Andrew Farnsworth
Long-distance Detection of Bioacoustic Events with Per-channel Energy Normalization
Nov 01, 2019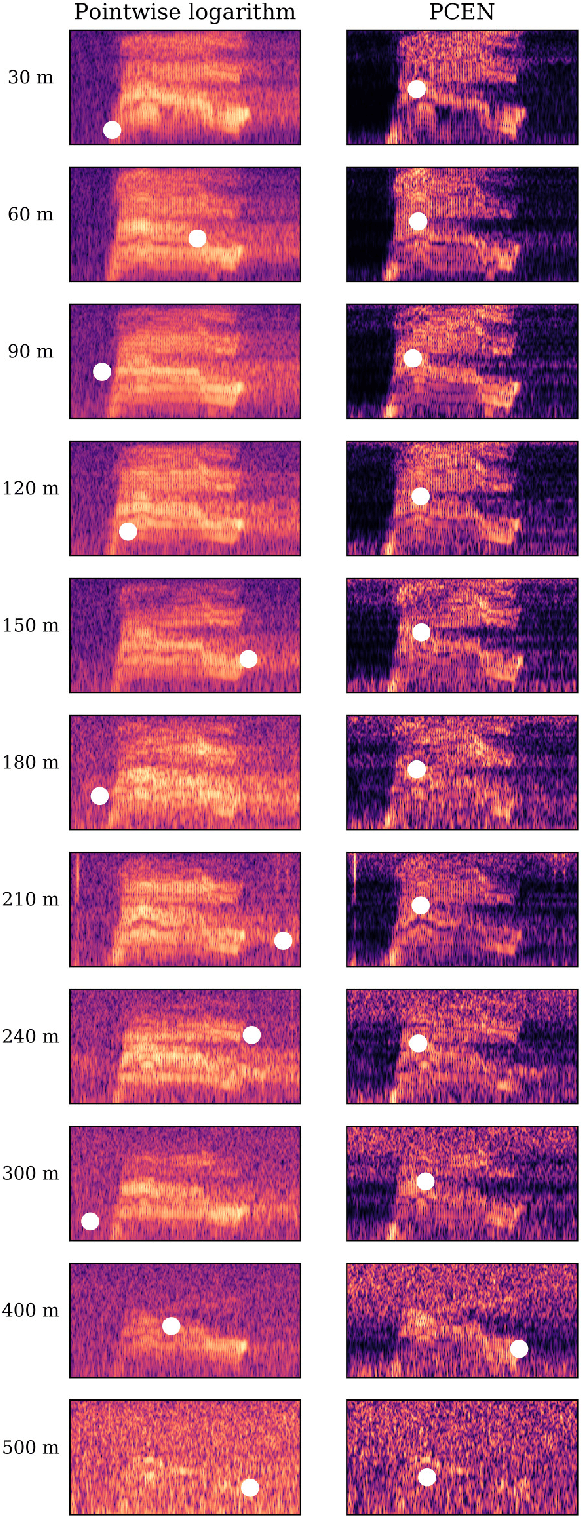


Abstract:This paper proposes to perform unsupervised detection of bioacoustic events by pooling the magnitudes of spectrogram frames after per-channel energy normalization (PCEN). Although PCEN was originally developed for speech recognition, it also has beneficial effects in enhancing animal vocalizations, despite the presence of atmospheric absorption and intermittent noise. We prove that PCEN generalizes logarithm-based spectral flux, yet with a tunable time scale for background noise estimation. In comparison with pointwise logarithm, PCEN reduces false alarm rate by 50x in the near field and 5x in the far field, both on avian and marine bioacoustic datasets. Such improvements come at moderate computational cost and require no human intervention, thus heralding a promising future for PCEN in bioacoustics.
Learning the helix topology of musical pitch
Oct 22, 2019
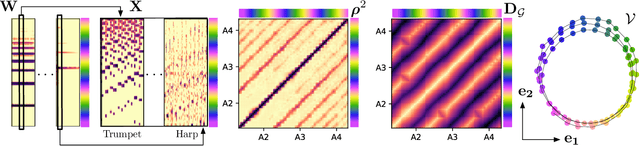
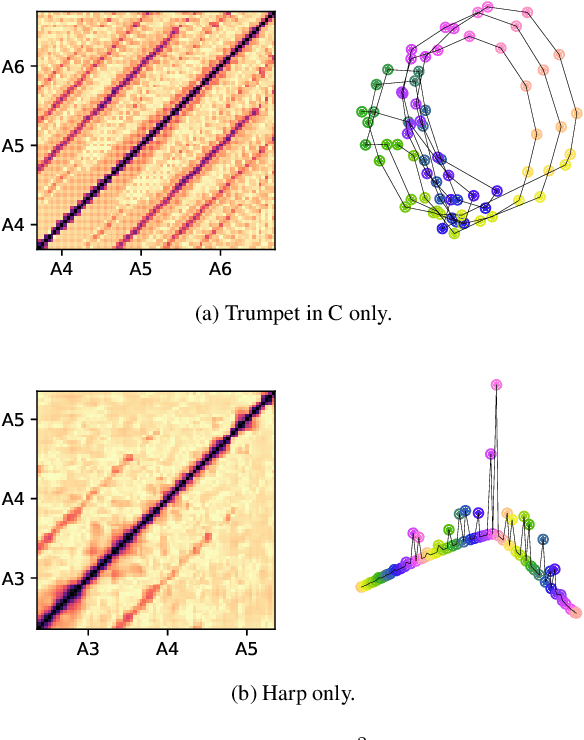
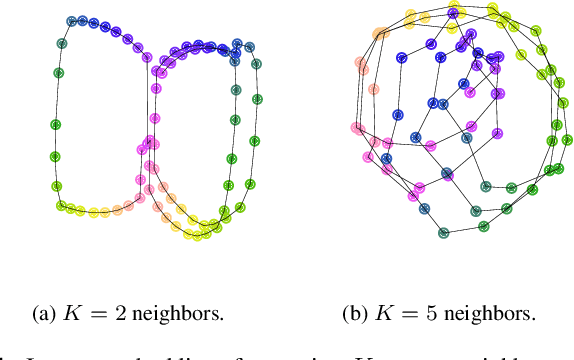
Abstract:To explain the consonance of octaves, music psychologists represent pitch as a helix where azimuth and axial coordinate correspond to pitch class and pitch height respectively. This article addresses the problem of discovering this helical structure from unlabeled audio data. We measure Pearson correlations in the constant-Q transform (CQT) domain to build a K-nearest neighbor graph between frequency subbands. Then, we run the Isomap manifold learning algorithm to represent this graph in a three-dimensional space in which straight lines approximate graph geodesics. Experiments on isolated musical notes demonstrate that the resulting manifold resembles a helix which makes a full turn at every octave. A circular shape is also found in English speech, but not in urban noise. We discuss the impact of various design choices on the visualization: instrumentarium, loudness mapping function, and number of neighbors K.
Robust sound event detection in bioacoustic sensor networks
May 20, 2019

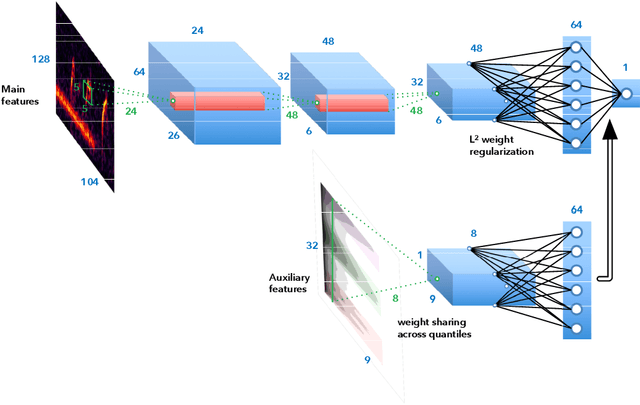
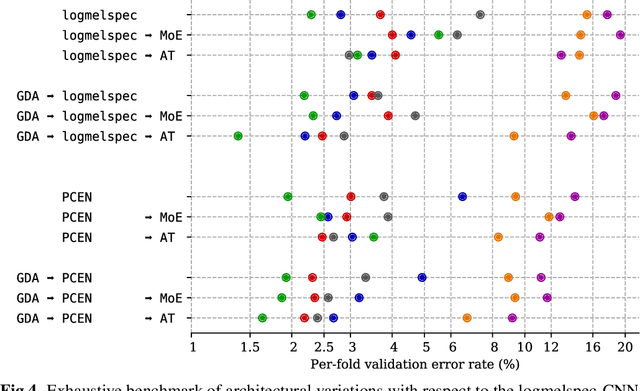
Abstract:Bioacoustic sensors, sometimes known as autonomous recording units (ARUs), can record sounds of wildlife over long periods of time in scalable and minimally invasive ways. Deriving per-species abundance estimates from these sensors requires detection, classification, and quantification of animal vocalizations as individual acoustic events. Yet, variability in ambient noise, both over time and across sensors, hinders the reliability of current automated systems for sound event detection (SED), such as convolutional neural networks (CNN) in the time-frequency domain. In this article, we develop, benchmark, and combine several machine listening techniques to improve the generalizability of SED models across heterogeneous acoustic environments. As a case study, we consider the problem of detecting avian flight calls from a ten-hour recording of nocturnal bird migration, recorded by a network of six ARUs in the presence of heterogeneous background noise. Starting from a CNN yielding state-of-the-art accuracy on this task, we introduce two noise adaptation techniques, respectively integrating short-term (60-millisecond) and long-term (30-minute) context. First, we apply per-channel energy normalization (PCEN) in the time-frequency domain, which applies short-term automatic gain control to every subband in the mel-frequency spectrogram. Secondly, we replace the last dense layer in the network by a context-adaptive neural network (CA-NN) layer, i.e. an affine layer whose weights are dynamically adapted at prediction time by an auxiliary network taking long-term summary statistics of spectrotemporal features as input. We show that both techniques are helpful and complementary. [...] We release a pre-trained version of our best performing system under the name of BirdVoxDetect, a ready-to-use detector of avian flight calls in field recordings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge