Andrea Migliorati
Playing the Lottery With Concave Regularizers for Sparse Trainable Neural Networks
Jan 19, 2025Abstract:The design of sparse neural networks, i.e., of networks with a reduced number of parameters, has been attracting increasing research attention in the last few years. The use of sparse models may significantly reduce the computational and storage footprint in the inference phase. In this context, the lottery ticket hypothesis (LTH) constitutes a breakthrough result, that addresses not only the performance of the inference phase, but also of the training phase. It states that it is possible to extract effective sparse subnetworks, called winning tickets, that can be trained in isolation. The development of effective methods to play the lottery, i.e., to find winning tickets, is still an open problem. In this article, we propose a novel class of methods to play the lottery. The key point is the use of concave regularization to promote the sparsity of a relaxed binary mask, which represents the network topology. We theoretically analyze the effectiveness of the proposed method in the convex framework. Then, we propose extended numerical tests on various datasets and architectures, that show that the proposed method can improve the performance of state-of-the-art algorithms.
Beyond cross-entropy: learning highly separable feature distributions for robust and accurate classification
Oct 29, 2020



Abstract:Deep learning has shown outstanding performance in several applications including image classification. However, deep classifiers are known to be highly vulnerable to adversarial attacks, in that a minor perturbation of the input can easily lead to an error. Providing robustness to adversarial attacks is a very challenging task especially in problems involving a large number of classes, as it typically comes at the expense of an accuracy decrease. In this work, we propose the Gaussian class-conditional simplex (GCCS) loss: a novel approach for training deep robust multiclass classifiers that provides adversarial robustness while at the same time achieving or even surpassing the classification accuracy of state-of-the-art methods. Differently from other frameworks, the proposed method learns a mapping of the input classes onto target distributions in a latent space such that the classes are linearly separable. Instead of maximizing the likelihood of target labels for individual samples, our objective function pushes the network to produce feature distributions yielding high inter-class separation. The mean values of the distributions are centered on the vertices of a simplex such that each class is at the same distance from every other class. We show that the regularization of the latent space based on our approach yields excellent classification accuracy and inherently provides robustness to multiple adversarial attacks, both targeted and untargeted, outperforming state-of-the-art approaches over challenging datasets.
Feature Fusion for Robust Patch Matching With Compact Binary Descriptors
Jan 11, 2019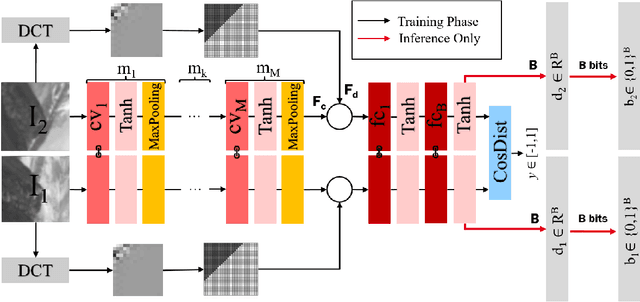
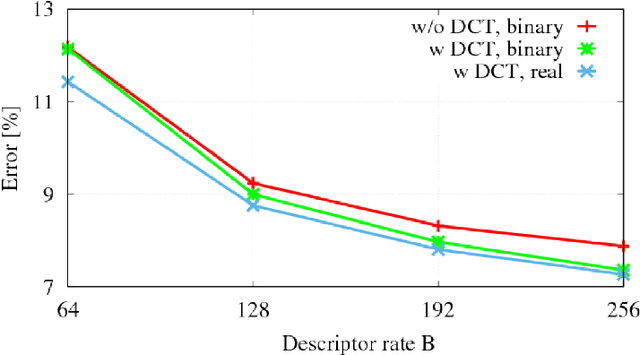
Abstract:This work addresses the problem of learning compact yet discriminative patch descriptors within a deep learning framework. We observe that features extracted by convolutional layers in the pixel domain are largely complementary to features extracted in a transformed domain. We propose a convolutional network framework for learning binary patch descriptors where pixel domain features are fused with features extracted from the transformed domain. In our framework, while convolutional and transformed features are distinctly extracted, they are fused and provided to a single classifier which thus jointly operates on convolutional and transformed features. We experiment at matching patches from three different datasets, showing that our feature fusion approach outperforms multiple state-of-the-art approaches in terms of accuracy, rate, and complexity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge