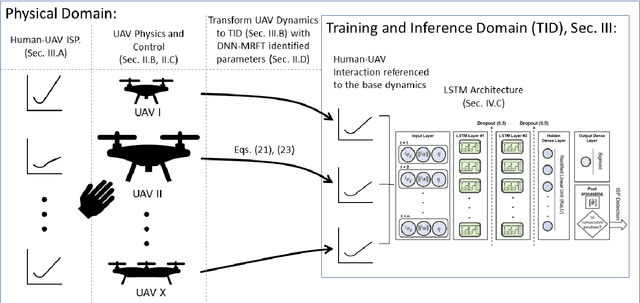
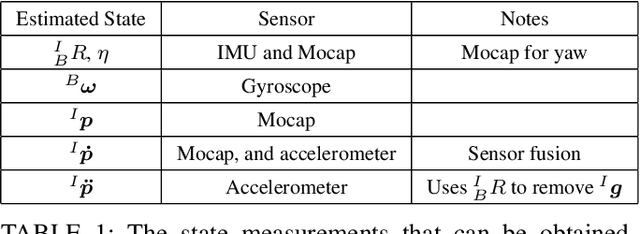
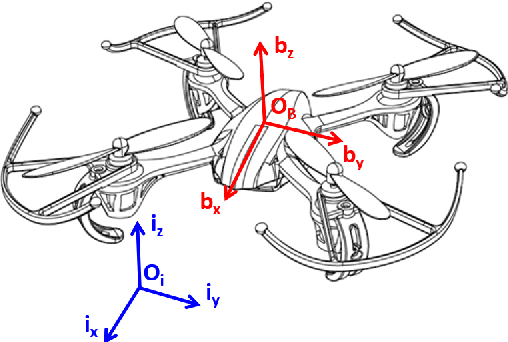
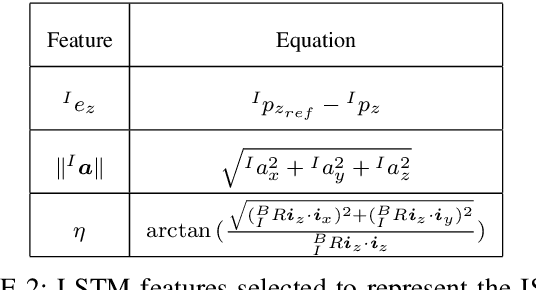
Abstract:The field of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) has reached a high level of maturity in the last few years. Hence, bringing such platforms from closed labs, to day-to-day interactions with humans is important for commercialization of UAVs. One particular human-UAV scenario of interest for this paper is the payload handover scheme, where a UAV hands over a payload to a human upon their request. In this scope, this paper presents a novel real-time human-UAV interaction detection approach, where Long short-term memory (LSTM) based neural network is developed to detect state profiles resulting from human interaction dynamics. A novel data pre-processing technique is presented; this technique leverages estimated process parameters of training and testing UAVs to build dynamics invariant testing data. The proposed detection algorithm is lightweight and thus can be deployed in real-time using off the shelf UAV platforms; in addition, it depends solely on inertial and position measurements present on any classical UAV platform. The proposed approach is demonstrated on a payload handover task between multirotor UAVs and humans. Training and testing data were collected using real-time experiments. The detection approach has achieved an accuracy of 96\%, giving no false positives even in the presence of external wind disturbances, and when deployed and tested on two different UAVs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge