Elly Knight
Long-distance Detection of Bioacoustic Events with Per-channel Energy Normalization
Nov 01, 2019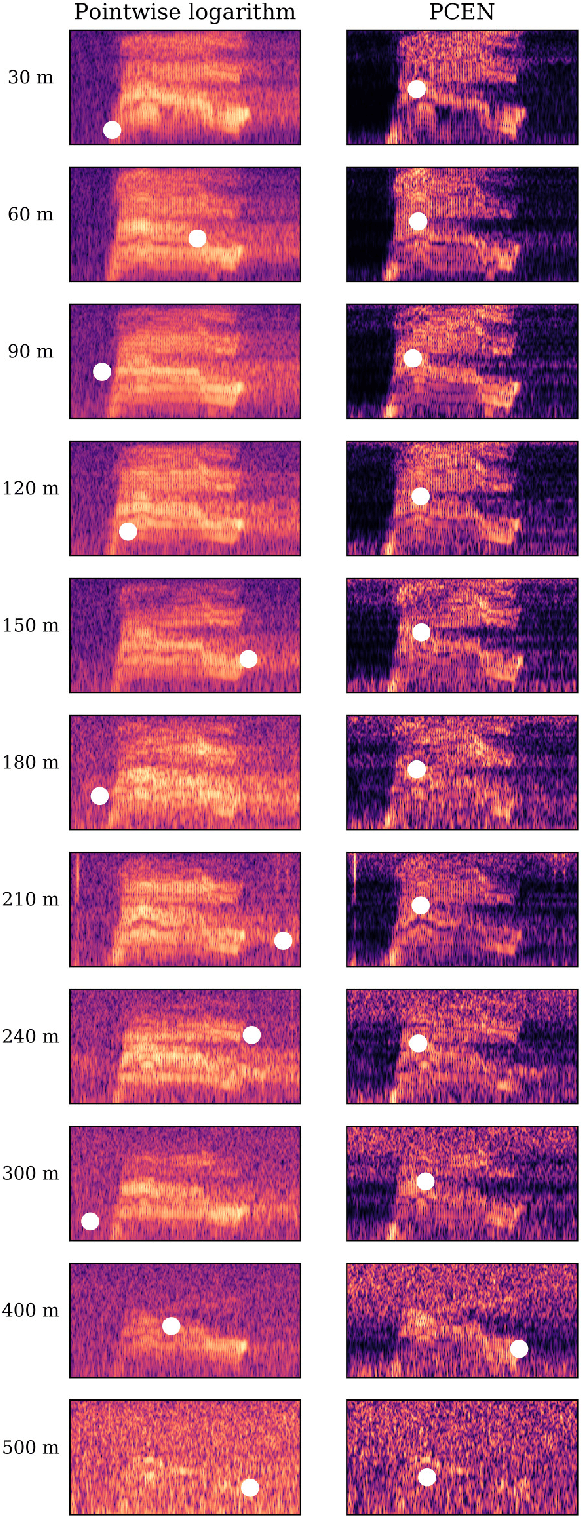


Abstract:This paper proposes to perform unsupervised detection of bioacoustic events by pooling the magnitudes of spectrogram frames after per-channel energy normalization (PCEN). Although PCEN was originally developed for speech recognition, it also has beneficial effects in enhancing animal vocalizations, despite the presence of atmospheric absorption and intermittent noise. We prove that PCEN generalizes logarithm-based spectral flux, yet with a tunable time scale for background noise estimation. In comparison with pointwise logarithm, PCEN reduces false alarm rate by 50x in the near field and 5x in the far field, both on avian and marine bioacoustic datasets. Such improvements come at moderate computational cost and require no human intervention, thus heralding a promising future for PCEN in bioacoustics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge