Andraž Pelicon
Evaluating and explaining training strategies for zero-shot cross-lingual news sentiment analysis
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:We investigate zero-shot cross-lingual news sentiment detection, aiming to develop robust sentiment classifiers that can be deployed across multiple languages without target-language training data. We introduce novel evaluation datasets in several less-resourced languages, and experiment with a range of approaches including the use of machine translation; in-context learning with large language models; and various intermediate training regimes including a novel task objective, POA, that leverages paragraph-level information. Our results demonstrate significant improvements over the state of the art, with in-context learning generally giving the best performance, but with the novel POA approach giving a competitive alternative with much lower computational overhead. We also show that language similarity is not in itself sufficient for predicting the success of cross-lingual transfer, but that similarity in semantic content and structure can be equally important.
Multi-Task Learning for Features Extraction in Financial Annual Reports
Apr 08, 2024



Abstract:For assessing various performance indicators of companies, the focus is shifting from strictly financial (quantitative) publicly disclosed information to qualitative (textual) information. This textual data can provide valuable weak signals, for example through stylistic features, which can complement the quantitative data on financial performance or on Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) criteria. In this work, we use various multi-task learning methods for financial text classification with the focus on financial sentiment, objectivity, forward-looking sentence prediction and ESG-content detection. We propose different methods to combine the information extracted from training jointly on different tasks; our best-performing method highlights the positive effect of explicitly adding auxiliary task predictions as features for the final target task during the multi-task training. Next, we use these classifiers to extract textual features from annual reports of FTSE350 companies and investigate the link between ESG quantitative scores and these features.
Online Hate: Behavioural Dynamics and Relationship with Misinformation
May 28, 2021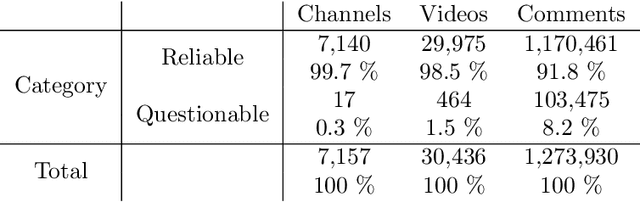
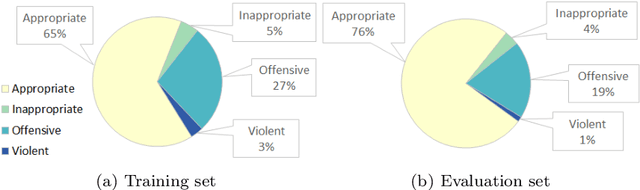
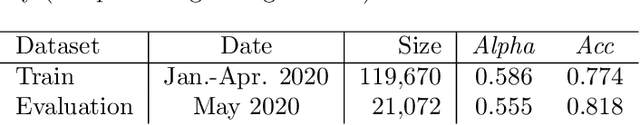
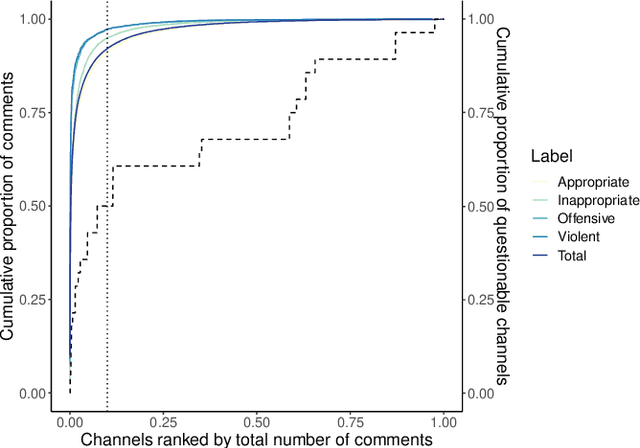
Abstract:Online debates are often characterised by extreme polarisation and heated discussions among users. The presence of hate speech online is becoming increasingly problematic, making necessary the development of appropriate countermeasures. In this work, we perform hate speech detection on a corpus of more than one million comments on YouTube videos through a machine learning model fine-tuned on a large set of hand-annotated data. Our analysis shows that there is no evidence of the presence of "serial haters", intended as active users posting exclusively hateful comments. Moreover, coherently with the echo chamber hypothesis, we find that users skewed towards one of the two categories of video channels (questionable, reliable) are more prone to use inappropriate, violent, or hateful language within their opponents community. Interestingly, users loyal to reliable sources use on average a more toxic language than their counterpart. Finally, we find that the overall toxicity of the discussion increases with its length, measured both in terms of number of comments and time. Our results show that, coherently with Godwin's law, online debates tend to degenerate towards increasingly toxic exchanges of views.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge