Andrew Chin
ATLANTIS: AI-driven Threat Localization, Analysis, and Triage Intelligence System
Sep 18, 2025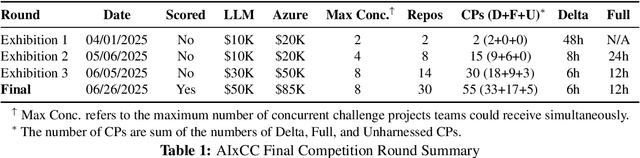
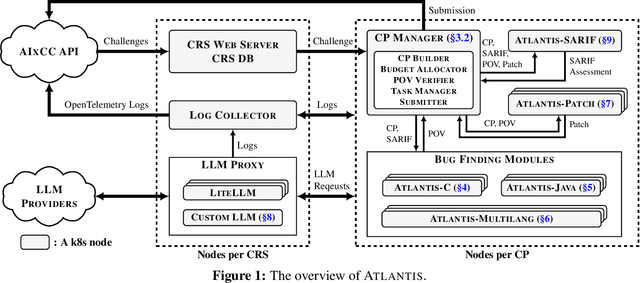
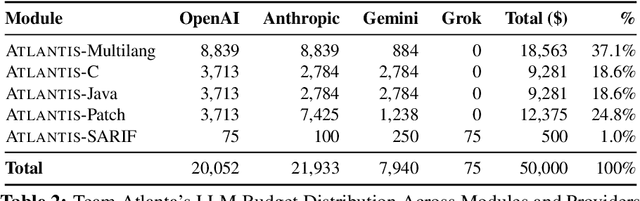
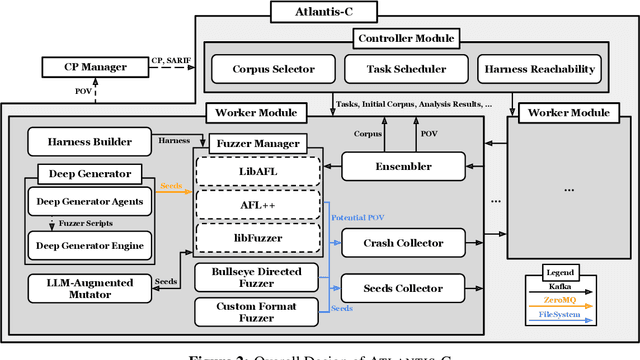
Abstract:We present ATLANTIS, the cyber reasoning system developed by Team Atlanta that won 1st place in the Final Competition of DARPA's AI Cyber Challenge (AIxCC) at DEF CON 33 (August 2025). AIxCC (2023-2025) challenged teams to build autonomous cyber reasoning systems capable of discovering and patching vulnerabilities at the speed and scale of modern software. ATLANTIS integrates large language models (LLMs) with program analysis -- combining symbolic execution, directed fuzzing, and static analysis -- to address limitations in automated vulnerability discovery and program repair. Developed by researchers at Georgia Institute of Technology, Samsung Research, KAIST, and POSTECH, the system addresses core challenges: scaling across diverse codebases from C to Java, achieving high precision while maintaining broad coverage, and producing semantically correct patches that preserve intended behavior. We detail the design philosophy, architectural decisions, and implementation strategies behind ATLANTIS, share lessons learned from pushing the boundaries of automated security when program analysis meets modern AI, and release artifacts to support reproducibility and future research.
Enhancing News Summarization with ELearnFit through Efficient In-Context Learning and Efficient Fine-Tuning
May 04, 2024Abstract:With the deluge of information delivered by the daily news cycle, there is a growing need to effectively and efficiently summarize news feeds for quick consumption. We leverage large language models (LLMs), with their advanced learning and generative abilities as compared to conventional language models, to generate concise and coherent summaries for news articles from the XSum dataset. Our paper focuses on two key aspects of LLMs: Efficient in-context Learning (ELearn) and Parameter Efficient Fine-tuning (EFit). Under ELearn, we find that increasing the number of shots in prompts and utilizing simple templates generally improve the quality of summaries. We also find that utilizing relevant examples in few-shot learning for ELearn does not improve model performance. In addition, we studied EFit using different methods and demonstrate that fine-tuning the first layer of LLMs produces better outcomes as compared to fine-tuning other layers or utilizing LoRA. We also find that leveraging more relevant training samples using selective layers does not result in better performance. By combining ELearn and EFit, we create a new model (ELearnFit) that leverages the benefits of both few-shot learning and fine-tuning and produces superior performance to either model alone. We also use ELearnFit to highlight the trade-offs between prompting and fine-tuning, especially for situations where only a limited number of annotated samples are available. Ultimately, our research provides practical techniques to optimize news summarization during the prompting and fine-tuning stages and enhances the synthesis of news articles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge